Nonpalpable, circumscribed lesions that vary in pigmentation from the surrounding skin
No elevations or depressions
Less than 1 cm in diameter
What are Macules?
These are firm 1-2mm, white, pearly papules. They appear predominantly on the face of newborns but may affect the trunk, genitalia, and extremities as well.
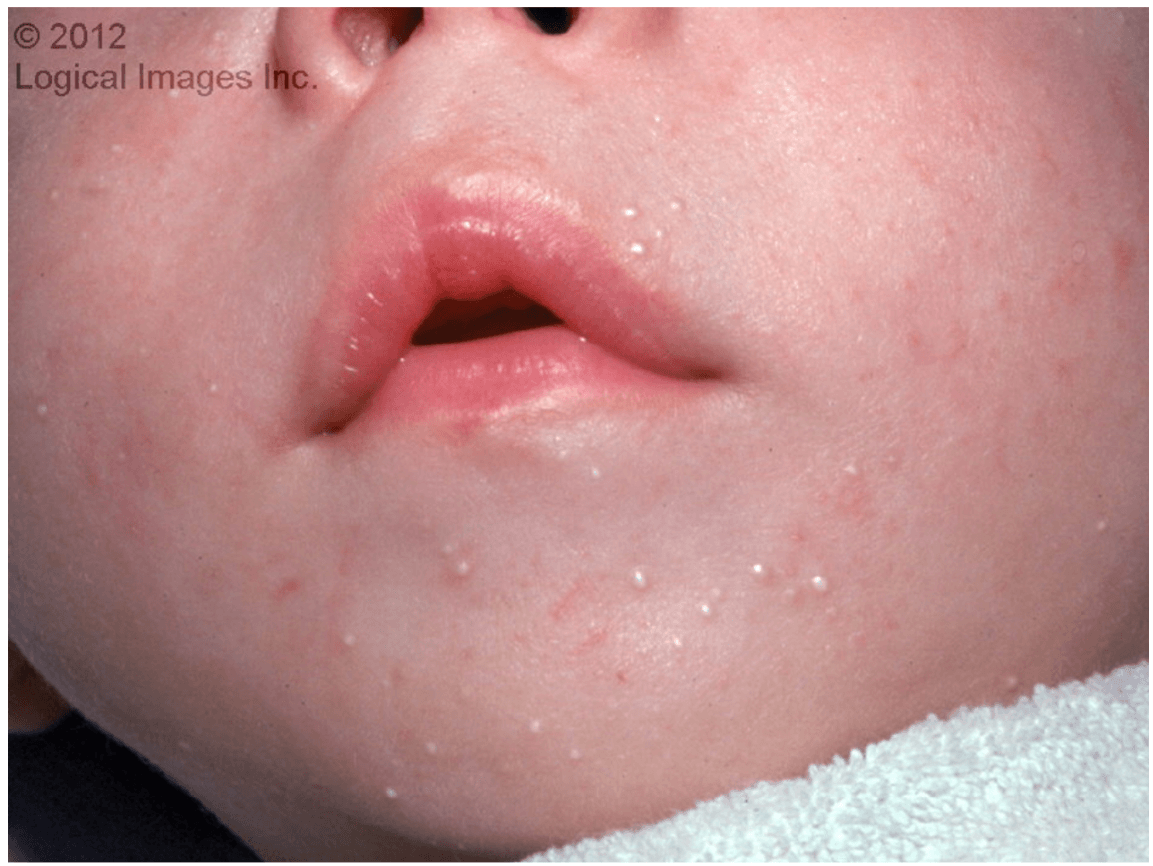
What is Milia?
A combination of blanching macules and papules that favors the trunk. The patient may be ill or well except for the rash which is often the most significant finding.
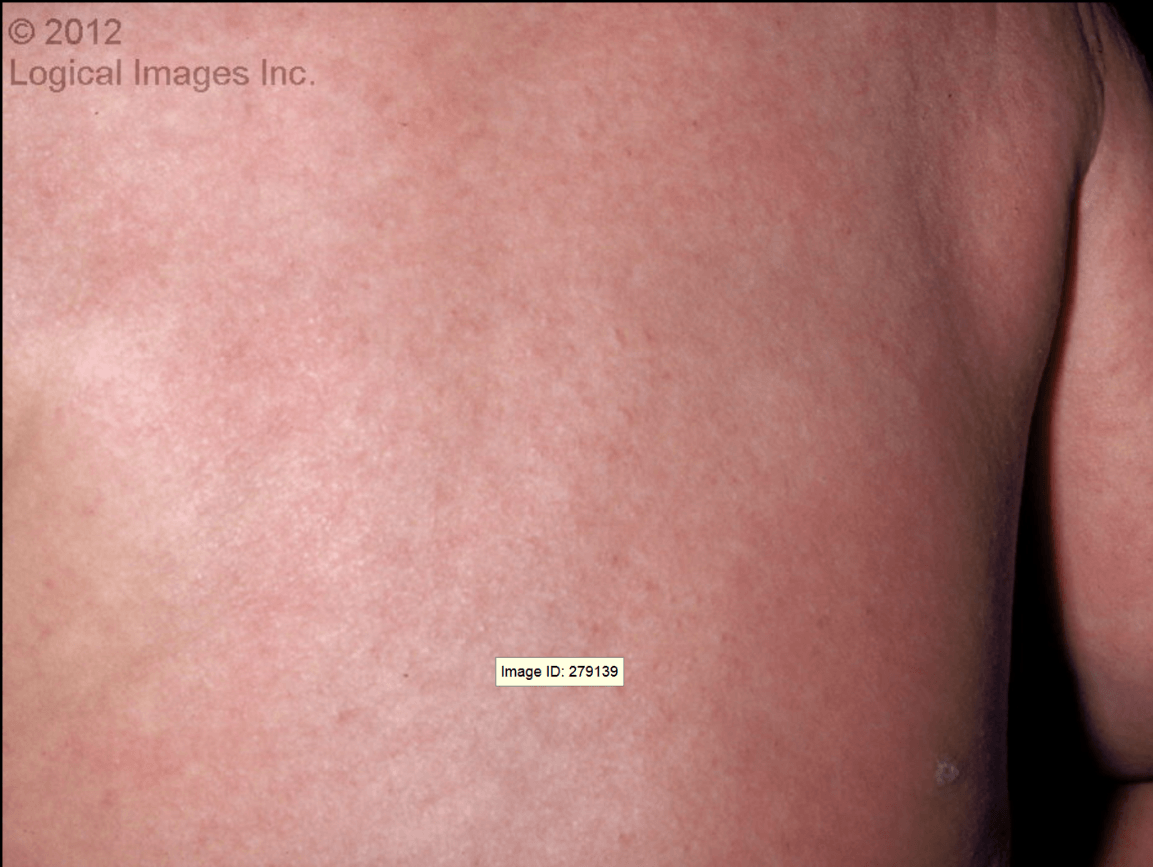
What is non-specific viral exantham
Smooth, skin-colored, 2-6 mm, domed papules with central umbilication (depression). May occur on any cutaneous or mucosal surface but are typically found on the face, trunk, and extremities, clustered near each other. Commonly seen in the skin folds of the axillae and groin.
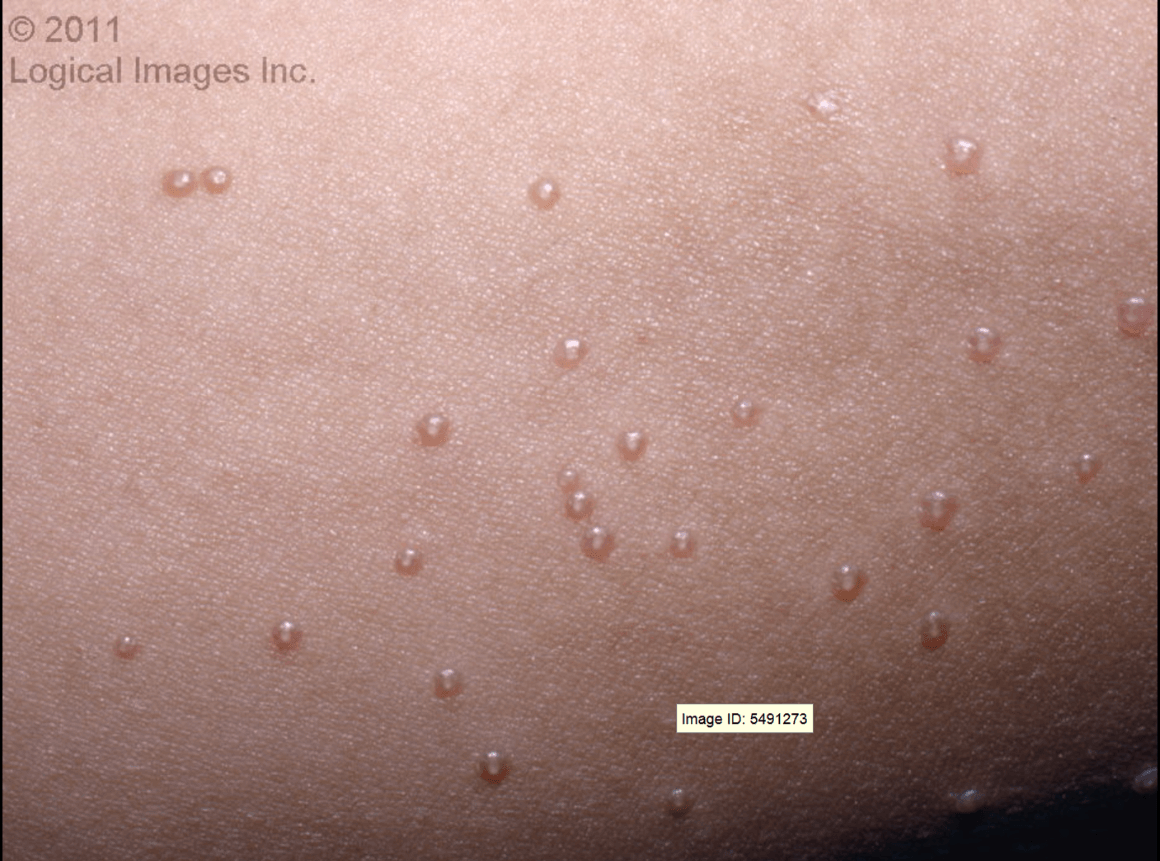
What is Molluscum Contagiosum?
Early lesion are well-defined, fixed erythematous macule or papule that rapidly develops a dusky grayish central discoloration. A vesicle may develop before the central color change.
Other lesions could appear as a well-defined wheal with a dusky or vesicular center that develops into concentric circles with a well-circumscribed erythematous border.
Individual lesions persist for 1-4 weeks.
Patients are otherwise well with, at most, mild systemic symptoms consisting of low-grade fever, malaise, arthralgias, or myalgias.
