Which vasoactive medication is used for a severe TET spell that is unresponsive to positioning (knee to chest), supplemental oxygen or morphine?
A. Nipride
B. Dobutamine
C. Phenylephrine
D. Nicardipine
C. Phenylephrine
Which patient is the LEAST likely to have JET postoperatively?
A. CCAVC repair
B. Bidirectional Glenn procedure
C. IAA and VSD repair
D. ASO and VSD repair
E. TOF repair
B. Bidirectional Glenn procedure
2 month old s/p TOF repair develops a narrow complex tachycardia with associated decreased Bp and retrograde “p” waves on 12 lead EKG. Patient most likely has this arrhythmia:
A. Ventricular tachycardia
B. Sinus tachycardia
C. JET
C. JET
When palpating the brachial and femoral pulses on a neonate who presented with increased irritability and poor feeding, you notice a difference in pulse amplitude between brachial and femoral pulses. What does this patient most likely have?
A. CCAVC
B. Coarctation of the aorta
C. TGA with intact ventricular septum
D. TAPVR
B. Coarctation of the aorta
Name the 3 stages/procedures performed for a patient born with HLHS:
1. Norwood
2. hemi-Fontan or Glenn
3. Fontan
Which drug improves cardiac contractility, cardiac relaxation (lusitropy) and induces vasodilation?
A. Phenylephrine
B. Epinephrine
C. Milrinone
D. Vasopressin
C. Milrinone
All of these can be used to treat CHB EXCEPT?
A. Isuprel
B. Cardioversion
C. Pacing
B. Cardioversion
Treatment for postoperative JET includes all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Cooling measures
B. AAI pacing
C. Amiodarone
D. Nipride
D. Nipride
1 day old admitted to the CICU for cyanosis. ECHO performed shows a large anterior malalignment type VSD with infundibular and valvar pulmonary stenosis:
A. Pulmonary atresia
B. TGA
C. TOF
D. TAPVR
C. TOF
Stage 1 Norwood procedure: name 2 different shunts used to provide pulmonary blood flow
1. BTT
2. Sano
Mechanism of hypocalcemia induced hypotension in newborns following cardiac surgery?
A. Elevated cortisol level
B. Hypernatremia
C. Immature sarcoplasmic reticulum
C. Immature sarcoplasmic reticulum
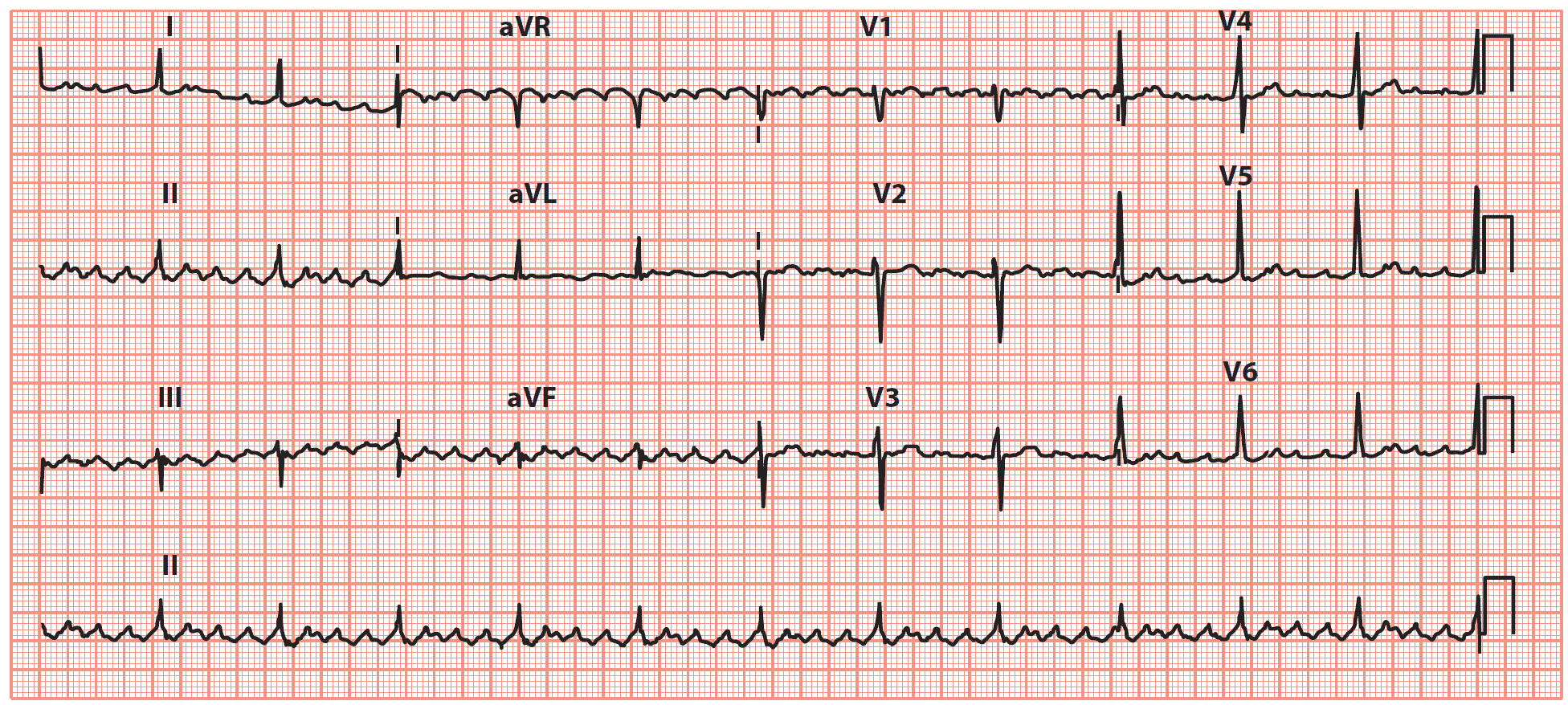
What is this rhythm?
A. V-tach
B. A-flutter
c. SVT
B. A-Flutter
Infant s/p repair IAA develops sinus tachycardia, hypotension, pulsus paradoxus, high CVP and poor perfusion. What postoperative complication is most likely?
A. Low cardiac output syndrome
B. Malignant hyperthermia
C. Cardiac Tamponade
D. Septic Shock
C. Cardiac tamponade

