Albuterol is what class of Medication?
What is a Beta-2 agonist / Bronchodilator
Primary treatment of a person with excited Delirium
What are benzodiazepines
Narcotics can be reversed with ______________ at ______ dose
Narcan 0.4mg
Which medication as variable effects dependent on the dose and is know for dissociation. Hint* can cause hypotension in catecholamine depleted patients.
What is Ketamine
Sympatholytic also known as ______________ *Hint end in -olol*
What is a Beta Blocker
You are preparing to administer a medication to a patient weighing approximately 270 pounds. Because the medication is dosed according to weight, you must convert the patient's weight to kilograms which equals ________.
123 kg
What medication is the antidote if your patient overdosed on their Metoprolol?
Glucagon 3 mg IV
Brand names for this respiratory medication include Proventil and Ventolin
What is albuterol?
Amiodarone is which class of antidysrhythmic
Class III: Potassium Channel Blockers : Ventricular Antidysrhythmic
All types of narcotics are known as a _____________, which allows them to create sedation.
CNS depressant
What class of medication is used to manage seizures?
What is Benzodiazepines?
Sympathomimetic that stimulates alpha, beta-1, and beta-2 receptor sites
What is Epinephrine
During the morning drug inventory of your unit, you notice that you have a solution of 10% calcium chloride available. Based on the commonly used weight/volume percentage, you know that this solution contains _________________
10 grams/100 cc.
You are dispatched to a local farm for a patient presenting with Respiratory distress and AMS. You find the patient altered, drooling, vomiting, diaphoretic, upon auscultation you hear wheezing and the patients pupils are constricted. What is the toxicological emergency and what is your antidote / dose.
Atropine, 2-4 mg or Pralidoxime (2 Pam Chloride) 1-2 g
What is the contraindications for the use of methylprednisolone prehospital?
There are no contraindications
Name the drug and dose and class: Also known as: Adenosine
Adenocard (Antidysrhythmic/organo-nucleopeptide) - 1st dose - 6mg rapid IV push, 2nd dose - 12mg rapid IV push
What are the adverse effects of Fentanyl?
Nausea, Vomiting, Chest Wall rigidity, Respiratory Depression.
Decreases Myocardial workload by reducing myocardial oxygen demand by reducing preload and afterload.
What is Morphine
You are ordered to give 2.0 mg of epinephrine 1:10,000 by the endotracheal route during cardiac arrest as the intravenous line has not yet been established. Epinephrine is supplied as 0.1 mg/mL. How many milliliters will you give?
20 mL
You patient presents with Hyperactivity, Dilated pupils, Psychosis, Hypertension, Tachycardia, Tachypnea, Chest pain, and Agitation. On your 3 lead you find a narrow tachycardia at 230 bpm, you have attempted vagal maneuvers, Adenosine and Synchronized cardioversion at 50 and 100J with no resolve. What did your patient take and how to you manage it?
Stimulates / Sympathomimetics: Cocaine, Crack, Bath salts, Speed.
ABC’s, IV, O2, Monitor, fluids, treat arrhythmias, treat seizures, benzodiazepines for refractory SVT or chest pain.
Anticholinergic brochodilator indicated for asthma, reversible bronchoconstriction secondary to COPD or inhaled irritants, and contraindicated in the presence of CHF, or an atropine, soy, or peanut allergy.
What is Ipratropium 500mcg in 3ml NSS via nebulizer at 6LPM
Common sedative that can cause hypotension in patients with severe catecholamine depleted states?
Ketamine
Class IV antidysrhythmic can not be administered with what type of medications
Class IV Calcium Channel Blockers can not be administered with Beta Blockers
List 5 major signs and symptoms of opiate overdose
Pinpoint pupils, Hypotension, Bradycardia, Respiratory Depression, Hypothermia (CNS Depression), Coma or death
What is the correct drug regime and doses for a hypoglycemic, chronic alcoholic?