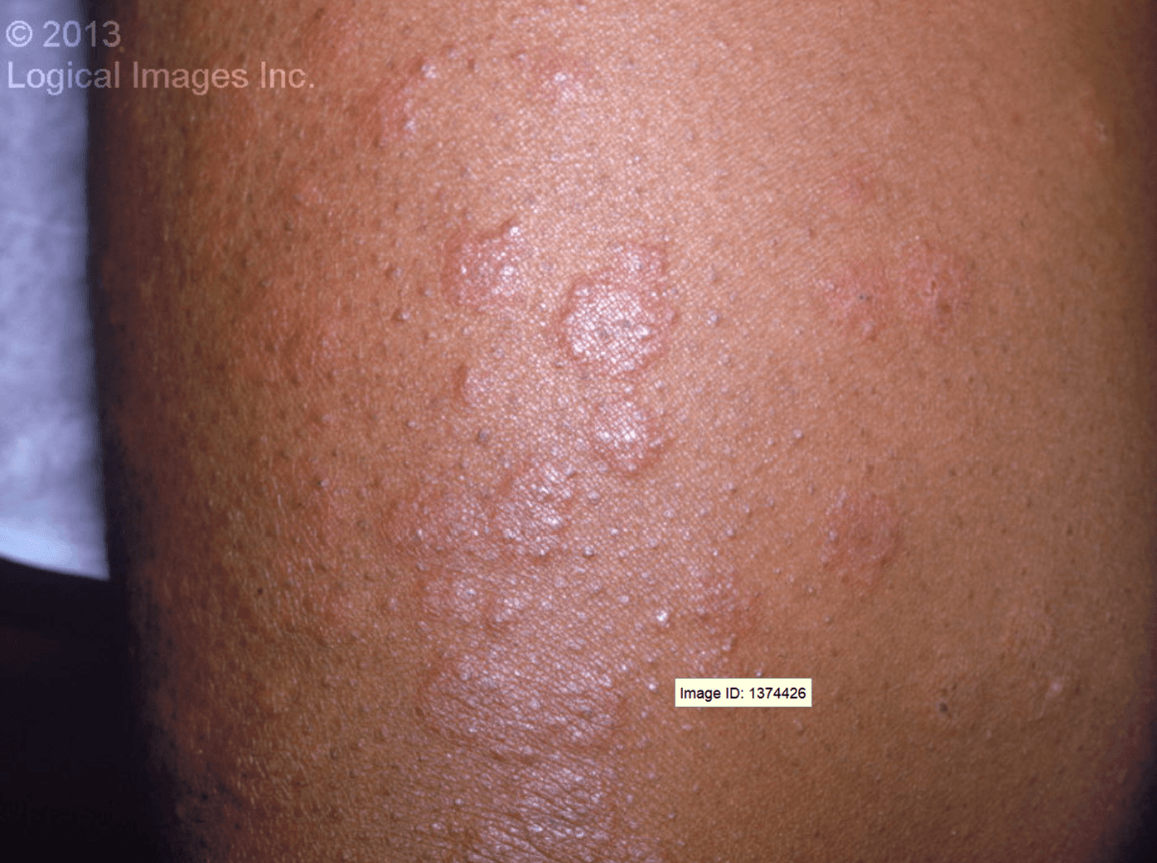
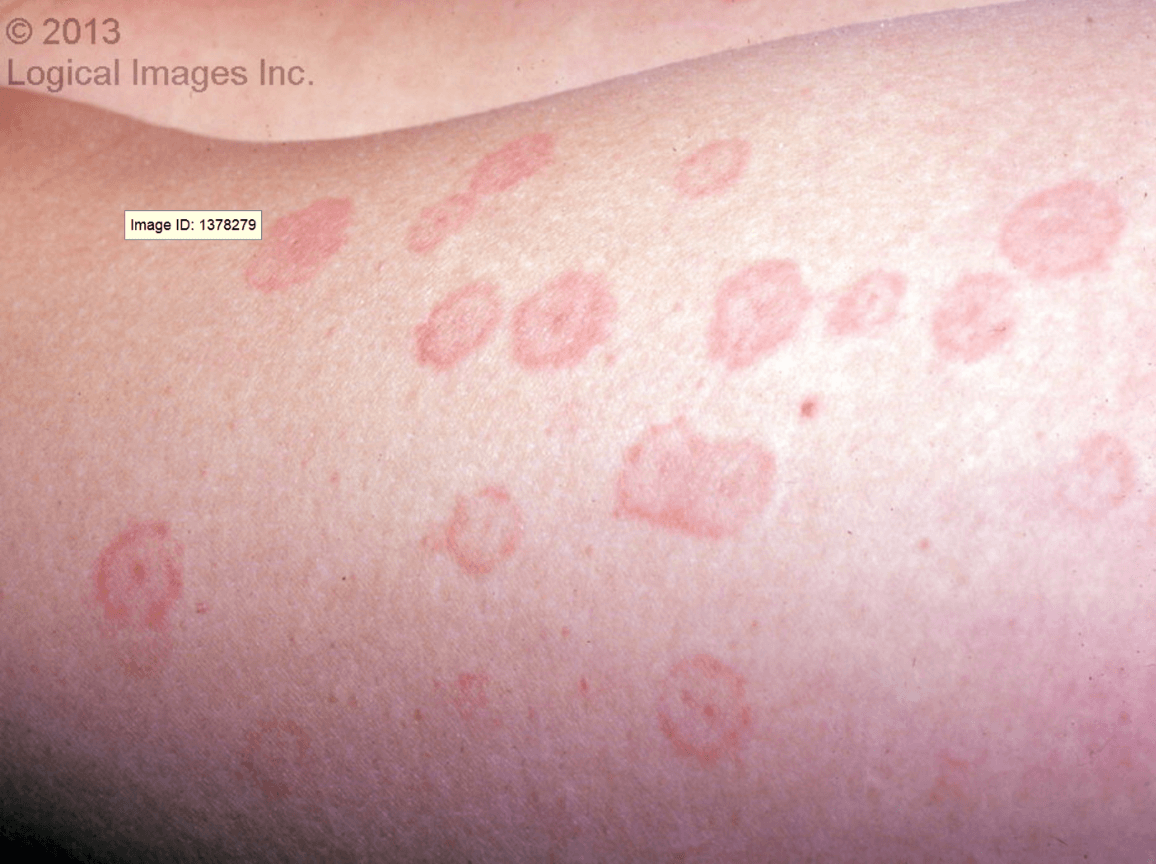
What is Erythema Multiform?
Palpable, discrete lesion that is solid, elevated, and measuring ≤1 cm diameter
May be isolated or grouped
What are Papules?
These are inflammatory papules, pustules, and open and closed comedones primarily at the cheeks but possibly elsewhere on the face. Commonly presents at age 3-6 months. 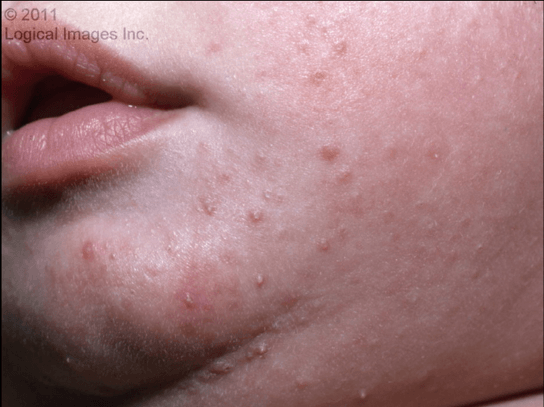
What is Infantile Acne?
This rash involves multiple rose-pink blanchable macules and papules 2-3 mm in diameter that begin on the trunk and may spread to the neck, upper and lower extremities. Symptoms begin with a high fever typically greater than 38.9 Celsius (102 Fahrenheit). The infant is otherwise well and the fever usually subsides on the fourth day. The fever is followed immediately by the onset of the rash. The rash typically lasts 1-2 days. Infants are typically between the age of 6 months and 1 year.
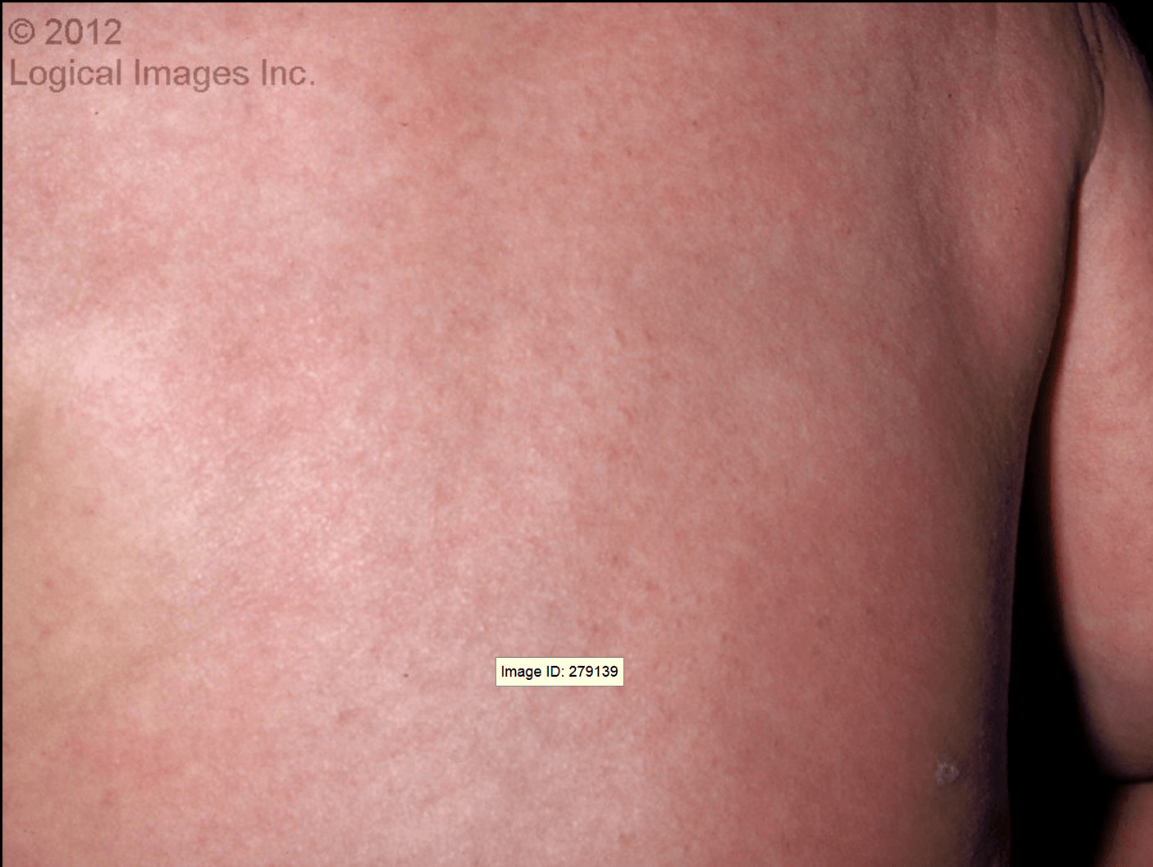
What is Roseola?
Hyperkeratotic, exophytic (growing out) papules or nodules on the dorsal hands, fingers, elbows, or knees. Look for tiny blackish-red dots which are thrombosed capillaries and foci of capillary hemorrhage.
