Which Cranial Nerve's function is vision? (sensory)
Optic CNII
what % of the gait cycle is stance phase?
60%
What are the two types of tests for a suspected ACL injury?
Ant drawer + Lachman's
Explain the Rhombergs test and normal finding.
Feet together standing erect with eyes closed 30 seconds
minimal swaying
Which Cranial Nerve's function innervates the lateral rectus to create eye movements? (motor)
Abducens. CNVI
In what phase of gait is the hip flexed to 25 degrees, and the knee and ankle are neutral?
Heel strike/initial contact
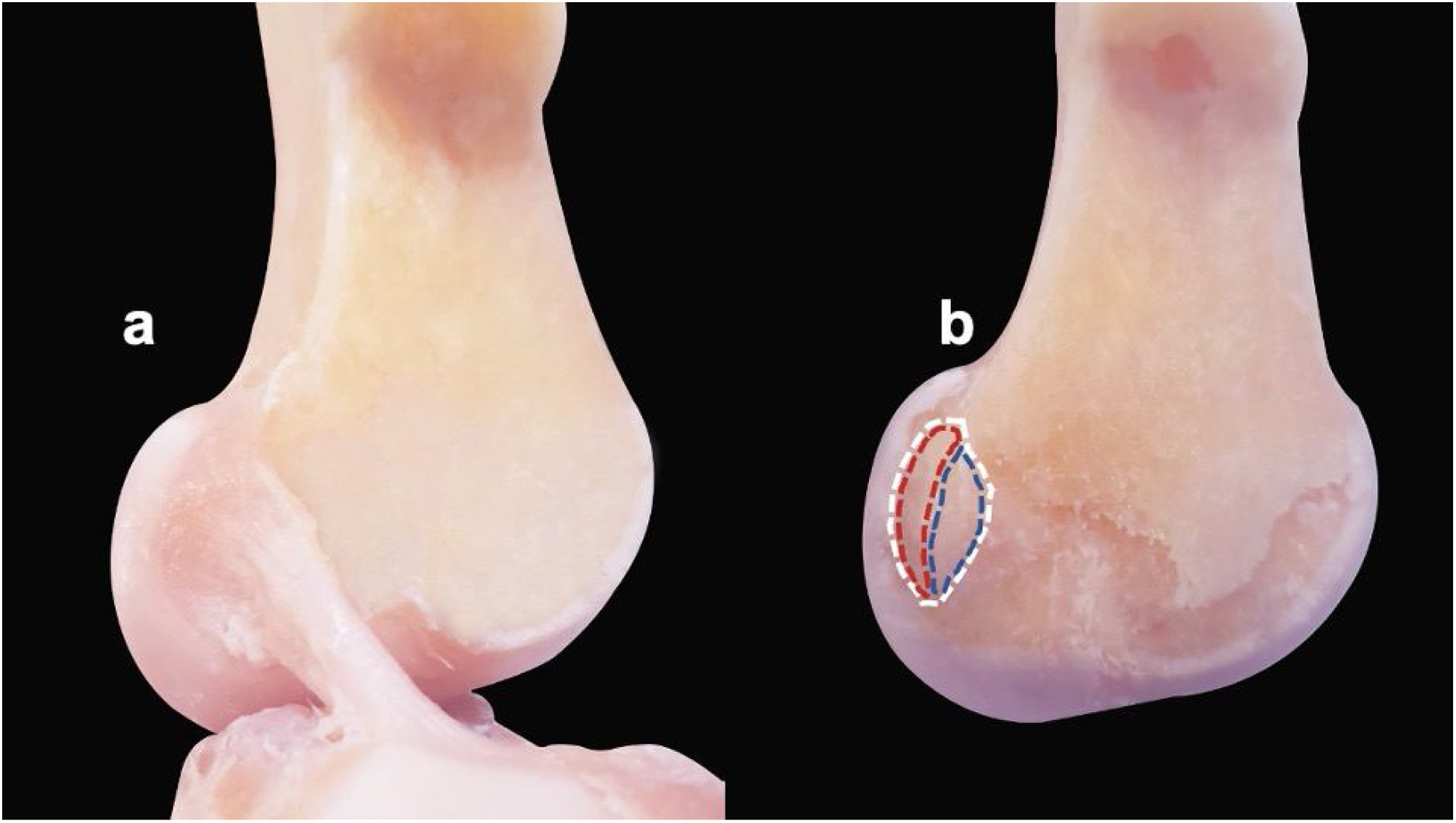
A valgus stress test will determine this type of knee injury.
MCL injury
What is the heel to shin test?
This tests lower extremity cerebellar function or coordination
Which Cranial Nerve's function involves taste, pharynx and salivary glands? (mixed)
Glossopharyngeal. CNIX
During toe-off, describe the position of the hip, knee, and ankle.
Hip = 0-10 degrees of extension
Knee= 30-40 degrees of flexion
Ankle= ~20 degrees of plantarflexion
What test do you assess both lateral and medial meniscus?
McMurray's
What are the 7 main aspects of a LL neuro exam?
Observe • Gait • Tone • Power • Reflexes • Sensation • Coordination
What does the trochlear nerve innovate? What is the action?
The superior oblique muscle.
Eye intorsion, depression and abduction
During the deceleration phase of the swing phase (aka terminal swing phase) the ankle is in which position, AND what muscles are working to keep the foot in that position?
Neutral ankle. Dorsiflexors are contracting to keep the foot from 'foot slap' aka plantarflexion
Knee hyperextension injury.
Commonly PCL. Can be most other ligaments + neurovasculature.
Explain the grading scale for muscle power testing
5. Normal strength
4. Some resistance but movement is possible
3. Movement is possible against gravity but not against resistance by examiner
2. Movement possible, but not against gravity
1. Muscle flicker but no movement
0. No muscle contraction
What are the branches of the trigeminal nerve and where do they exit the skull?
Ophthalmic = superior orbital fissure
Maxillary = foramen rotundum
Mandibular = foramen ovale
Please describe the gait pattern of a pt with parkinsonism symptoms.
- Hypokinesia + bradykinesia (decreased step length with decreased speed)
- Decreased coordination
- Festination (decreased step length with increased cadence)
- Freezing of gait (the inability to produce effective steps at the initiation of gait or the complete cessation of stepping during gait)
- Difficulty with dual tasking during gait
- Wide BOS
What is happening in this XRAY?

R) lateral tibial fracture.
*Occurs in 75-100% of ACL ruptures (from Radiopedia). Due to the rotatory forces that occur with an ACL. Likely a strain of ITB too.
What is the spinal pathway for light touch, vibration and proprioception?
Doral column (medilemniscus tracts)