Classes of antibiotics prescribed for infections such as otitis media in children
PCN, Cephalosporins
Always check an apical pulse for this class of medications
Antihypertensive
Treatment of choice for prolong seizure management
diazepam (Valium)
Time frame to reassess temperature after antipyretic
30-60 minutes
Gastric motility
Decreased
Often an antibiotic this should be room temperature and administered by properly positioning and pulling pinna back (up or down) according to age
Otic medications
Methods for calculating pediatric dosages
Weight (kg) or body surface area (BSA)
2.2 lbs = ?
One kilogram
Side effect demonstrating ototoxicity potentially resulting hearing loss
tinnitis
Heart Failure medications used in pediatrics
diuretics, beta-blockers, digoxin
Main used of dexamethasone (corticosteroid) for traumatic brain injury
Reduce inflammation and cerebral edema to lower ICP
Medication for pruritus that frequently comes in ointment or cream form
Hydrocortisone, Diphenhydramine
Two enzymes related to liver and are decreased in comparison to adults
Amylase & Lipase
Viscosity, type of medication, muscle mass, number of medications all influence this route of administration
Intramuscular (IM)
This is defined as therapeutic care minimizing psychological & physical distress for children/families
Atraumatic care
85 lb= ? kg
(Round to 2 decimal places)
38.63
Class of antibiotics frequently prescribed for infections such as otitis media in children with potential cross sensitivity if allergic penicillin
Cephalosporins-ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
Hemmorhagic shock from DIC medication used in treatment
vasopressin, desmopressin
Mannitol is an ____________
osmotic diuretic
(move fluid from brain tissue to vascular space to reduce ICP)
True/False
Kids do not feel pain like adults
False
antiemetic promethazine (Phenergan)- common side effect
sedation
When giving an aminoglycoside, such as gentamycin, these interventions must be performed by the nurse especially for children
Assess blood levels to prevent toxicity
Assess for S/S of toxicity- hearing problems (tinnitus), kidney function (immature)
Special considerations are noted for pediatric clients due to the _______________ of their system structures & processes.
Immaturity
25 kg= ? lb
55
Treatment for Rock Mountain Spotted fever
Doxycycline
Medication to maintain a patent PDA
prostaglandins
- Monitor for drug interactions
- Require blood level checks
- Potential long term effects
- Abrupt cessation may precipitate status epileptics
All these are nursing interventions for what class of drugs
Anti-seizure/Anticonvulsant
Commonly OTC analgesic medications
acetaminophen (Tylenol), ibuprofen (Motrin)
In order to administer oral medications to neonates and infants a nurse must assess for this
Ability to suck and swallow
Child with an oral yeast infection (thrush) must receive nystatin mouth rinse. The nurse must advise the child not to do this
Swallow the medication- Child should swish and spit medication out
Chemicals can be passed from mother to newborn via this feeding method
Breastfeeding
Calculate the dosage in mcg with information provided: (round to 1 decimal place)
2 mcg/kg for a client weighing 80 lb
72.7
Common routes for antibiotic therapy
oral/topical-dermal, ear, eye
Two medications used to treat Kawasaki's
IV Immunoglobulin and aspirin
Barbiturate used to control tonic clonic seizures
phenobarbital
This medication is commonly used for childhood infestation of pediculosis capitis & scabies
Pediculocide (Permethrin)
You often must do this to oral medications to administer by mouth
Add a sweetner or flavoring to mask any unpleasant taste
Amount for SQ injection
0.5 mL
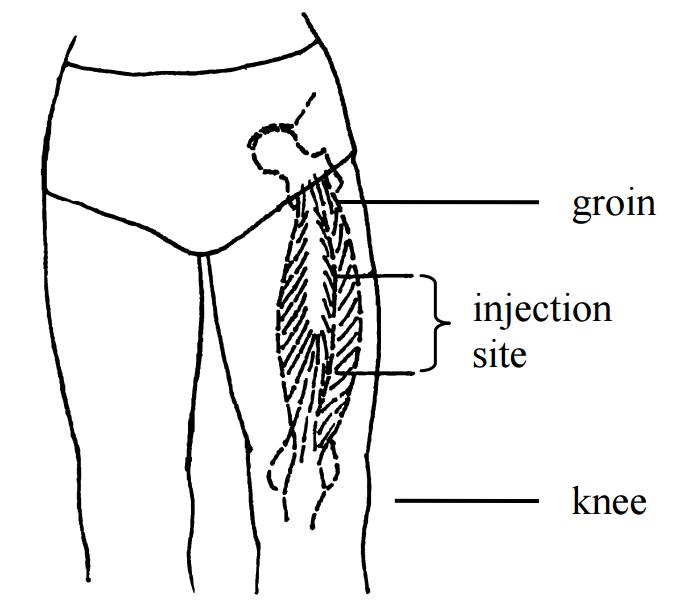
Vastus Lateralis
Ordered: Medication A 50 mg/kg PO 3 times/day
Weight 25.5 kg.