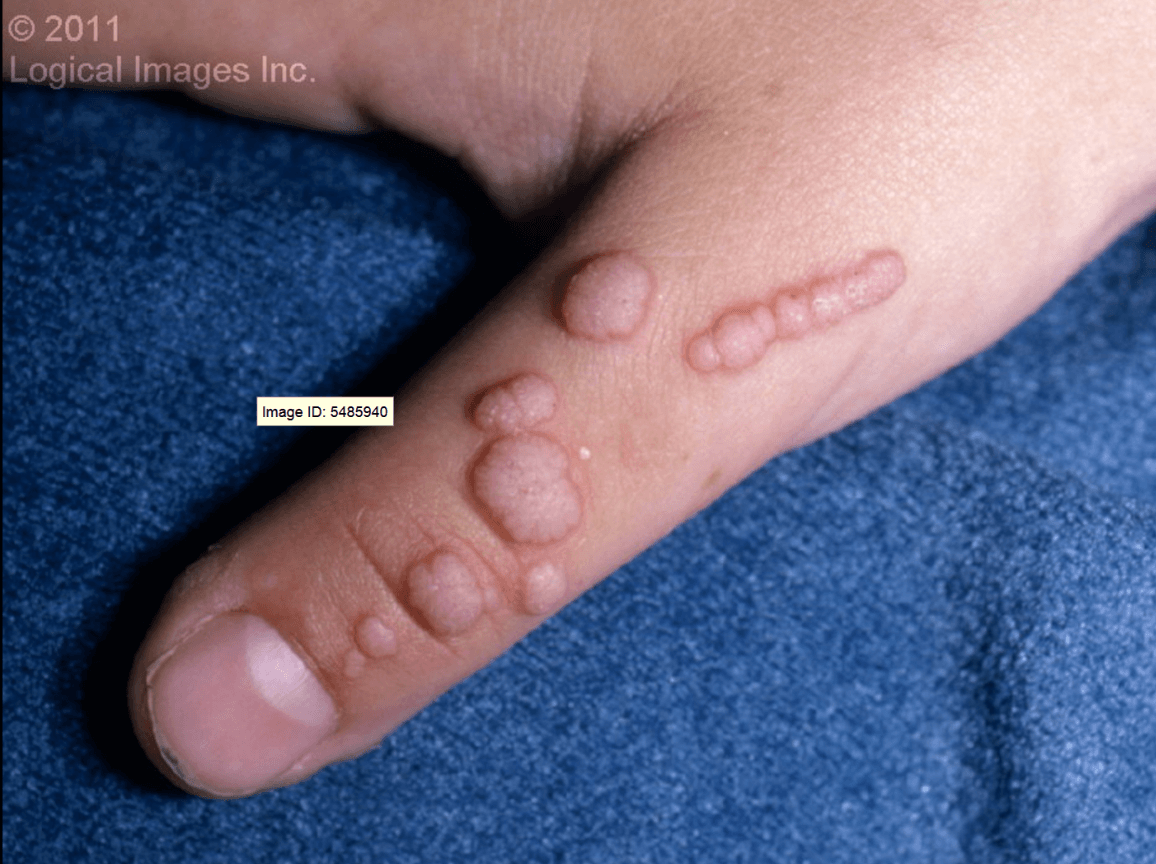
What is a Common Wart?
Well-circumscribed, blanching, erythematous, edematous, annular, or geographic papules and plaques. Lesions vary in size from 2-5 mm to over 30 cm. Lesions may occur anywhere on the body but the trunk is most common. Children are otherwise well and usually have significant pruritus.
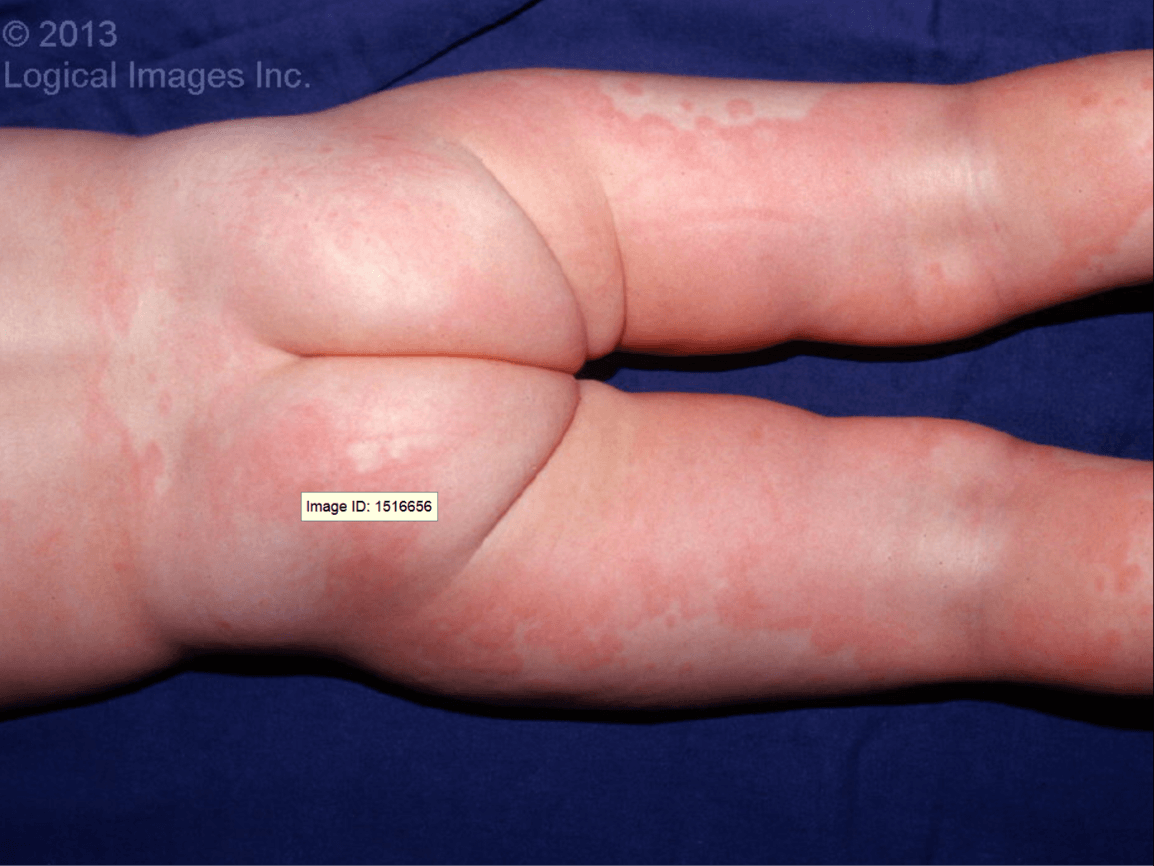
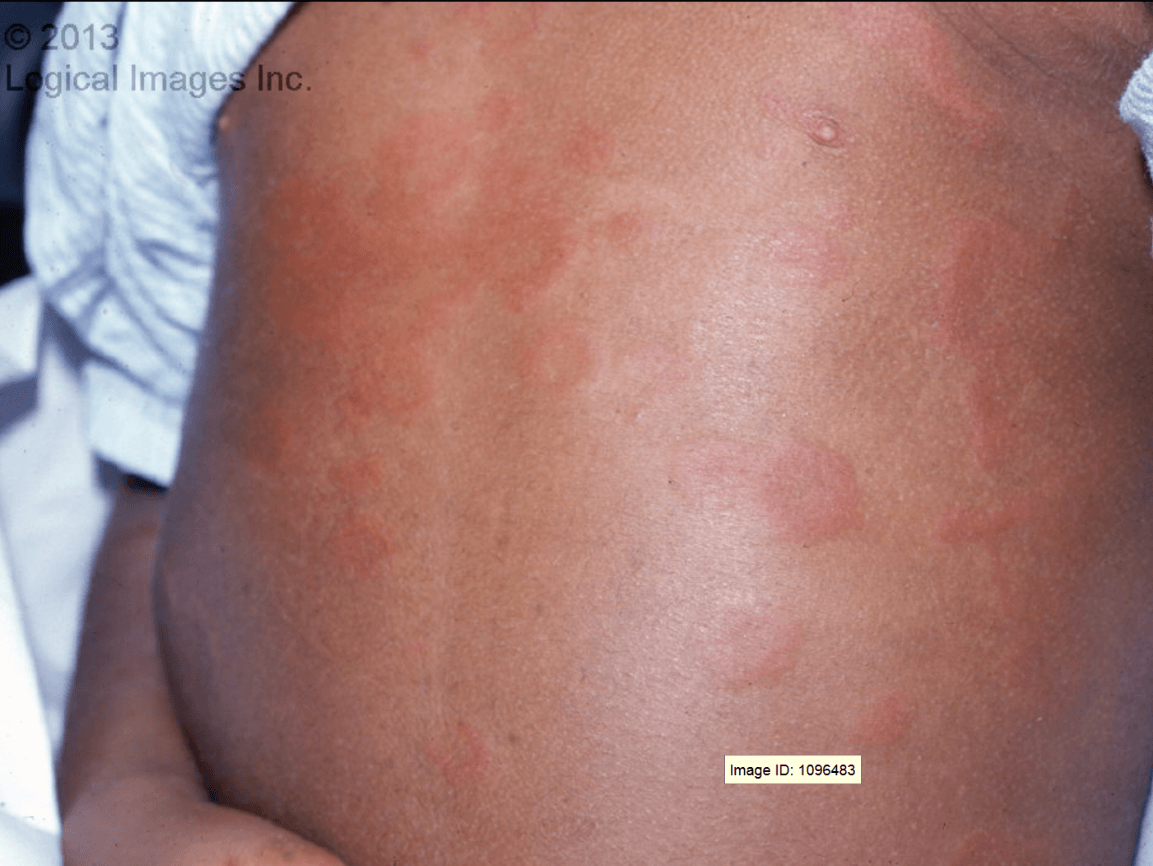
What is Urticaria?
Large (>5 mm) superficial lesions
Often formed by a confluence of papules
May have a silvery appearance
What are plaques?
This is a 1–2 mm pale-to-yellow papule or pustule within a large (over 1 cm) inflammatory wheal. Early on, however, the rash may only consist of blotchy, irregular erythematous macules. Any skin surface may be involved, usually sparing the palms and soles. The rash develops in most infants between the second and fourth day of life and resolves within hours to days.
