Health & Wellness
& Treatments
This disorder is named for having an extra copy of chromosome 21
What is Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21)?
Down Syndrome is associated with an increased risk of developing this disorder of the brain
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
Recent population-based studies of adults with Down syndrome have observed Alzheimer-type dementia in approximately 10% of those aged 40 to 49 years and 26% of those aged 50 and over
A 15 year old female comes into your office and states that she recently became sexually active and would like to begin oral contraceptives but does not want her parents to know that she is taking them. The best response in this situation would be.
What is prescribe the OCP without informing her parents?
This disorder usually presents by age 8 and is defined by a child who is revengeful, and often times hostile towards authoritative figures.
What is Oppositional Defiant Disorder (ODD)?
Many children tend to disobey, argue with parents, or defy authority. They may often behave this way when they are tired, hungry, or upset. But in children and teens with ODD, these symptoms happen more often. They also interfere with learning and school adjustment. And in some cases, they disrupt the child’s relationships with others.
Other symptoms include frequent temper tantrums, arguing with parents, hostility and defiance towards authoritative figures, doing things that intentionally annoy people.
According to AAFP guidelines, these medications (in addition to cognitive behavioral therapy) are considered first line treatment for cases of pediatric depression
What are Fluoxetine (Prozac) and Escitalopram (Lexapro)?
Major depressive disorder in children and adolescents is a common condition that affects physical, emotional, and social development. Risk factors include a family history of depression, parental conflict, poor peer relationships, deficits in coping skills, and negative thinking. Diagnostic criteria are the same for children and adults, with the exception that children and adolescents may express irritability rather than sad or depressed mood, and weight loss may be viewed in terms of failure to reach appropriate weight milestones.
This disorder is named for having an extra copy of chromosome 13
What is Patau Syndrome (Trisomy 13)?
Turner Syndrome is associated with this congenital heart abnormality that results in a phenomenon known as Brachial-Femoral Delay
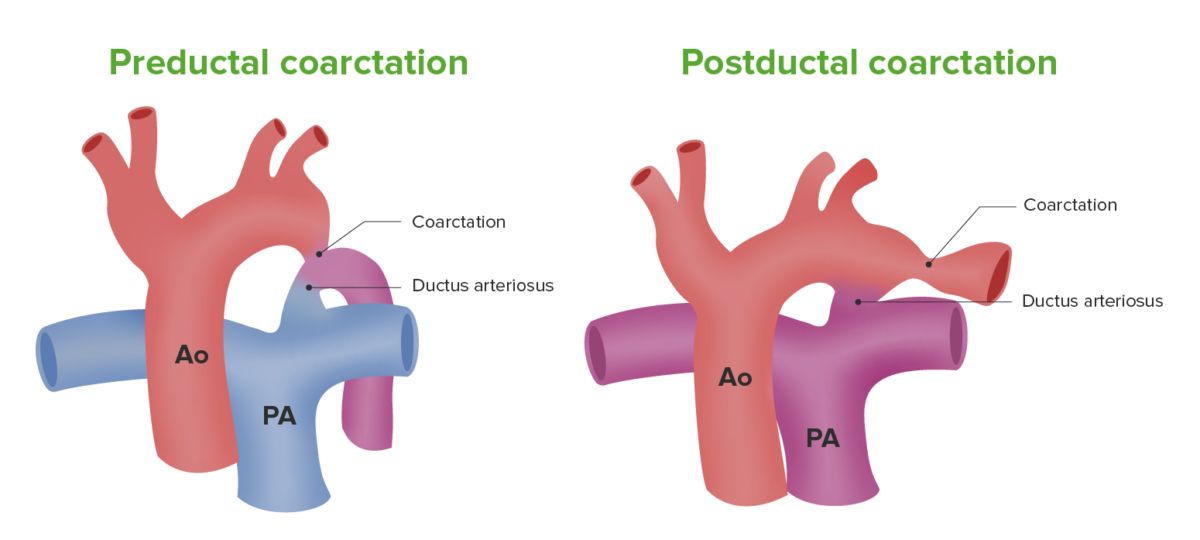
What is Coarctation of the Aorta?
The defect occurs when a baby’s aorta does not form correctly as the baby grows and develops during pregnancy. The narrowing of the aorta usually happens in the part of the blood vessel just after the arteries branch off to take blood to the head and arms, near the patent ductus arteriosus, although sometimes the narrowing occurs before or after the ductus arteriosus.
A 16 year old male comes into the office accompanied by his mother for a yearly well child visit. The patient is in good health, is physically active, and follows a regular healthy diet. Near the end of the visit, the physician should recommend what?
