This is the most common cause of chronic renal failure.
What is Diabetes mellitus?
Most common disease of the gallbladder.
What are gallstones (cholithiasis)?
A common complication of renal transplantation.
What is a renal artery stenosis?
Composed of extravasated pancreatic enzymes that escape into the peripancreatic soft tissue. Fluid begins to collect and eventually a thickened wall of collagen and granulations develops.
What is a Pancreatic Pseudocyst?

A normal spleen can vary in size; however, a length of ≥ 12 cm is considered to be enlarged.
What is splenomegaly?

Often the first sign of urinary diesase, and may occur anywhere in the urinary system.
What is hematuria?
Commonly caused by Cholelithiasis that create a cystic duct obstruction.
What is acute cholecystitis?

The most common cause of IVC obstruction leading to enlargement.
What is Right-sided heart failure?
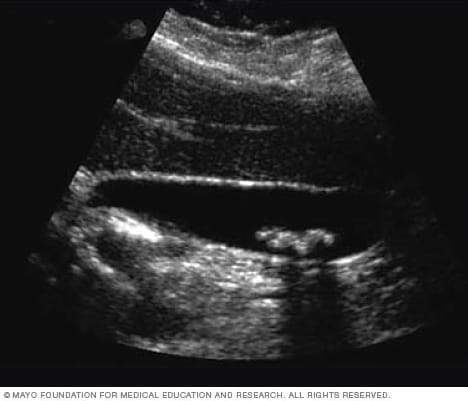
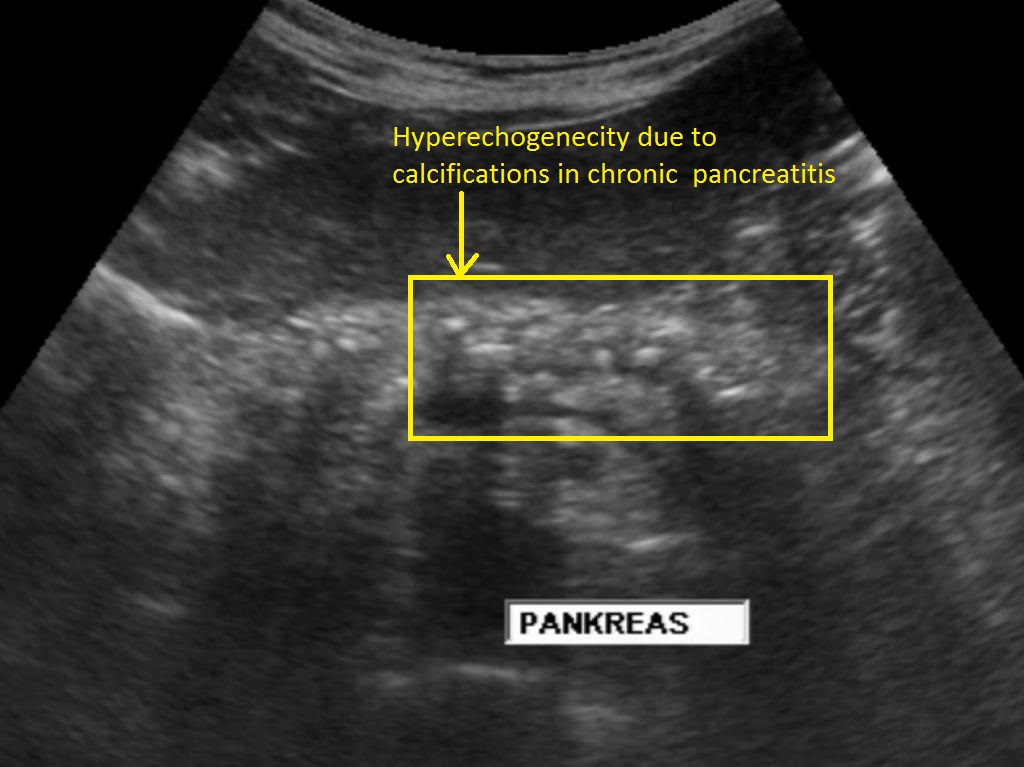
Pancreas generally appear smaller than normal and hyperechoic because of scarring and fibrosis.
What is chronic pancreatitis?
Decreased physiologic function of the spleen, associated with impaired function of absence of the spleen.
What is hyposplenism?

This pathology occurs in patients with calyceal diverticulum.
What is Milk of calcium cysts?
The gallbladder wall is thickened and edematous, with focal areas of exudate, hemorrhage, and necrosis. (Air in gallbladder wall and lumen)
What is gangrenous cholecystitis?
Characterized by decreased outflow from the left renal vein, into the inferior vena cava due to extrinsic Left renal vein compression.
What is Nutcracker Syndrome?
Most common form of pancreatic cancer. A highly aggressive tumor that arises from the pancreatic ductal epithelium and rarely from the acini.
What is Adenocarcinoma?

The most common disseminated calcifications.
What are Granulomas?
This disease has sonographic findings of shadowing calculi, clubbing of calyces, round or triangular anechoic medullary pyramids, and hydronephrosis
What is Papillary necrosis?
This disease has a clear relationship with oral contraceptives and decreasing, then increasing with pregnancy. it is worrisome because of its risk of hemorrhage and increased risk of developing into HCC.
What is Hepatocellular adenoma?
Development of a fibrous mass that covers the Abdominal Aorta, Inferior vena cava, and ureters. The cause is unknown and is linked with infections, headache medication,and aneurysm rupture.
Have a tendency for malignancy and constitute ~30% of this type of cell tumors.
What are non-functioning islet cell tumors?

When clinical symptoms are present, they may include pancytopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia.
What is a Hamartoma?

Chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by a mass originating in the renal parenchyma. This illness results from long term renal obstruction and infection. This disease is usually unilateral, and patients are often immunocompromised.
What is Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis
Puss containing lesions most commonly the result of biliary tract disease, but also seen with infection via the hepatic artery or portal vein, trauma or surgery.
What is Pyogenic Abscess?
A complex and difficult to recognize disease associated with poor blood supply to the intestinal tract because of underlying vascular compromise.
What is mesenteric insufficiency?
May also appear similar to pseudocysts, polycystic disease, cystic fibrosis, and von Hippel-Lindau disease.
What are cystadenomas?
A rare vascular tumor that may be isolated to the spleen or involve multiple organs. Mostly in childhood. Presents as: LUQ pain, nausea, or abdominal distention.
What is a Lymphangioma?