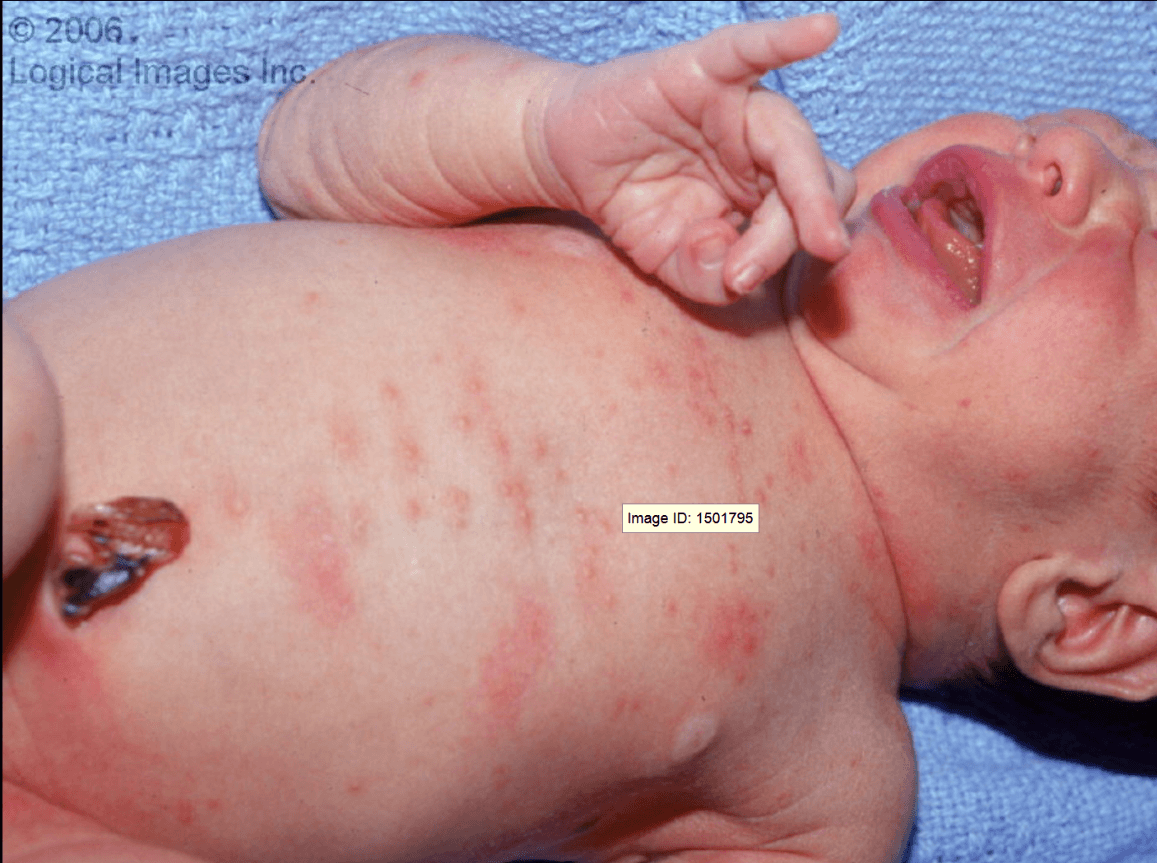
What is Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum?
Erythematous macules and papules beginning behind the ears and at the forehead, spreading down the neck, upper extremities, trunk, and finally the lower extremities. Confluent lesions can occur on the face. Look for oral lesions called Koplik spots, minute red papules with a central bluish-white speck. The spots are usually opposite the second molars on the buccal mucosa. Bluish-gray or white spots can also be seen on the tonsils.
Symptoms start with fever; a runny nose; red, watery eyes; and a cough. Rash develops a few days later.
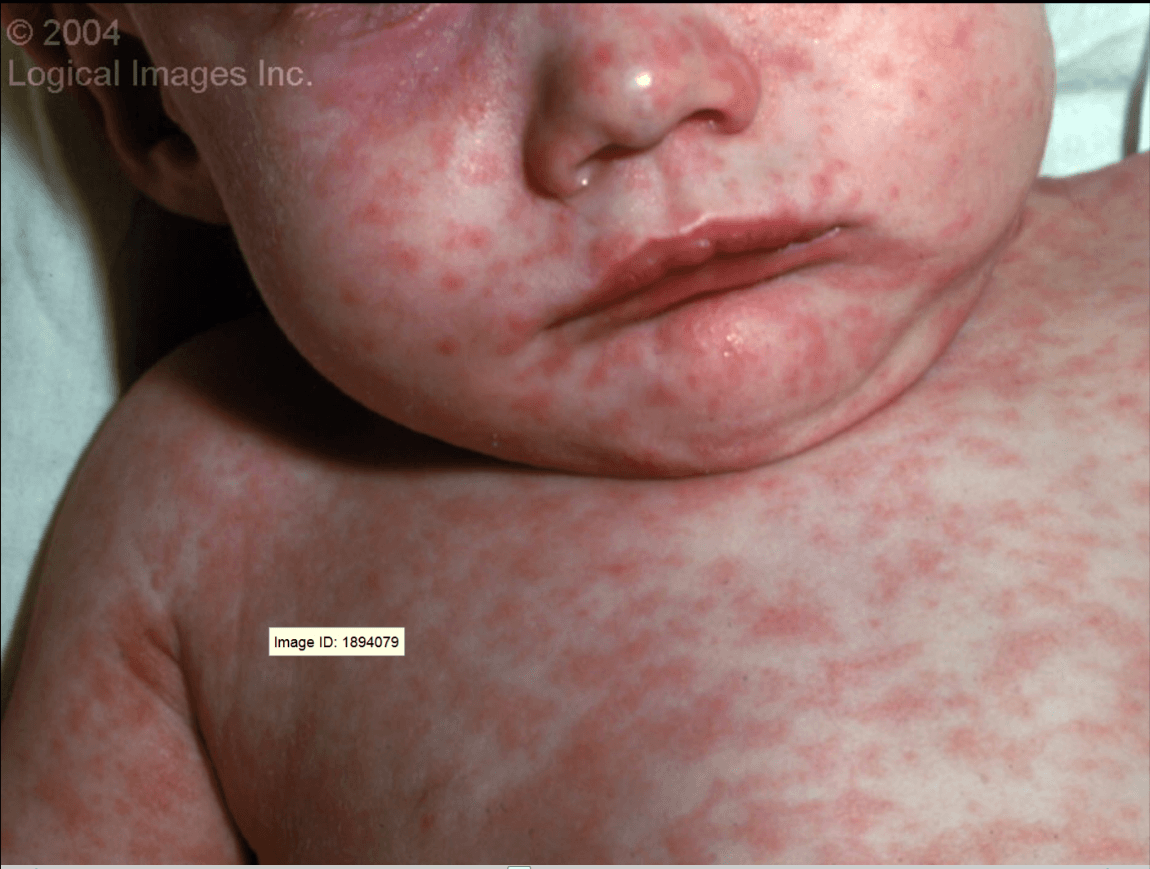
What is Measles?
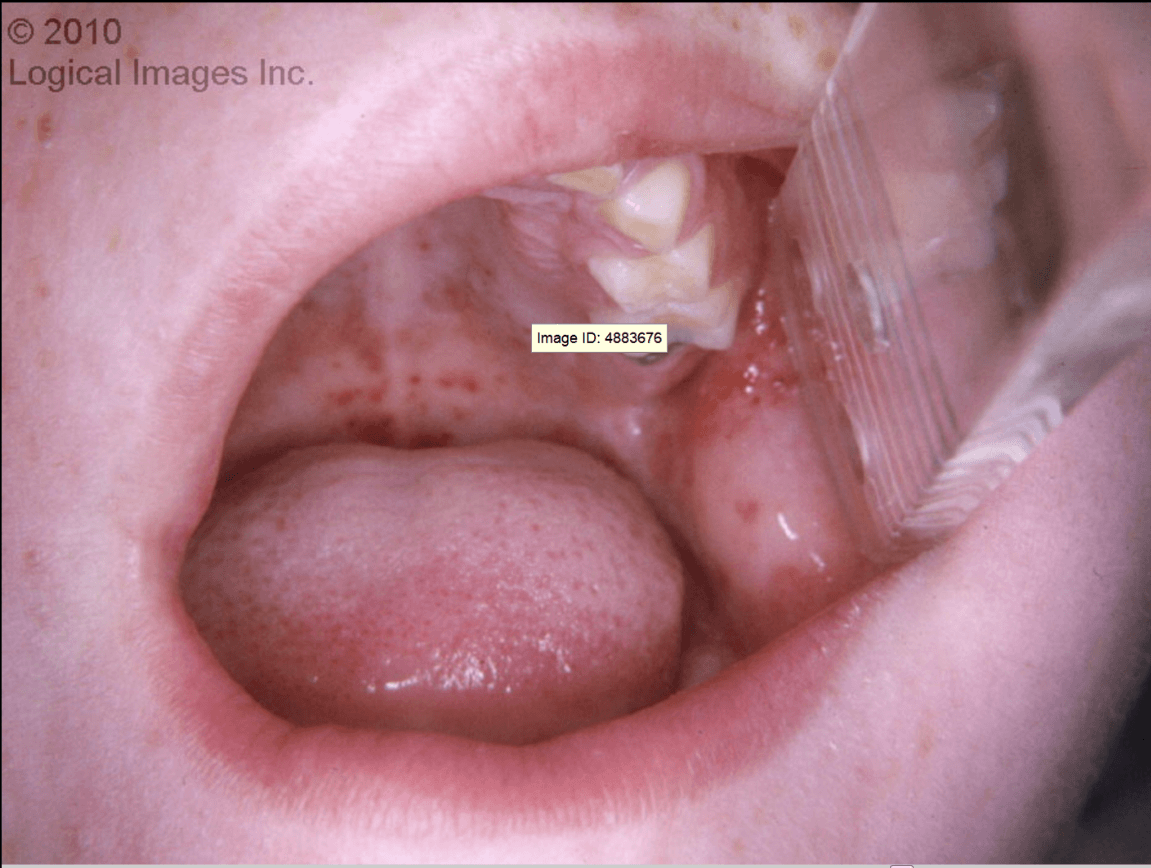
Small macules and papules that develop into 1-3 mm vesicles and rapidly ulcerate. Lesions develop a shallow yellow-gray base and a red areola. Oral lesions involve the buccal mucosa, tongue, soft palate, and gingival. Lesions on extremities typically involve the palms and soles. They begin as erythematous macules and vesiculate to produce 3- to 7- mm oval or elliptical vesicles surrounded by a red halo.
The illness begins with a mild fever with temperature up to 38°C (101°F), sore throat, sore mouth, cough, headache, malaise, diarrhea, and occasionally arthralgias. One or two days after the beginning of fever, small oral vesicles develop.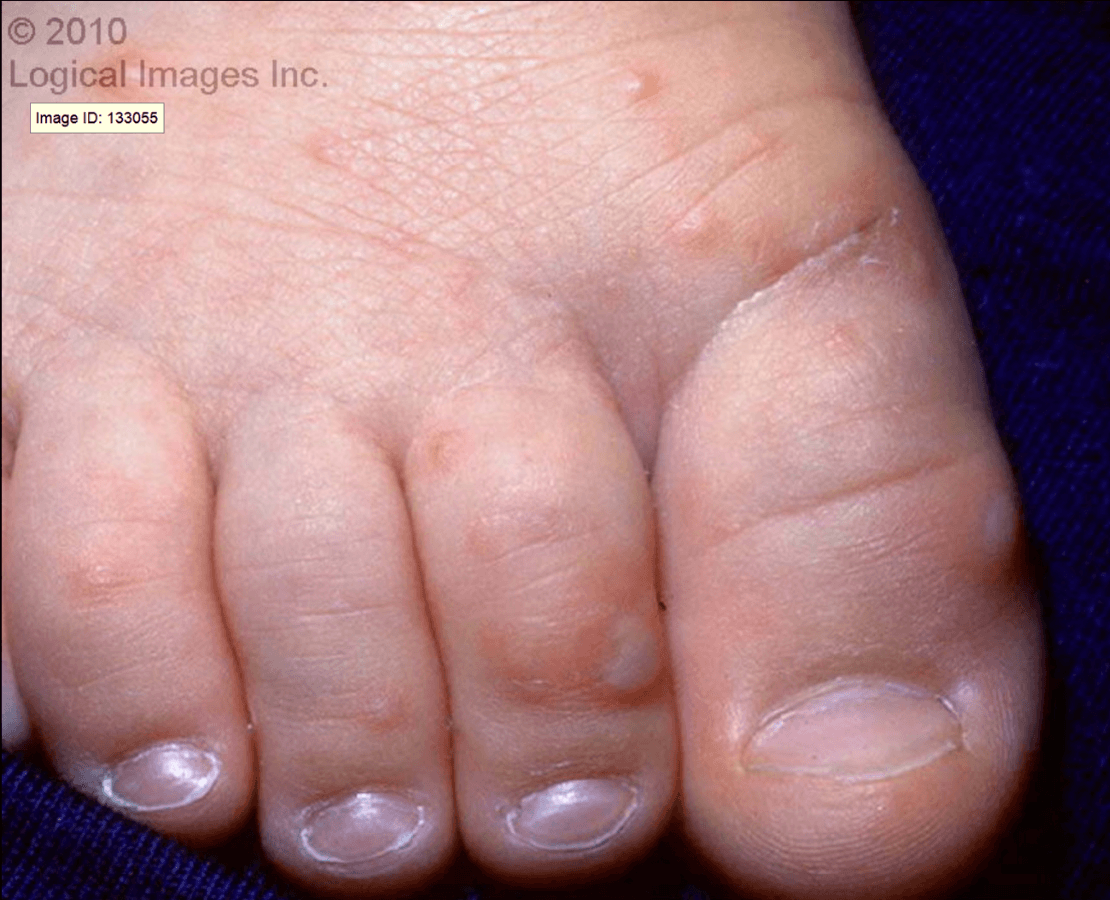

What is Hand-Foot-Mouth Disease?
