Identify the state of matter below:
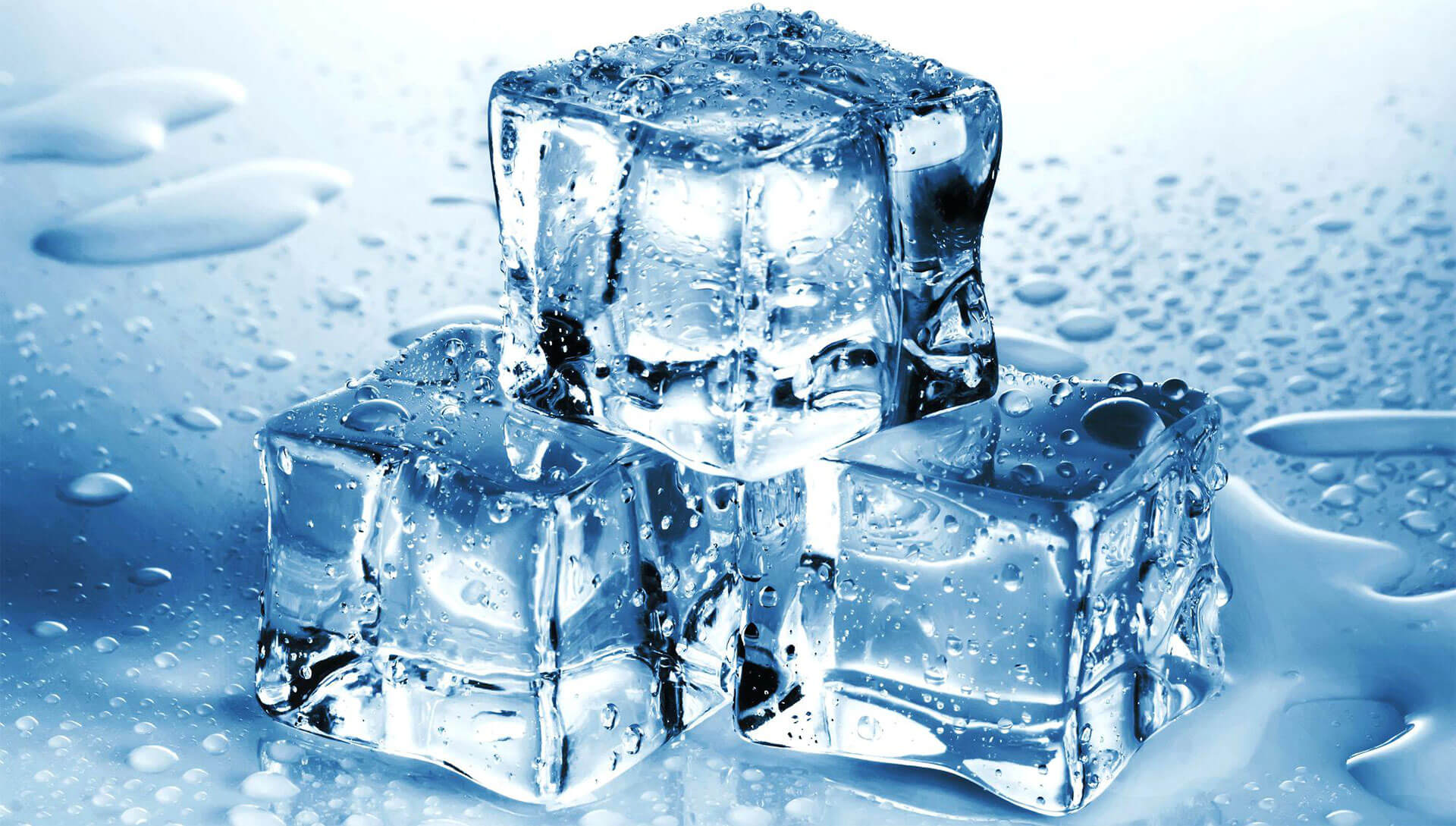

Solid
What is Matter?
Matter is anything that has mass and volume
The spreading out of perfume in a room demonstrates this process.