What is "request to speak with the child alone"?
According to AMA guidelines, teenagers are encouraged to speak alone with their Pediatricians or Family Medicine providers beginning at age 13. Despite this, most teenagers do not speak with or do not get the opportunity to speak privately with their doctor until the age of 17-18. As a provider, briefly speaking with teenagers alone can be an opportunity to discuss sexual health, mental health, and substance abuse. These are topics that teenagers are often unwilling to discuss in front of their parents and are areas that often can go under-treated due to this.
This disorder usually presents around age 6 and is associated with sudden, repetitive, and unwanted movements or vocal sounds.
What is Tourette Syndrome?
Tourette syndrome is a disorder that involves repetitive movements or unwanted sounds that can't be easily controlled. Tics typically show up between ages 2 and 15, with the average being around 6 years of age. Males are about three to four times more likely than females to develop Tourette syndrome.
Tourette Syndrome is commonly associated with ADHD, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder, and Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Treatment is aimed at controlling tics that interfere with everyday activities and functioning. High potency anti-psychotics such as Haloperidol and Fluphenazine are typically first line treatment for Tourette. Behavioral Therapy is also an adjuvant therapy used in the treatment of Tourette Syndrome.
A 18 month old child comes to your office accompanied by their parents who note that their child has shown little interest in playing with others and has exhibited poor eye contact with others. You explain to the parents that the child is exhibiting signs of this disorder.
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder?
ASD can sometimes be detected at 18 months or younger. By age 2, a diagnosis by an experienced professional can be considered very reliable. However, many children do not receive a final diagnosis until much older.
Early signs of ASD can include:
- Avoiding eye contact
- Having little or no interest in other children or caretakers
- Having limited display of language and communication skills
- Getting upset by minor changes in routine
AAP recommends that all children be screened specifically for ASD during regular well-child doctor visits at 18 months and 24 months
This disorder is named for having an extra copy of chromosome 18
What is Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)?
This autosomal recessive disorder is associated pediatric kyphoscoliosis and can be a potential cause of hypertrophic or severe dilated cardiomyopathy
What is Friedreich's Ataxia?
People with this condition develop impaired muscle coordination that worsens over time. Other features of this condition include the gradual loss of strength and sensation in the arms and legs, muscle stiffness, and impaired speech, hearing, and vision. Individuals with Friedreich ataxia often have a form of heart disease called hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which enlarges and weakens the heart muscle and can be life-threatening.

According to the CDC, these are some of the factors that play into a higher prevalence of mental illness. (name 1)
What are age (increasing age), gender (males > females), and socioeconomic status?
According to the CDC, amongst children living below 100% of the federal poverty level, more than 1 in 5 (22%) had a mental, behavioral, or developmental disorder.
This disorder presents as a child who is repetitively deceitful, aggressive, and destructive with an intent to harm.
What is Conduct Disorder?
Most symptoms seen in children with conduct disorder also happen at times in children without this problem. But in children with the disorder, these symptoms occur more often. They also interfere with learning, school adjustment, and sometimes with the child’s relationships. Symptoms most often include aggressive behavior, destructive behavior, deceitfulness, and violation of rules.
Treatment for Conduct Disorder most often centers around therapy including CBT, family therapy, and peer group therapy. Medications are not usually used for treatment of Conduct Disorder but can be used if there is a co-existing disorder present such as ADHD.
After age 18, Conduct Disorder is reclassified as Antisocial Personality Disorder.
A 14 year old boy presents to you with his mother who states that recently the patient's grades in school have begun to slip and she has noticed that he seems easily distracted at home. She also notes that he has had trouble doing homework but that he has always been a good student in the past. You explain to the patient's mother the most likely diagnosis and plan to prescribe a medication for this patient's diagnosis. You explain to the mother that the most likely adverse reaction to this medication is this.
What is loss of appetite?
Methylphenidate is the most commonly prescribed drug for ADHD worldwide. It’s known by a number of brand names, including Ritalin, Concerta, Metadate, Daytrana, and Quillivant.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends waiting until age 6 to start ADHD medications. The most common adverse reactions include:
- low or no appetite
- weight loss
- sleep problems
- social withdrawal
This disorder is caused by a deletion on the short arm of chromosome 5
What is Cri-du-chat syndrome?