Papules, vesicles, and pustules on the finger, wrists, elbows, axillae, buttock, groin, and genitalia. Associated with severe nocturnal itching.
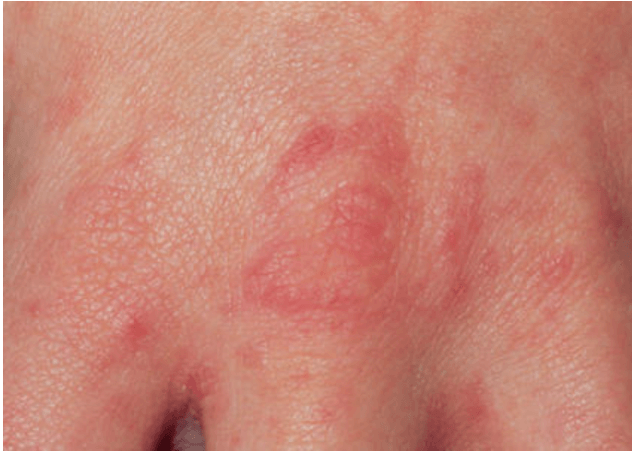
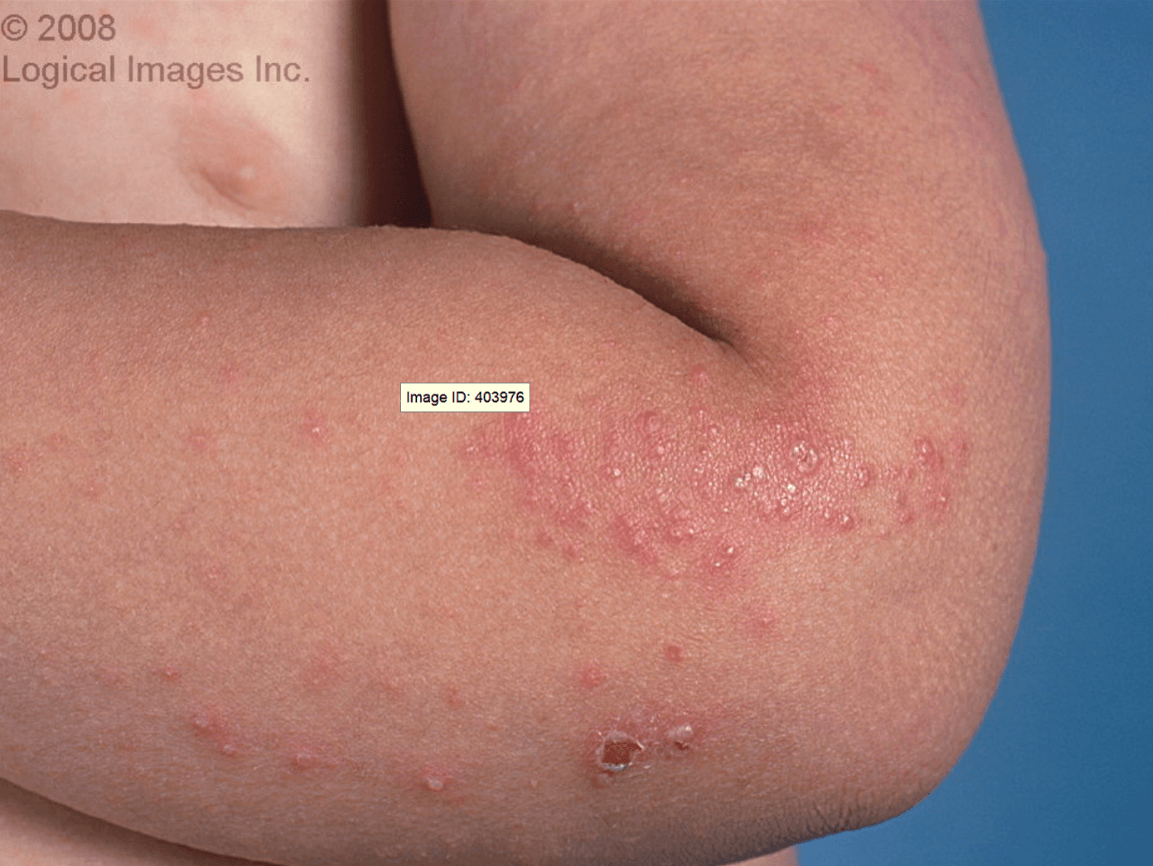
What is Scabies?
Small, circumscribed skin papules containing purulent material.
Small 1-3 mm, erythematous, non-follicular papules on the upper trunk, back, and flexor aspect of the arms and body folds.
What is Miliaria Rubra?
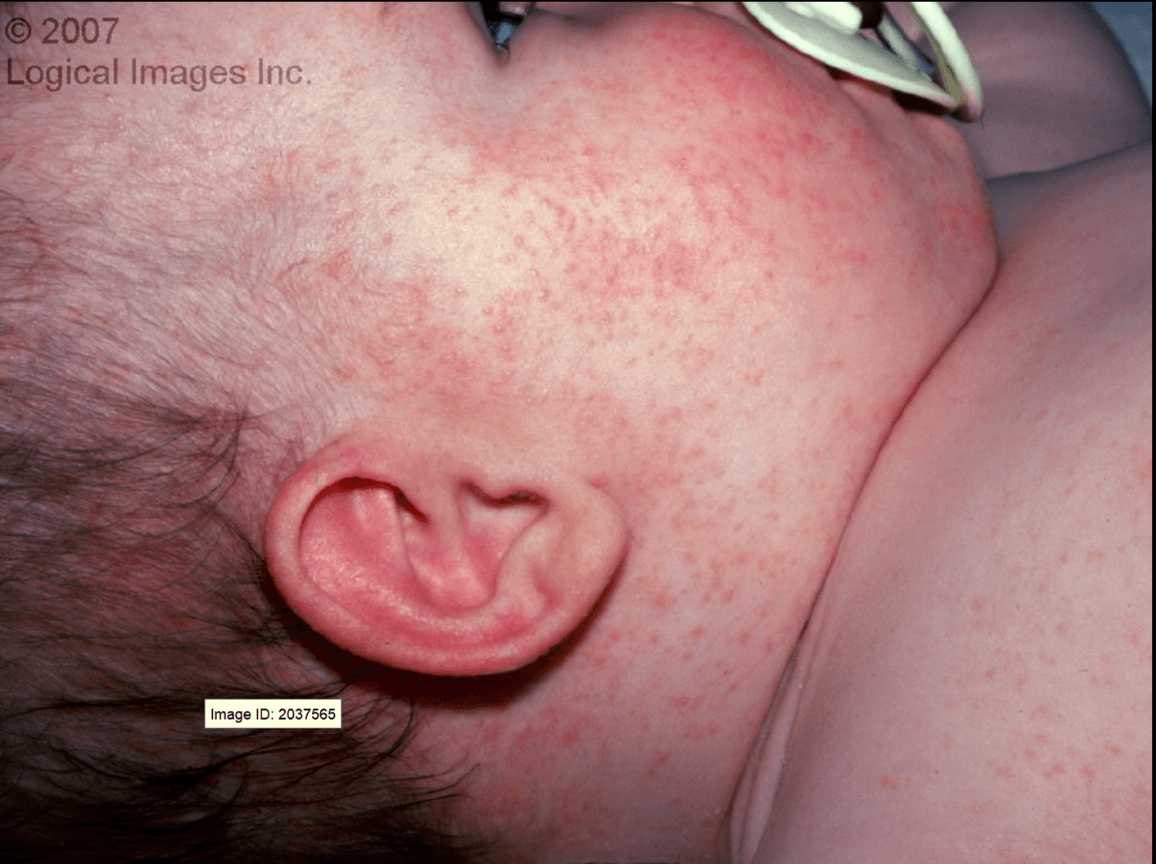
Pink macules begin on the face and later coalesce. Within one day the rash fades from the face and spreads to the trunk and extremities. The pink macules coalesce on the trunk. Child may have a mild fever, swollen lymph nodes behind the ears, a runny or stuffy nose, a headache, and a sore throat.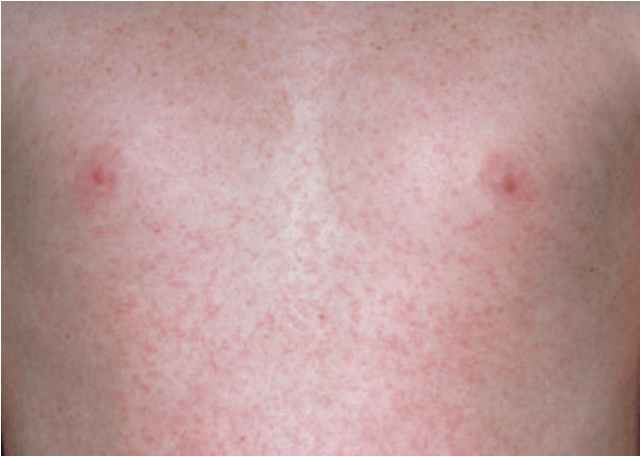
What is Rubella (German Measles)
"Honey-crusted," or golden-yellow-crusted plaques, sometimes with small inflammatory halos.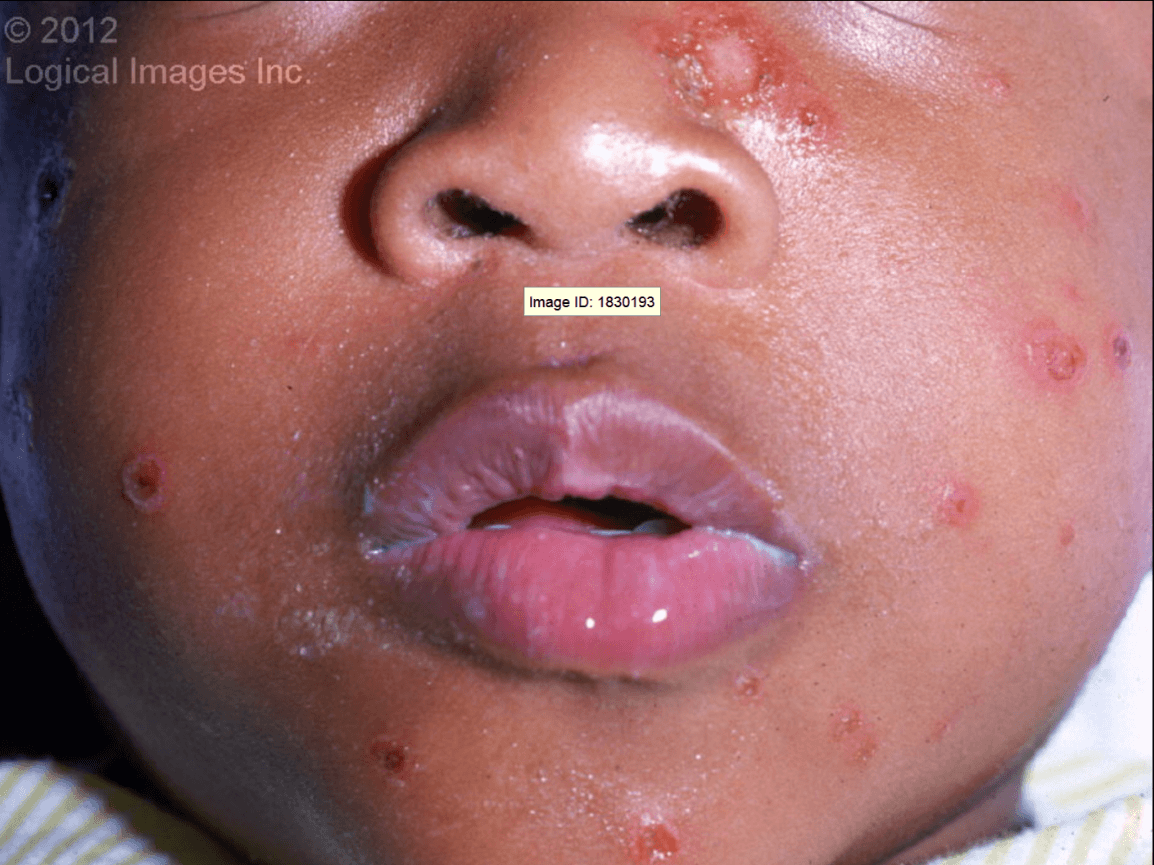
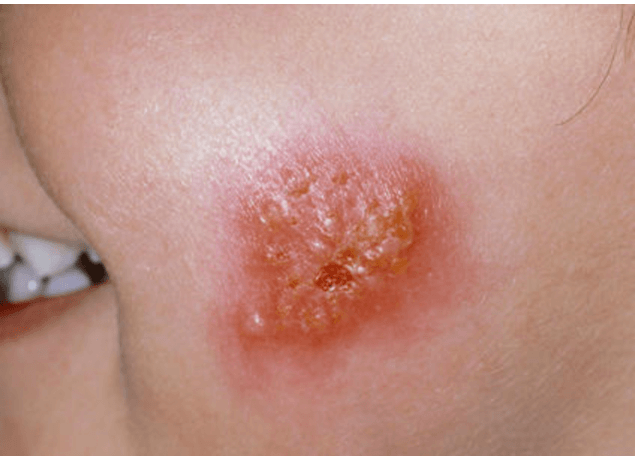
What is Impetigo?