Dextrose 50% 25g and 100 mg of thiamine
What is the class and dose of Succinycholine?
You are treating a pediatric patient for bradycardia. The patient weighs approximately 10 kilograms. Protocol indicates that 0.01 mg/kg IV/IO should be given. What is the dose of epinephrine for this patient?
0.1 mg
Calcium is important in the management of two toxic exposures / overdoses.
What is Calcium channel blockers and hydrofluoric acid.
Sympathomimetic/tocolytic indicated for reversible bronchospasm and to inhibit labor. Contraindicated in hypertension, dysrhythmias, and seizures. Also known as Brethine.
Terbutaline - Bronchodilator - 0.25mg SQ (max 0.5mg in 4 hours). Premature Labor - 2-5-10mg/min IV/IO
Name the drug and dose and class: Also known as: Romazicon. Hint* Benzodiazepine antagonist
Flumazenil 0.1-1mg
What class of antiarrhythmic has a very therapeutic index, patients cannot receive CA Channel blockers while taking and with toxicity can produce visual disturbances, bradycardia and ventricular arrhythmias
What is cardiac glycosides, (Digoxin / Quinidine / Lanoxin; Digitoxin; Digitalis)
What routes can Fentanyl be administered?
IV, IN
Cold sepsis should receive which vasopressor?
Epinephrine
Receptor in the sympathetic nervous system that causes increased inotrophy and chronotrophy as well as vasodilation.
What is the Beta Receptor
You are ordered to give 250 ml of 0.9% normal saline to a patient over 20 minutes. You are using a macroinfusion set (10 gtts/ml). What will you set your drip rate at?
125 gtts/min
Your patient presents with Tachycardia, Tachypnea, Respiratory Depression, Hypotension. On scene you find a bottle of Desipramine. What did you patient OD and what is your management? 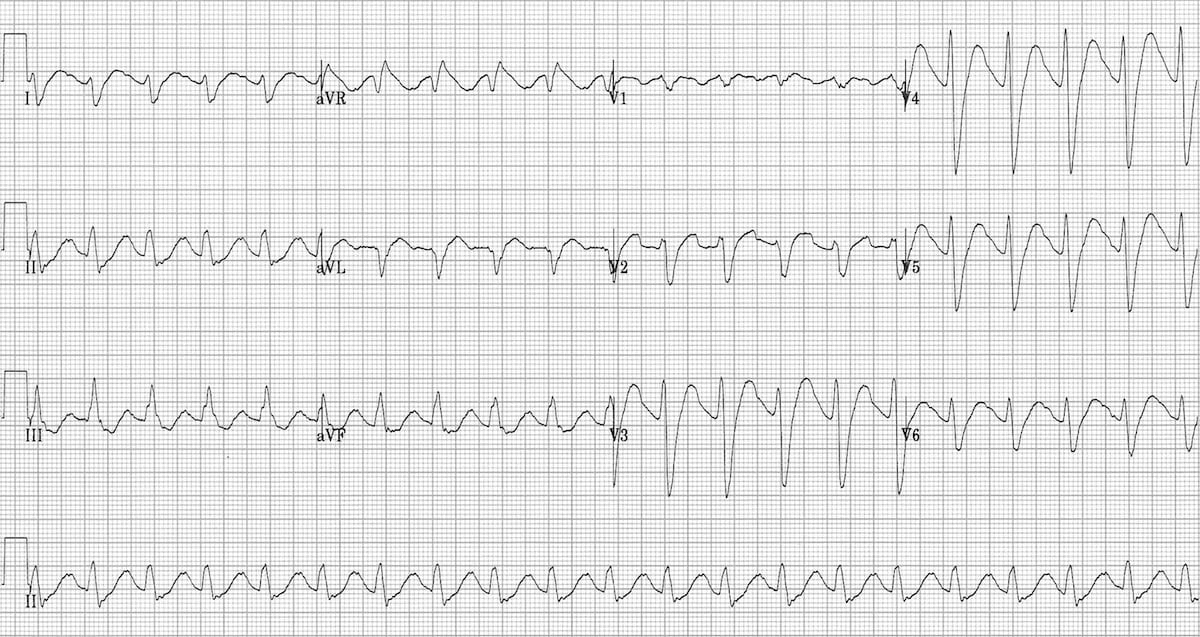
Tricyclic antidepressants
ABC’s, IV, O2, Monitor, fluids, Treat dysthymias, if prolonged QT interval, torsades or hyperkalemia present on 12 lead: 1mEq/kg Sodium Bicarb
A beta agonist drug is given only by inhalation, can be used to treat croup and is associated with rebound worsening after the medication has worn off.
