Type of digestive disorder
What is obstructive?
The device used to help administer a metered-dose inhaler (MDI) to a young child
What is a spacer or aerochamber?
Developmental theorist focusing on psychosocial development
Who is Erikson?
Type of ear infection seen here
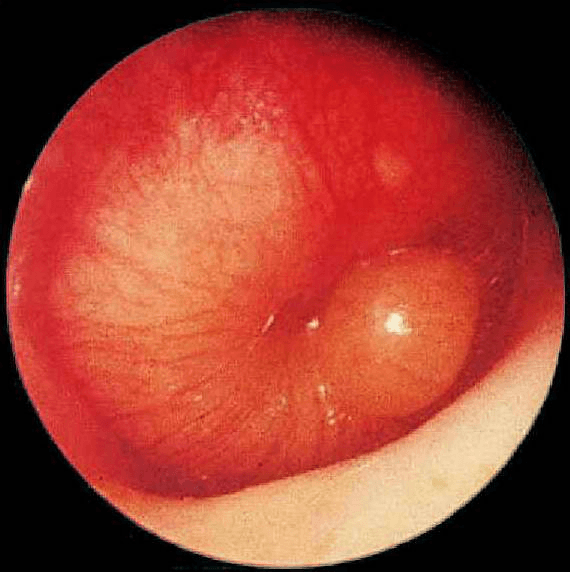
What is acute otitis media?
The 3 mainstays of treatment for sickle cell crisis
What are hydration, oxygenation, and pain management?
RSV occurs more frequently during this time of year
What is winter and early spring (November-March)?
Diagnostic test to confirm pyloric stenosis
What is an abdominal ultrasound?
The written document that provides detailed instructions to help prevent, control, and treat asthma
What is an asthma action plan?
Length of time required to count a heart rate and respiratory rate in a pediatric patient
What is one full minute (60 seconds)?
How a toddler demonstrates pain when they have an ear infection and the pain scale used to assess
What is pulling at the ear and the FLACC scale?
Medication that children take daily to try to reduce the risk of infection
What is Penicillin?
The best way to stop or prevent the spread of RSV
What is hand hygiene?
Name at least 2 of the 4 "P's" of pyloric stenosis
What are projectile vomiting, persistent hunger, palpable mass, and peristaltic waves?
Out of the choices below, choose the highest priority nursing diagnosis:
1. Fatigue r/t difficulty sleeping at night
2. Ineffective health maintenance r/t non-compliance with treatment
3. Risk for deficient fluid volume r/t increased respiratory rate
4. Ineffective airway clearance r/t bronchoconstriction
What is Ineffective airway clearance r/t bronchoconstriction?
Most sensitive indicator of fluid loss or gain in children
What is weight?
This can be seen behind the tympanic membrane in a child who has serous otitis media (OME)
What is fluid or air bubbles?
Type of sickle cell crisis characterized by cough, chest pain, and trouble breathing that is the most common of death in children aged 2-4 with sickle cell anemia
What is acute chest syndrome?
Diagnostic test for RSV
What is a nasopharyngeal swab?
The time in which to start feedings postoperatively
What is within 4-6 hours?
The reason why a patient would need to "step-up" asthma treatment and go from mild intermittent asthma to mild persistent asthma
What is the use of a SABA (like Albuterol) is more than twice per week?
Way to move the pinna of the ear when instilling ear drops for an 18-month-old
What is down and back?
Drug of choice for otitis media
What is Amoxicillin?
Name at least 3 precipitating factors for sickling episodes
What are infection, dehydration, high altitude, low body temp, stress, surgery, trauma, fever?
Name of immunoglobulin given to at risk infants and young children to prevent RSV
What is Synagis?
Name the surgical procedure
What is a pyloromyotomy?
The peak flow value falls to this percentage in the yellow zone of the asthma action plan (AAP)
What is 50-79%?
The safe dose range for Ibuprofen is 5-10 mg/kg/dose. If a 3-year-old child who weighs 14 kg is ordered Ibuprofen 100 mg PO Q6h prn fever, is this a safe dose?
What is yes?
5 x 14 = 70 mg/dose
10 x 14 = 140 mg/dose
100 mg falls between these numbers
The amount (mL) of Amoxicillin the nurse should administer if the provider orders 600 mg and the concentration of the medication is 400 mg/5 mL
What is 7.5 mL?
If both parents have sickle cell trait, what percent chance does the child of inheriting sickle cell anemia?
What is 25%?
Reason why RSV/Bronchiolitis affects infants and young children more seriously than older children and adults
What is the size of their airway makes them easier to become obstructed by thick secretions?