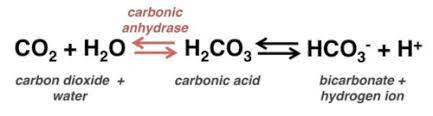Causes of Hypovolemic Shock include Trauma (such as lacerated arteries or GI bleeds) but also can include atraumatic causes such as this:
What is Dehydration or loss of fluids
Cardiogenic shock occurs when this organ cannot pump a sufficient amount of blood to maintain an effective Cardiac Output
What is the Heart

In general all distributive shock is due to this phenomenon:
What is Uncontrolled Vasodilation
Obstructive shock is caused by this
What is a Physical Obstruction blocking the forward flow of blood through the circulatory system
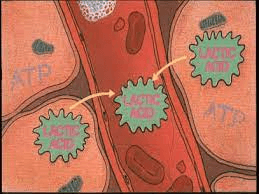
In the absence of oxygen, cells may rely on the following type of metabolism to create ATP, resulting in the buildup of Lactic Acid and a 'dirty burn.'
What is Anaerobic Metabolism

This cause of respiratory acidosis leads to lack of Oxygen reaching the tissues to perform internal respiration and buildup of CO2 in the blood
What is Hypoxia
Decrease in perfusion of tissues and organs due to insufficient blood volume in the vascular space leads to stimulation of this part of the nervous system
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System
This is the most common cause of Cardiogenic shock:
What is a large Myocardial Infarction
This type of Distributive Shock is due to an exaggerated immune response to an Antigen (foreign protein)
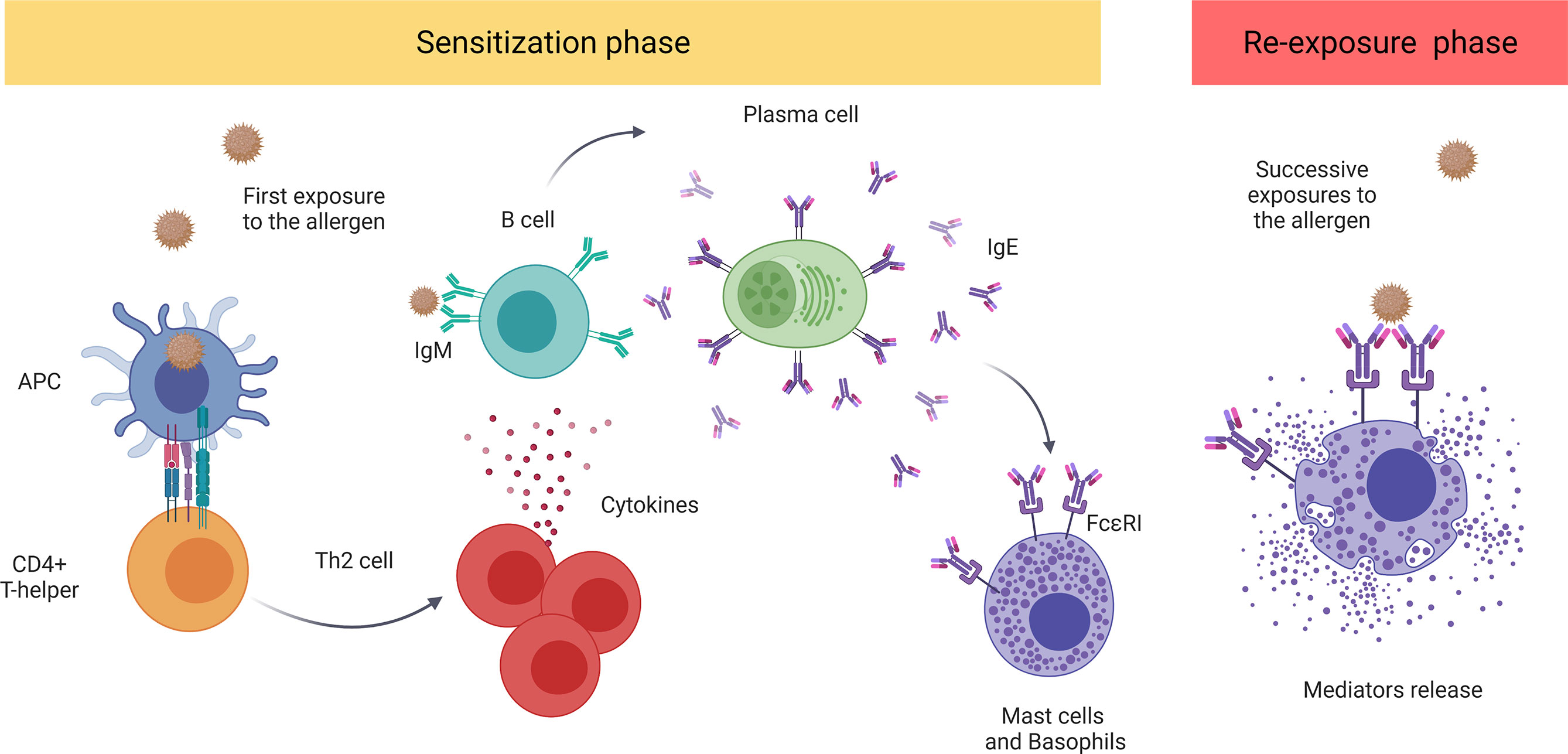
What is Anaphylactic Shock
These are the three main causes of Obstructive Shock
What are:
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Tension Pneumothorax
- Cardiac Tamponade
This metabolic waste product builds up during Anaerobic metabolism, accumulating in tissues and contributing to metabolic acidosis
What is Lactic Acid
(or Lactate)

Overdosing on aspirin (salicylic acid) is a potential toxin that can cause this acid base disturbance:
What is metabolic acidosis OR respiratory alkalosis
(this is a trick question, it can cause either!)