These are macules in an oval or circular pattern with an associated fine, central scale. It usually begins with one larger plaque and then new patches and plaques form on the trunk. Patient is asymptomatic.
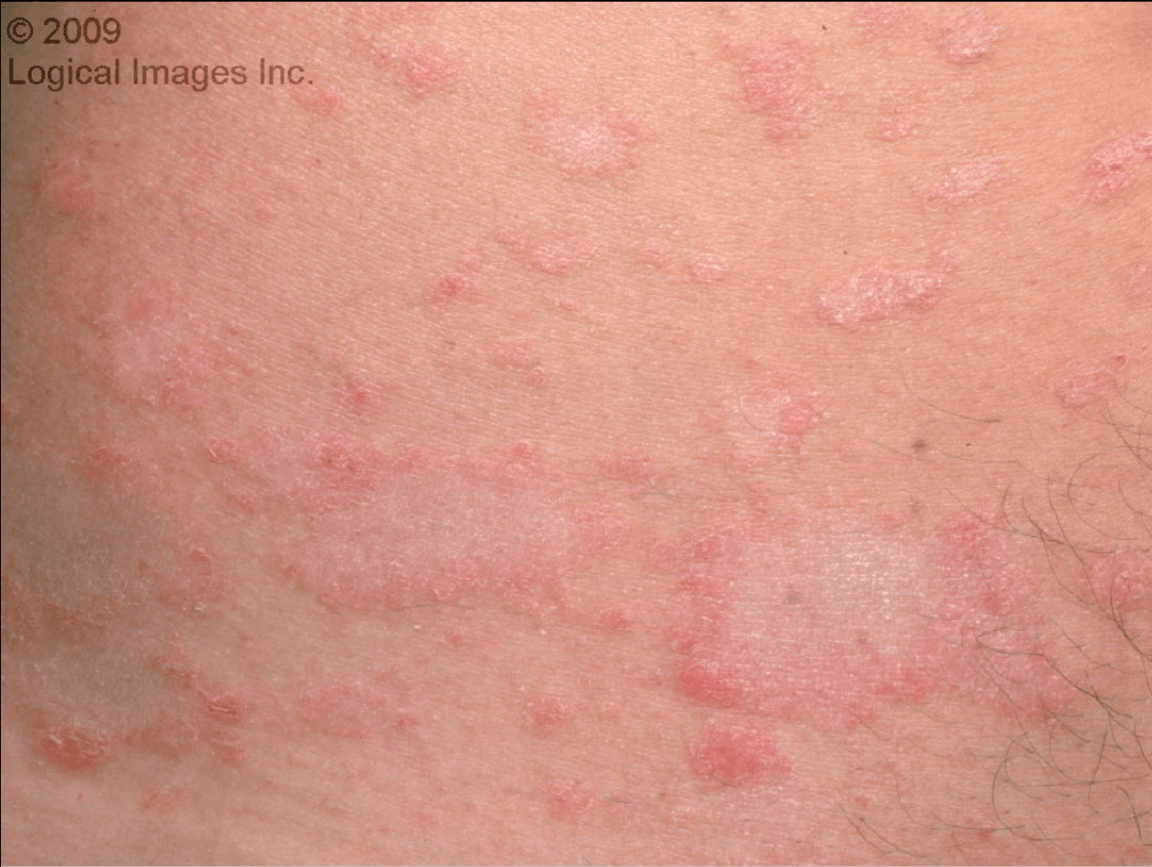
What is Pityriasis Rosea?
Small (<5 mm diameter), circumscribed skin papules containing serous material
What are Vesicles?
Well-defined, erythematous macules and plaques with varying degrees of greasy, yellow scale. The scale adheres to the skin and may be confluent. Common sites of involvement include the scalp, face, skin folds, behind the ears, and sternal area of the chest. The rash begins within the first month of life and gradually resolves by 4 months of age.
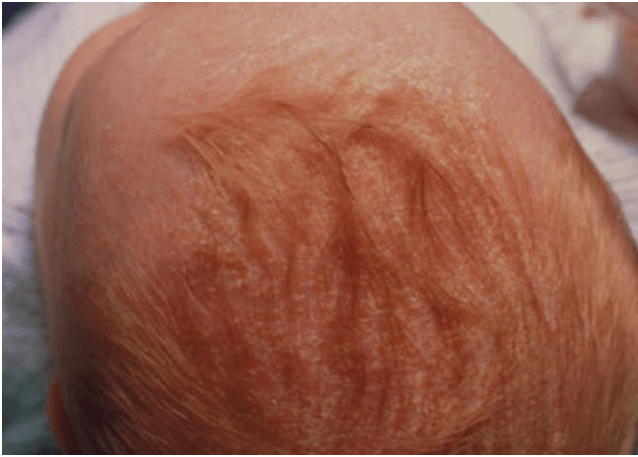
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis- Cradle Cap?
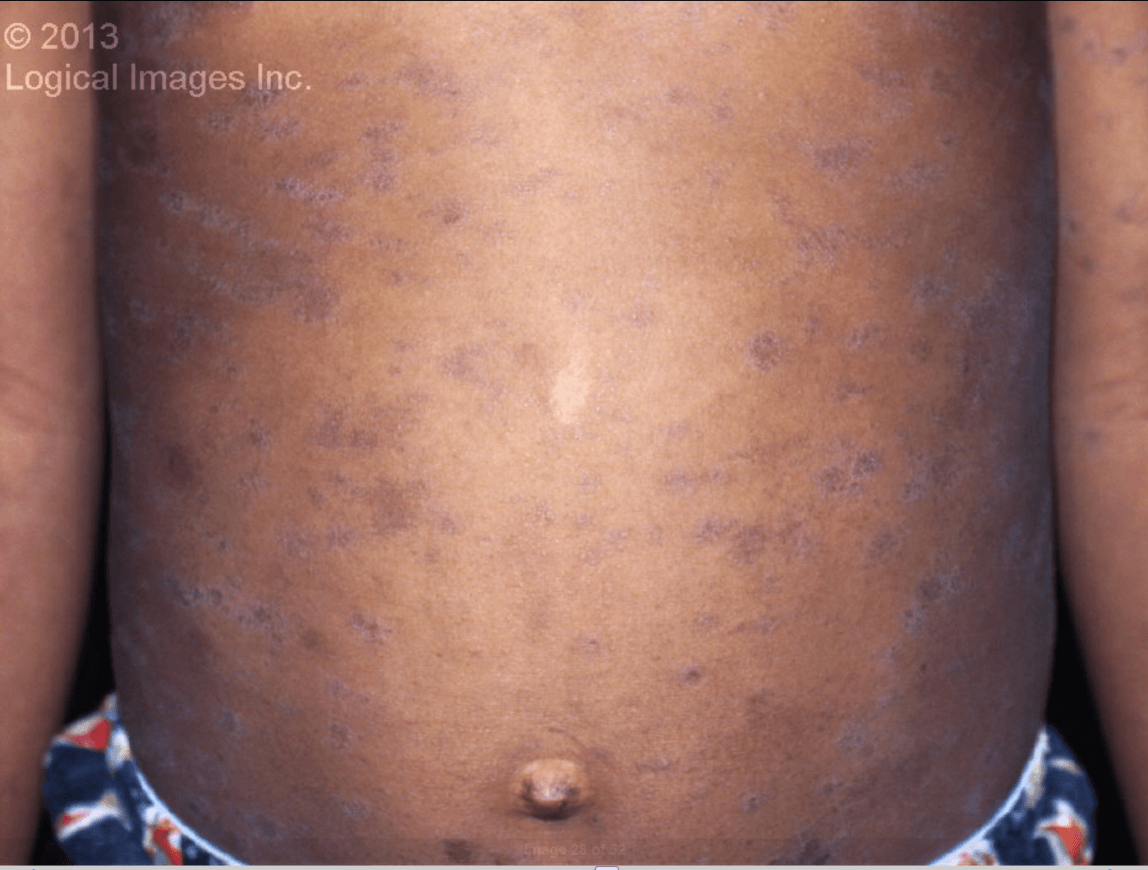
This is an asymptomatic, macular, diffuse erythema involving the bilateral cheeks. It is most intense beneath the eyes, with sparing of eyelids, chin, and perioral area. One to four days later, a lacy reticulated eruption consisting of discrete erythematous macules and papules appears on the proximal extremities. The trunk later becomes involved.