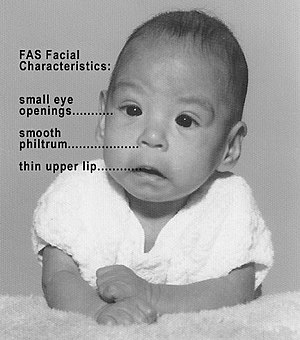
This disorder is the most common preventable causes of intellectual disability and is associated with congenital cardiac defects and facial abnormalities
What is Fetal Alcohol Syndrome?
This organization specializes in suicide prevention amongst the LGBTQ youth community.
What is the Trevor Project?
The Trevor Project provides 24/7 crisis support services to LGBTQ young people.
The Trevor Project is an American nonprofit organization founded in 1998 focused on suicide prevention efforts among lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, and questioning (LGBTQ) youth. Through a toll-free telephone number, it operates The Trevor Lifeline, a confidential service that offers trained counselors.
A 15 year old female presents to your office for an annual well visit. She notes that she is a dancer and plays tennis in school. She also goes running every day after dinner. The child's mother notes that lately the child has been acting differently and doesn't seem like herself. She states her daughter is always looking in the mirror and trying to fit into old clothes. The patient states that she is fine and nothing is wrong with her. On physical examination, you note that the patient is tachycardic. You also note small calluses on the back of her hands which the patient contributes to playing tennis. Upon speaking with the patient and her mother you come up with the most likely diagnosis and discuss treatment. You note that a specific medication is contraindicated in the treatment of this disorder.
What is Buproprion (Wellbutrin)?
This 15 year old is showing classic signs of Bulimia Nervosa. Bulimia Nervous is commonly characterized by negative self esteem, repetitive patterns of binge eating with compensatory purging, dehydration, tachycardia or irregular heart rhythm, tooth and gum decay, absence of periods in females, and associated anxiety or depression. There may also be presence of parathyroid gland hypertrophy, electrolyte imbalances, and dorsal hand calluses.
Treatment for Bulimia Nervosa most often centers on CBT, family therapy, or interpersonal psychotherapy. The medication currently used to treat Bulimia is Fluoxetine (Prozac).
Wellbutrin is specifically contraindicated due increased risk of seizures in patients with Bulimia and Anorexia.
A mother presents to your office with her 3 month old infant and states that he has suddenly become lethargic and difficult to arouse. She notes that she left the baby alone with the baby's father this morning while she went out to get groceries. On physical exam you note that the infant is lethargic and apneic and has multiple intraretinal hemorrhages present in both his eyes. You explain to the mother that the most likely diagnosis is this.
What is Shaken Baby Syndrome?
Shaken Baby Syndrome is most common in 3-4 month old infants and presents early with nonspecific symptoms including lethargy, irritability, poor feeding, vomiting and later with seizures or apnea. Subdural hematoma and edema account for most neurological findings. Retinal hemorrhages in shaken baby syndrome typically manifest as numerous, multilayered hemorrhages of the entire retina in both eyes, many of them with a white spot in the center (Roth spots).
This disorder is associated with a Trinucleotide Repeat mutation in the FMR1 gene
What is Fragile X Syndrome?
DiGeorge Syndrome, a chromosomal deletion of 22q11, is associated with a cardiac abnormality consisting of these 4 primary complications
What is Tetralogy of Fallot:
1) Pulmonary stenosis
2) Right ventricular hypertrophy
3) Overriding aorta
4) Ventricular septal defect

This organization focuses on partnering volunteers with those with intellectual and developmental disabilities to foster a friendship or mentorship.
What is Best Buddies?
Best Buddies consists of volunteers that create opportunities for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities (IDD). The program's main purpose is to allow volunteers to be paired up with a buddy with an intellectual and developmental disability and provide them with a friend or a mentor. Best Buddies is the world's largest organization dedicated to ending the social, physical and economic isolation of the 200 million people with IDD.
Name the 3 main characteristic symptoms that describe ADHD.
What are: hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention in multiple settings?
ADHD is characterized >6 months of symptoms which include hyperactivity, impulsivity, and inattention that must be present in at least two settings. Hyperactivity is commonly defined as being fidgety, talking when inappropriate, moving around a lot. Impulsivity is commonly defined as acting without thinking about the consequences, talking or acting out of turn. Inattention is commonly defined as being easily distracted, being disorganized and often off task. Inattention must be present in at least two settings (usually at home and at school).
This questionnaire, recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics, is considered the most appropriate self assessment tool when screening children for childhood anxiety.
What is the Screening for Childhood Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) questionnaire?
The SCARED is a child and parent self-report instrument used to screen for childhood anxiety disorders including general anxiety disorder, separation anxiety disorder, panic disorder and social phobia.
https://www.tnaap.org/documents/scared-child.pdf