When the patient's blood pressure falls we say that they have entered this stage of shock:
What is Decompensated shock
Cardiac Output is a product of these two things
What are Stroke Volume and Heart Rate

This type of Distributive Shock is not characterized by cool, pale skin but instead the skin can be warm with normal color, or sometimes a line of demarcation like seen below:
What is Neurogenic Shock
The pulmonary vasculature is most often affected by blood clots for this reason
What is:
It is the first point where the vasculature narrows after returning from the venous system
This cellular pump is one of the largest consumers of ATP in the human body. Lack of ATP can cause this pump to stop functioning, causing Na to build up in cells
What is the Sodium/Potassium pump
Ingestion of this toxic substance could cause this acid-base disturbance in your patient

What is Metabolic Acidosis due to Ethylene Glycol (antifreeze) poisoning

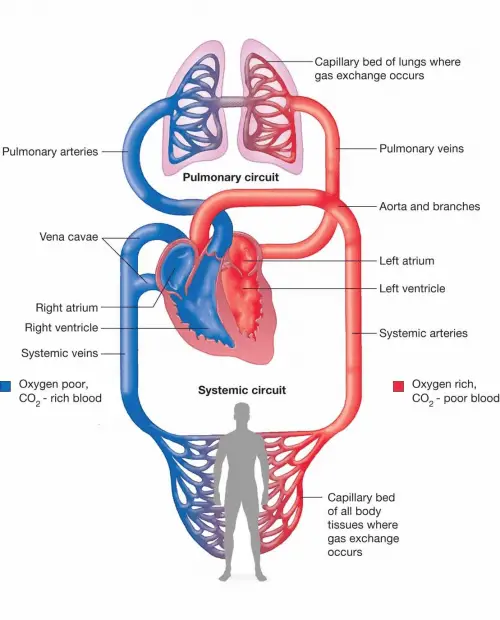
What happens to a patient's Cardiac Output in the initial stages of Hypovolemic Shock?
Cardiac Output is decreased (Fig. 10-11)
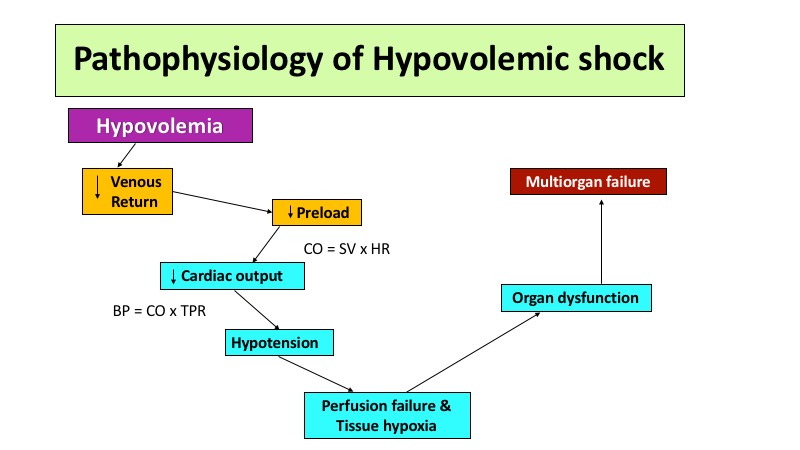
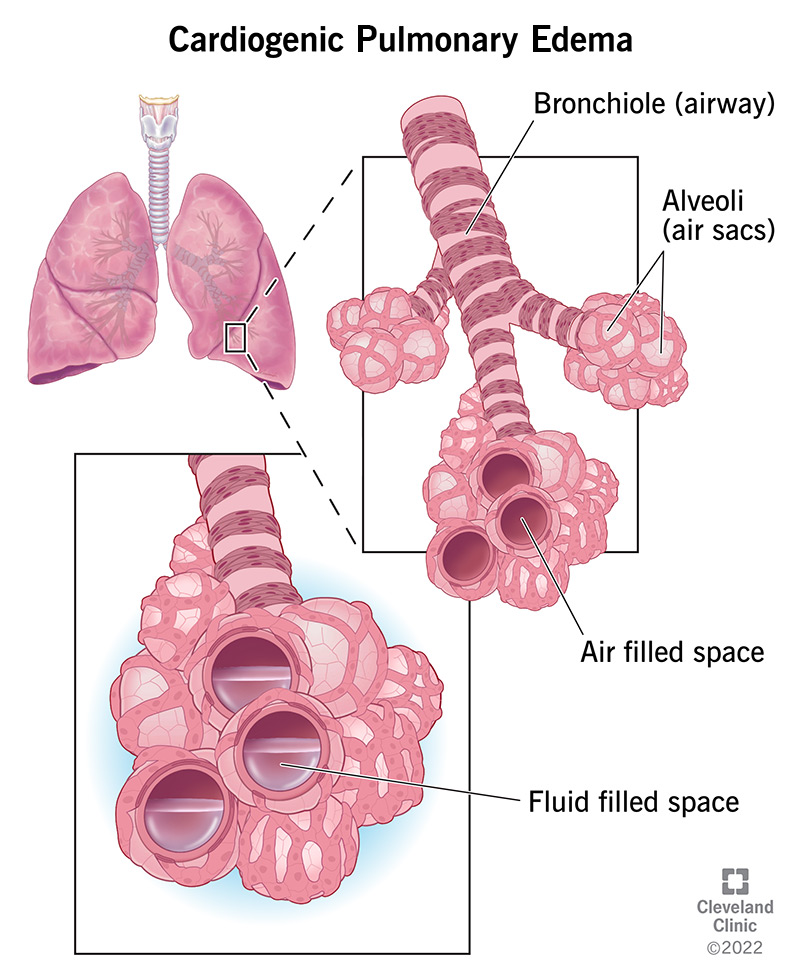
Pulmonary edema often occurs with Cardiogenic shock for this reason
What is:
The left ventricle cannot accept all the blood trying to return from the lungs, so blood backs up into the pulmonary circulation and increases hydrostatic pressure, forcing fluid through the capillaries into the interstitial spaces around the Alveoli and the air sacs themselves
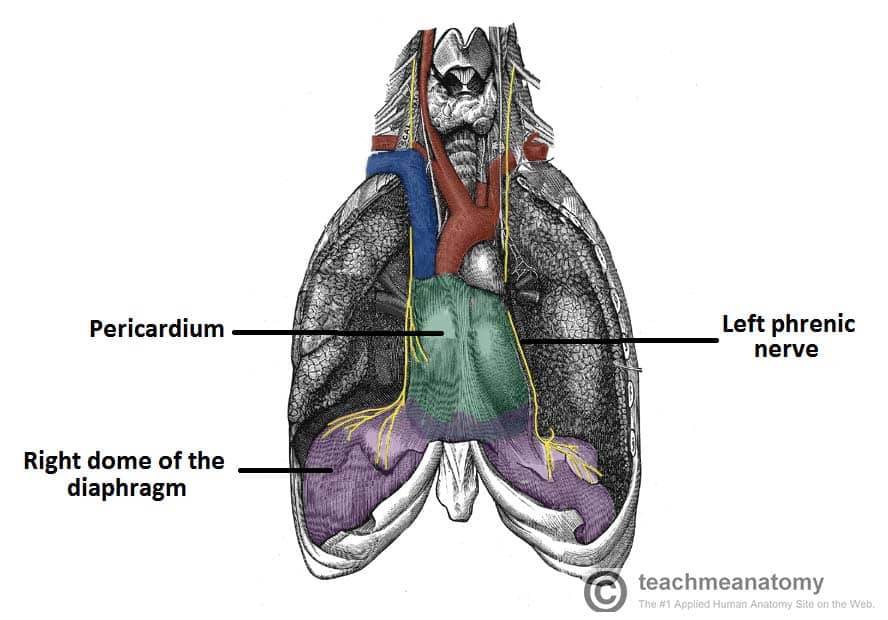