Rash appears after several days of a non-specific flu-like illness.
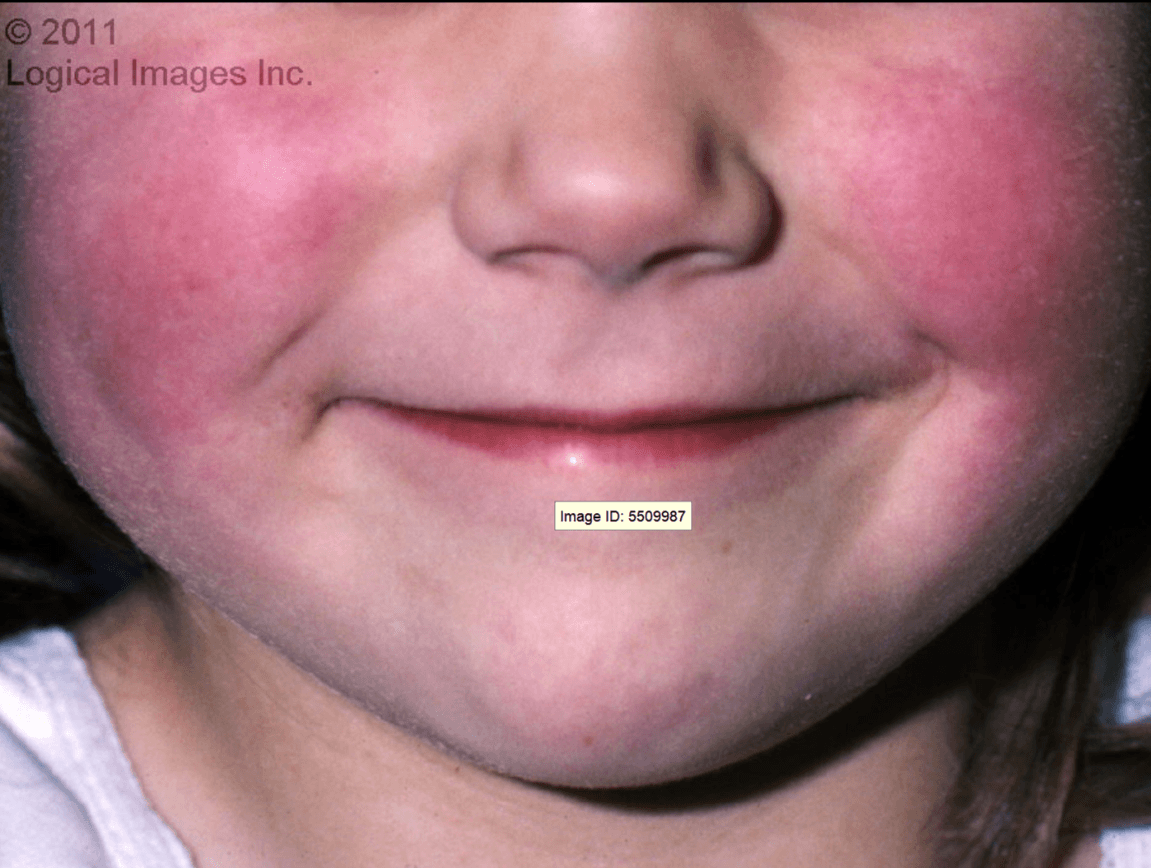
What is Erythema infectiousum (Fith Disease).
A sandpaper-like exanthem, 1-2 mm in diameter, with minute, confluent red papules, which begins on the neck, moves to the trunk, and finally to the extremities. There might be beefy red enlargement of the tonsils, tonsillar exudate, and tender submandibular adenopathy. The tongue initially has a white coating, giving a "white strawberry" tongue appearance that then sheds to reveal a bright red strawberry tongue.
The rash usually begins 1-2 days after the onset of pharyngitis, fever, nausea, vomiting, chills, and malaise.
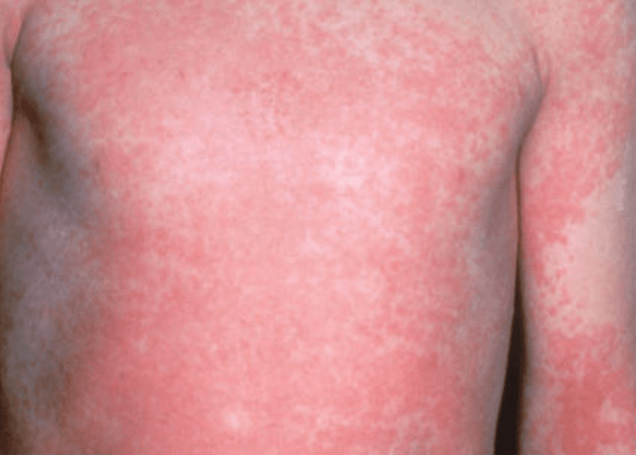
What is Scarlet Fever?
Circular or annular, red, scaly plaques anywhere on the body. Vesicles may also be seen at the periphery of the plaque. Often the lesion has a central clearing.
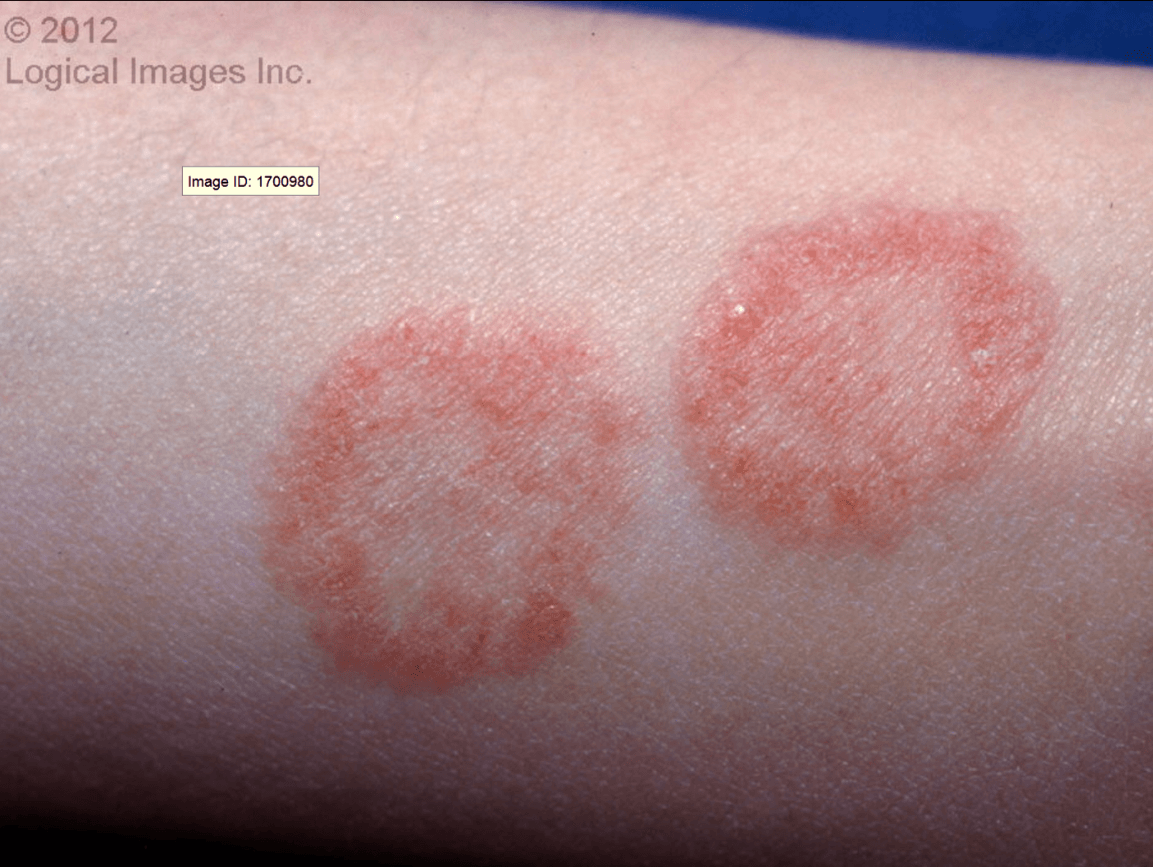
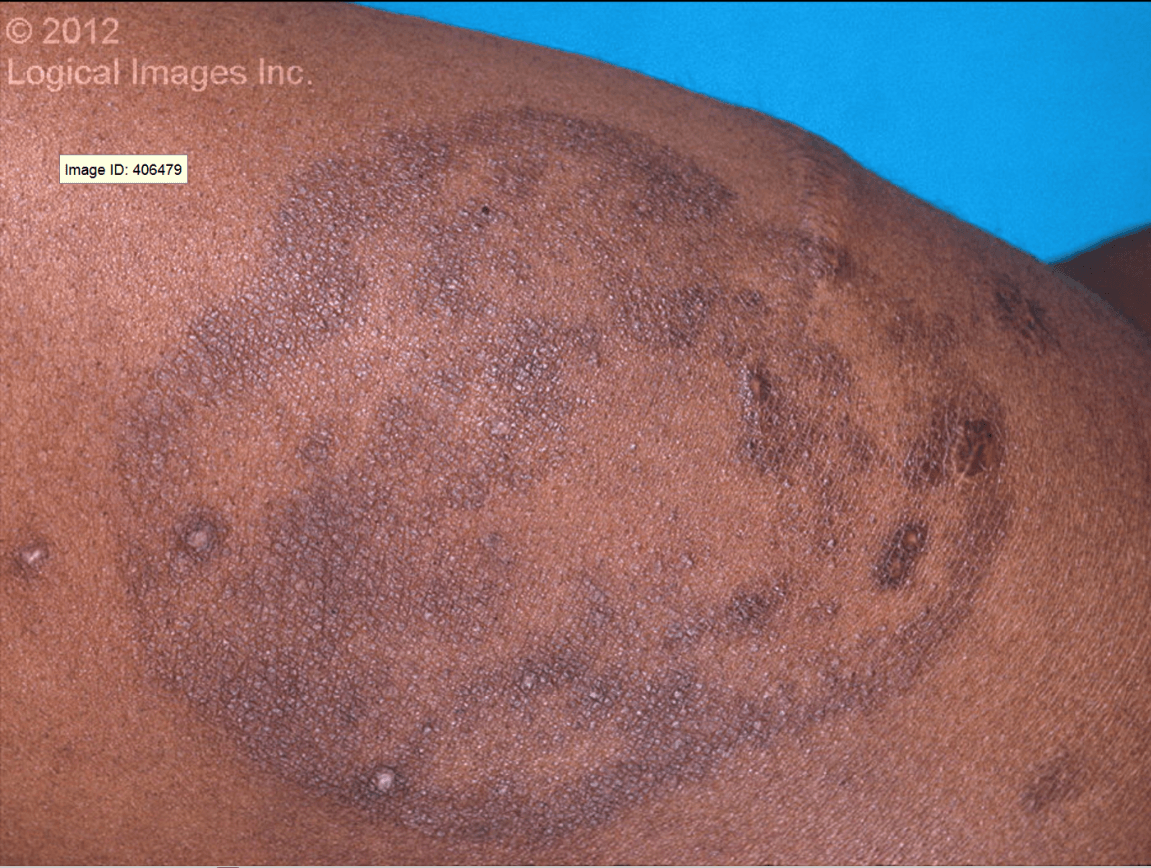
What is Tinea Corporis
Irregularly elevated edematous skin areas that are often erythematous
Borders are sharp but not stable- hey may move to adjacent uninvolved areas over periods of hours.