Truncus Arteriosus
What emergency procedure may need to be performed on a neonate born with the aorta arising from the right ventricle,pulmonary artery arising from the left ventricle, restrictive atrial communication and an intact ventricular septum?
Rashkind procedure (BAS)
Of the following inotropic agents, which mediation would increase myocardial oxygen consumption the MOST?
A. Epi @ 0.4 mcg/kg/min
B. Dopamine @ 5 mcg/kg/min
C. Milrinone @ 0.25 mcg/kg/min
A. Epi @ 0.4 mcg/kg/min

A postoperative patient with a prolonged QTc develops this arrythmia. Which medication is used to treat?
A. Adenosine
B. Isuprel
C. Magnesium Sulfate
D. Digoxin
C. Magnesium sulfate
3 week old born with HLHS now POD#14 following stage 1 Norwood procedure with 3.5 mm right modified BTT shunt. Previous 24 hours infant noted to have increased loose stools and emesis. Nurse at beside calls team to bedside for acute desaturation. What postoperative complication is most likely the cause of acute desaturation?
A. Decreased RV systolic function
B. Viral illness
C. Hypovolemia
D. BTT shunt occlusion
E. Sepsis
D. BTT shunt occlusion
Newborn with this initial CXR. What is the most likely congenital heart defect?
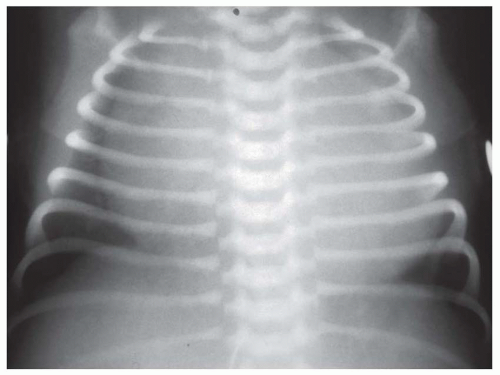
Ebsteins anomaly of the tricuspid valve
Name the surgical maneuver performed that involves repositioning the main pulmonary artery and its branches anterior to the aorta.
LeCompte maneuver
Which vasoactive medication increases HR, BP and decreases splanchnic perfusion?
A. Dopamine
B. Epinephrine
C. Vasopressin
D. Phenylephrine
A. Epinephrine

Name this rhythm:
A. Sinus bradycardia
B. Complete heart block (3rd degree)
C. 2nd degree heart block (Mobitz type I)
D. 2nd degree heart block (Mobitz type II)
D. 2nd degree heart block (Mobitz type II)
2 year old patient is POD#1 following heart transplant. Child becomes irritable with increased respiratory distress. You note decreased perfusion and new frequent ventricular ectopy on the monitor. What complication does this patient most likely have?
A. Ventricular tachycardia
B. Sepsis
C. Hypovolemia
D. Acute rejection
D. Acute rejection
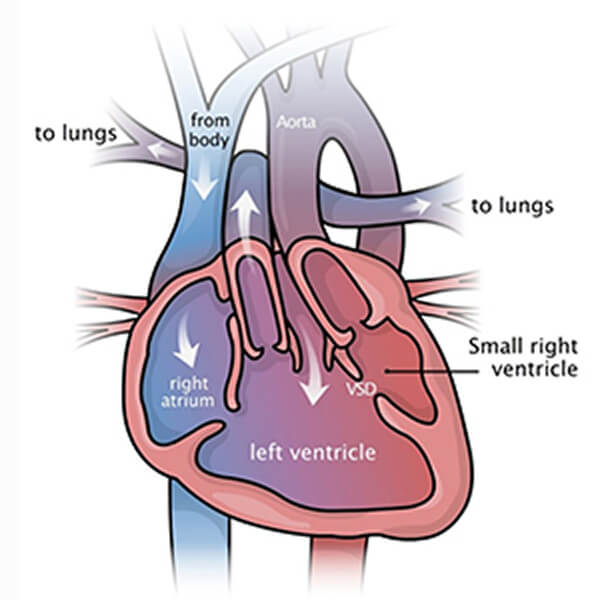
DILV
Neonate born with aortic atresia, IAA, VSD (normal mitral valve and small but apex forming left ventricle). Which of these procedures can be performed that preserves biventricular function?
A. Stage 1 Norwood
B. BTT shunt
C. Glenn procedure
D. Yasui procedure
D. Yasui