Available: Medication A 100 mg/mL.
Amount _____mL dose
(Round to 1 decimal place)
12.8
Suppression of stem cell production
mylenosuppression
This is a vasodilator used to manage hypertension/heart failure in children and is contraindicated in valvular disease
Hydralazine
Best route to administer diazepam during a sustained seizure
rectal
Increased ______ results in more absorption of medication
BSA (body surface area)
Used for managing constipation in children
polyethylene glycol (miralax)
Cream used to "numb" area prior to IV insertion
prilocaine (EMLA)
This is how IVF maintenance is calculated
Body weight
Medication A is ordered for 9-month-old infant who weighing 8.6 kg. The recommended dosage is 25 to 50 mg/kg/day in four equally divided doses.
This is the minimum amount of 1 scheduled dose. (round to 2 decimal places)
53.75
Most common side effects for oral antibiotic
abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting
Binding agent for iron toxicity
deferoxamine
_______________ is a life threatening condition resulting in hypoxia
Status epilepticus
Topical analgesia cream for invasive procedures
EMLA cream
This is often used to treat neurogenic bladder for children with spina bifida
Oxybutynin (Ditropan)
Often these are options used to mix medications in prior to administration
juice, ice cream, apple sauce
This is often required for injections, venipuncture, or intravenous procedures
Numbing medication, local anesthetic, lidocaine, emla cream
Ordered: 45 mg/kg/day by mouth in 3 divided doses Weight=66 lbs.
Available: 75 ml stock medication labeled 125 mg/ml.
This is _____mL administer per dose.
(Round to 1 decimal place)
3.6
Prevent discoloration of teeth with administration of this medication
tetracycline
Narcotic used to treat tet spells
Morphine
1st choice of antiepileptic drug that causes gingival hyperplasia
phenytoin (Dilantin)
Medications called ____________ can result in injury to tissues
vesicants
Diuretics often given for children with congenital heart defects in fluid overload
Furosemide (Lasix), spironolactone (Aldactone)
When using an inhaler for bronchodilators, this is used to ensure the dose medication is properly delivered to children with asthma
Spacer
Measurement equivalents for urine output (diaper) weights
1 g = 1 mL
Medication A is ordered for 5 y/o child who weighing 48 lbs. The recommended dosage is 25 to 60 mg/kg/day in four equally divided doses.
This is the potential maximum amount for 1 scheduled dose.
(Round to 2 decimal places)
327.27
Common chemotherapeutic agents used in peds
hydroxurea, methotrexate, 6-FU
Digoxin toxicity causes what electrolyte toxicity
Hyperkalemia or high potassium
antispasmodic that can be administered via an implanted pump into the nervous system
lioresal (Baclofen)
Most common side effect of topical medications
Erythema, Redness
Given for gas in colicky newborns and infants
When giving high alert medications the nurse can do this as a safety measure
Verify with 2nd nurse
Calculate safe dosage (ensure within appropriate range)
Contact provider/pharmacy with questions
These affect ABSORPTION of medication in children
PO, IM, SQ, Topical (minimum of 1 from each)
PO: Slower GI emptying, higher pH, faster intestinal motility, lower amylase/lipase secreted
IM: Less muscle mass/Vasomotor instability
SQ:Decreased perfusion/absorption
Topical: More BSA & permeability of skin
This is the daily IV fluid maintenance requirement for a child weighing 18 kg in mL
1400
The nurse must provide education on this when a child is receiving antineoplastic medications
Infection control and preventing illness
Antidote for digoxin
Digibind
Reversal for benzodiazepines
__________ to ________ pain is treated with morphine
Moderate to severe
Antibiotics are often given for this pathogen due to the risk for acute glomerulonephritis
streptococcus bacteria
This tool may be used to find a vein in children prior to IV insertion
Transilluminator (vein finder)
Factors affecting DISTRIBUTION of medications in children
(Must list ALL SIX)
Higher % of H2O (amt H2O relative to the body fat amt)
Rapid extracellular fluid exchange
Decreased body fat
Liver immaturity (altering first-pass elimination)
Decreased plasma proteins/less binding ability
Immature blood–brain barrier (neonates)
This is the rate in mL/hr for IV fluid maintenance requirement for a child weighing 55 lbs
67