What is Racemic Epinephrine?
Which medication can not be administered to patients with Adrenal insufficiency or sepsis when performing a RSI?
Enalapril (Vasotec) is what type of medication
ACE Inhibitor / Antihypertensive
Narcotics should not be administered to patients who are?
ETOH intoxication, Hypotensive, No way to maintain respirations or ventilations
Which medication and dose is administered for a Acute extrapyramidal symptom following administration of Haldol?
Diphenhydramine 25-50 mg
You are treating a patient who is experiencing status epilepticus. After initial management of the airway, breathing, and circulation, what is your first line drug for management and dose?
Valium / Diazepam 5-10 mg IV
You are ordered to administer 2 mg/min of lidocaine to a patient who has received a bolus of lidocaine during cardiac arrest. You have prepared the lidocaine by placing 1 gram in 250 cc of D5W. You are utilizing a microdrip (60 gtts/mL) administration set. What is the correct drip rate?
30 gtts/min
Medication is used in severe bronchospasm for patients refractory respiratory distress following typical asthma treatment. Know to relax the smooth muscles.
What is magnesium sulfate.
Metadone is what class of medication
Opioid
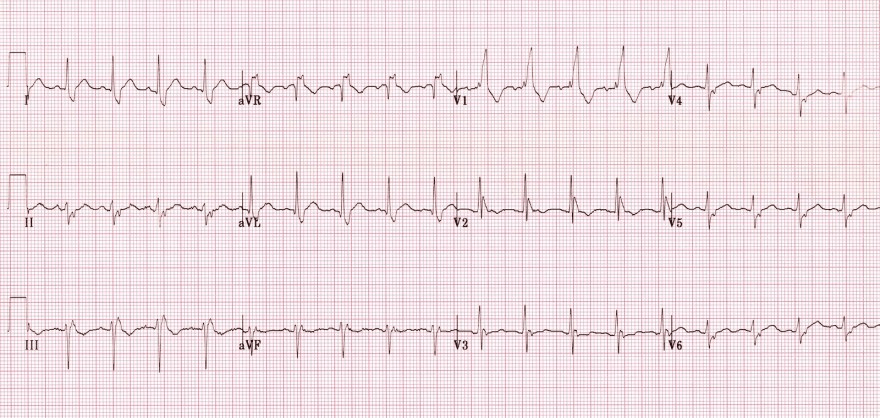
What medication should you NOT administer to your patient?
What is Amiodarone or Lidocaine?
A Semisynthetics Opiate commonly sold over the counter cold, flu and cough medication that is commonly used by adolescents.
Dextromethophan
Which antipyretic inhibits production of prostaglandins to reduce fever?
Ketorolac (Toradol)
Naturally occurring hormone; antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secreted by pituitary gland; sympathomimetic effects
What is Vasopressin
You are treating a 220-pound male patient in cardiogenic shock. The physician has ordered that you administer 5 mcg/kg/min to this patient. You prepare the infusion by placing 200 mg of dopamine into 250 mL of D5W. Using a microdrip (60 gtts/mL) administration set, what will you set the rate of infusion at (gtts/min)?
38 gtts/min