Diffusion
When a solid is heated, its particles gain this.
Kinetic Energy
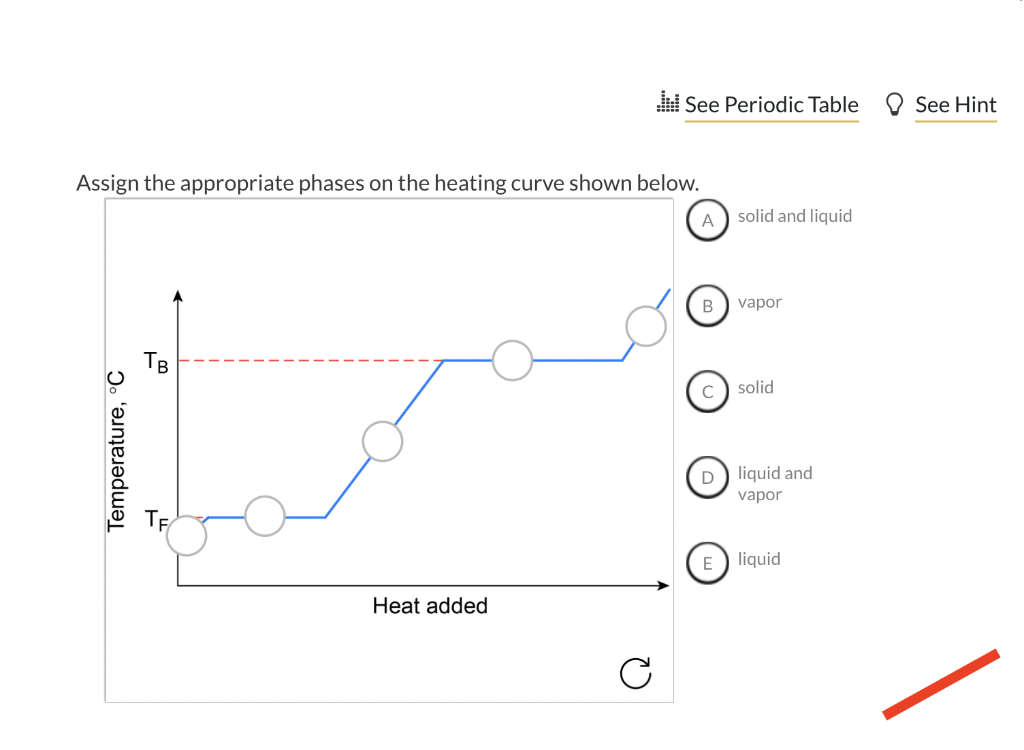
On a heating curve, a flat section indicates what?
A change of state.
Which state of matter has no fixed shape but has a fixed volume?
Liquid
According to the theory, all matter is made up of these.
Particles
Ice melting shows that particles can ______.
Change arrangement or gain energy
The process by which a liquid changes to gas at the surface.
Evaporation
Define ‘Melting Point’
The melting point of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid.
Particles in this state move freely and spread to fill their container. Identify the state of matter.
Gas
The strength of this between particles determines whether a substance is solid, liquid, or gas.
Forces of Attraction
The brown gas nitrogen dioxide spreading through air provides evidence for what property of particles?

Constant motion / diffusion
Explain what happens to the forces of attraction when ice melts.
They weaken as particles gain energy and move apart.
What happens to particle motion as temperature rises in the solid region of the curve?
Particles vibrate faster around fixed positions.
Identify the state of matter below:

Solid
In which state are particles arranged in a fixed lattice structure?
Solid
The experiment using ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases in a tube produces what evidence of particles moving?
Formation of a white ring of ammonium chloride closer to the HCl side due to diffusion.

Below are images showing dry ice being used at events. Identify the name of change of state being demonstrated in the diagrams below.


Sublimation
In a cooling curve, the flat region represents what happening?
A change of state with heat loss while temperature remains constant.
Name two property that distinguishes gases from liquids.
Compressibility / Arrangement of particles / volume not fixed / diffusion rate
State 3 of the main points of the particulate theory.
-Matter is made up of tiny particles.
-Particles are in constant motion and temperature affects the speed of motion.
-Particles have spaces between them.
-Forces of attraction exist among particles.
Give and define two pieces of experimental evidence that matter is made of particles.
Diffusion - movement of particles from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration until evenly distributed.
Osmosis - movement of water molecules from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration across a selectively permeable membrane until evenly distributed.
Why does heating a liquid cause it to boil?
Particles gain enough energy to overcome intermolecular forces and escape as gas.
Identify on the diagram where “liquid and vapor” falls.