What are Wheals?
Creamy white or yellow elevated plaques on the lips, tongue, gums, inner buccal mucosa, and palate. Scraping the plaques may leave behind punctate bleeding and patches of reddened mucosa. The infant may be symptomless or may be generally irritable and show a decreased willingness to feed.
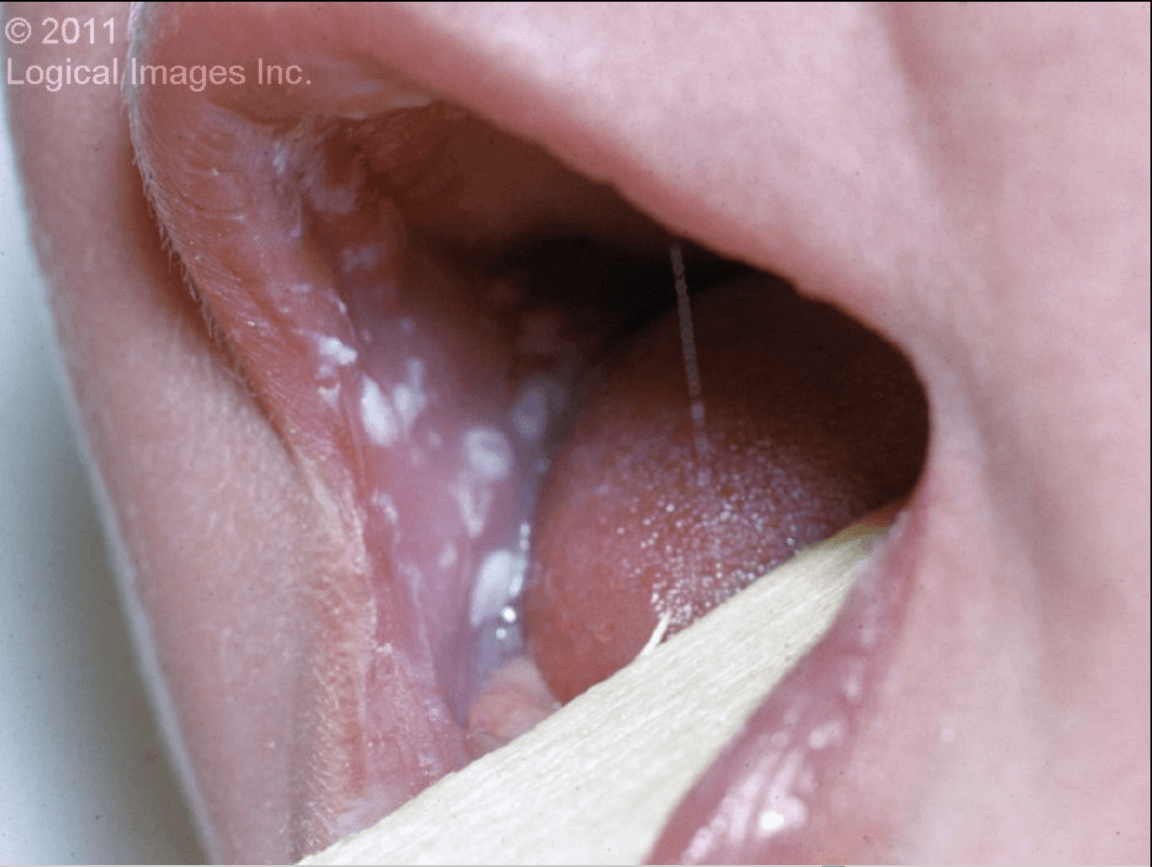
What is oral candidiasis- Thrush?
Crops of erythematous macules that develop central papules, which progress into 2-3 mm diameter vesicles, pustules, and crusts within 12-48 hours. Crops of lesions continue to develop over 3-4 days before becoming completely crusted over by 6-7 days. The rash begins with a 1-3 day prodrome of fever and malaise followed by a rapidly progressive vesiculopustular eruption.
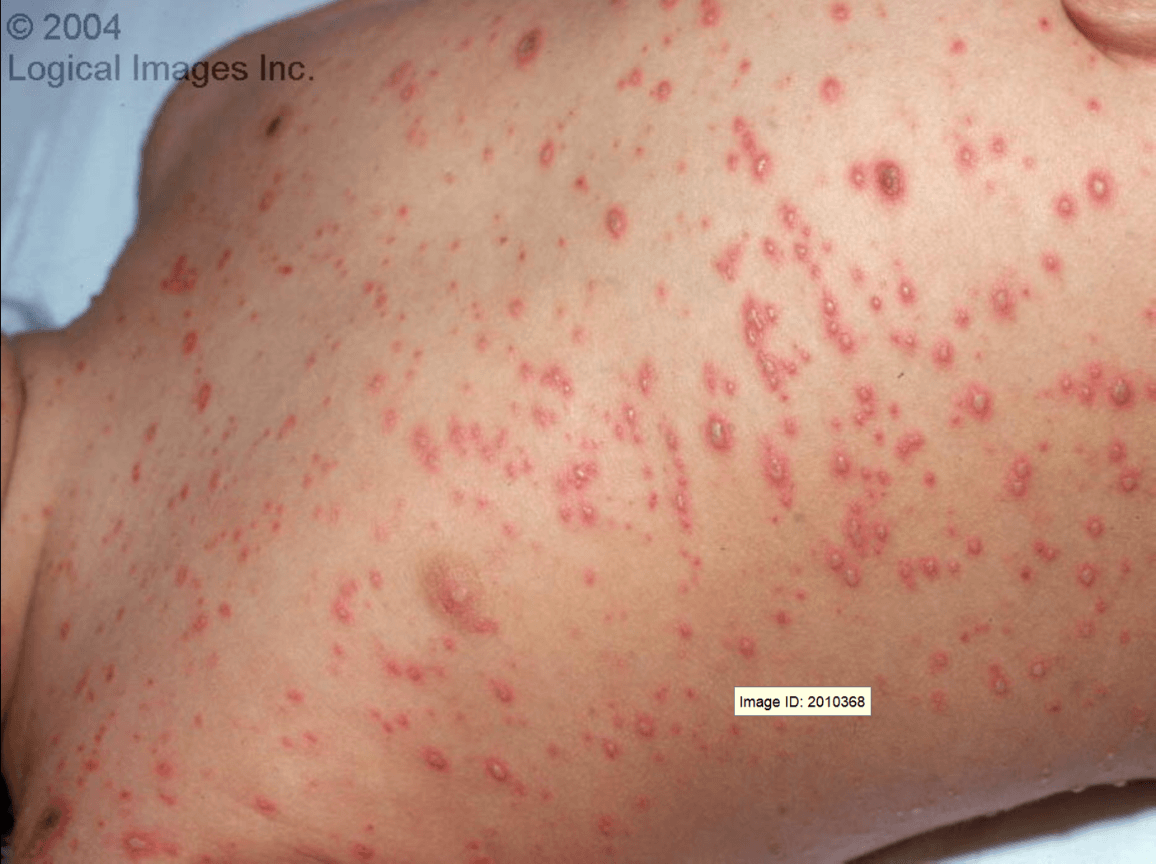
What is Varicella (Chicken Pox)?
Lice and nits in the scalp and hair.

What is Pediculosis Capitis?
Intensely pruritic erythematous papules and vesicles with exudation and crusting, whereas subacute or chronic lesions present as dry, scaly, or excoriated erythematous papules. Skin thickening from chronic scratching (lichenification) and fissuring may develop over time. In many patients, lesions in different stages may be present at the same time.
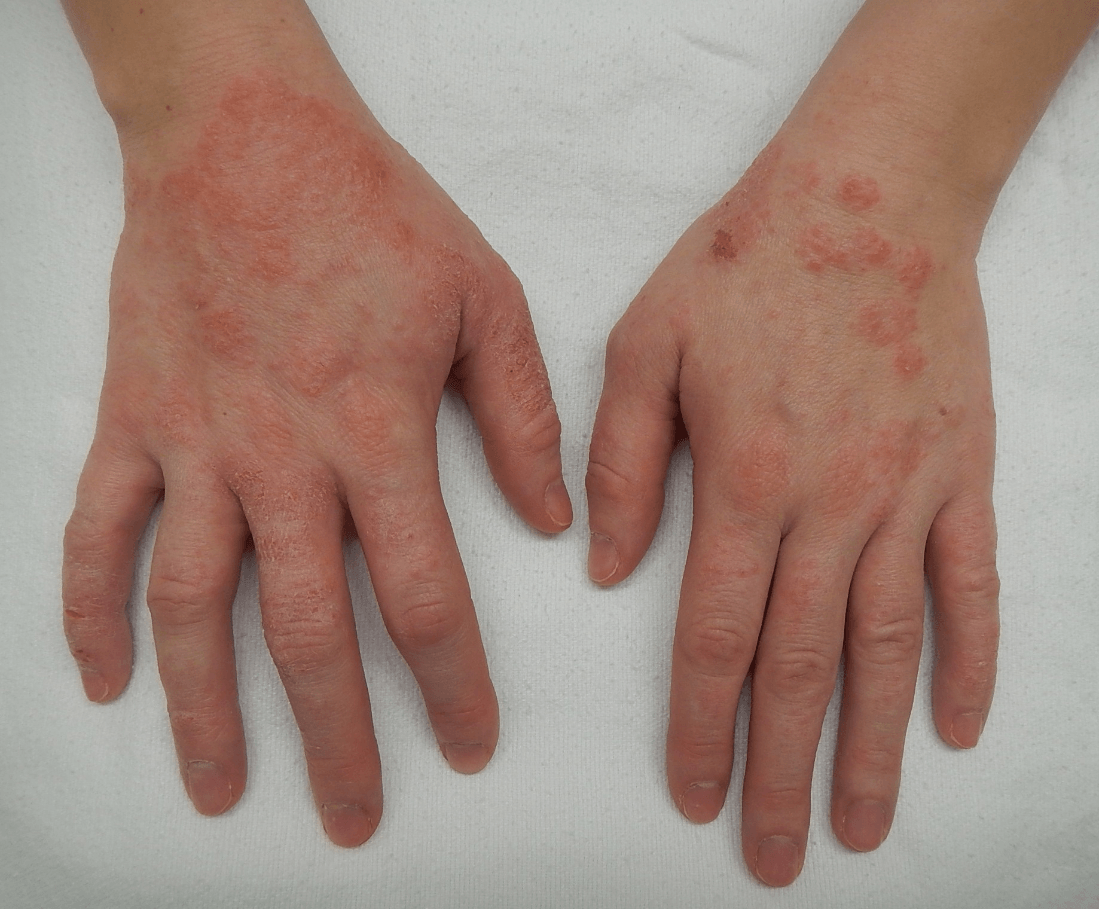

What is Eczema?