Cervical spine injuries to C3-C5 may cause impairment to the function of this muscle, common in Neurogenic Shock
What is the Diaphragm
A late sign of this cause of Obstructive Shock involves shifting the mediastinum away from the affected side
What is Tension Pneumothorax

The body can compensate for decreased tidal volume of respirations by increasing this:
What is Respiratory Rate
This serious acid base disturbance results when the body can't produce enough Insulin and the body starts to break down fat as fuel, causing a buildup of ketones in the blood
What is Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)

This causes the Washout Phase of Hypovolemic Shock
The post capillary sphincters fail, allowing the stagnant blood with accompanying microscopic blood clots and lactic acid to washout of the capillaries and reenter the circulation
This can cause Jugular Vein Distension (JVD) in patients in Cardiogenic shock
What is blood from the Right Ventricle backing up into the systemic circulation

The pathophysiology of Neurogenic Shock includes this type of traumatic injury
What are Severe High Spinal Cord Injuries (above T6)

Low-velocity, penetrating chest trauma is a common cause of this type of Obstructive shock
What is Pericardial Tamponade

Of the 500mL of air in the average adult tidal volume, 150mL remains in the conducting portions of the airway and is not able to participate in gas exchange. These part of the airway are called the:
What is Anatomical Dead Space

What are the missing terms from the bicarbonate buffer system equation below:
______ <=> H2CO3 + H2O <=> H+ + HCO3-
What are Water & Carbon Dioxide
H2O + CO2