Infection, Inflammation and Infarction
Development
Neoplasms
Syndromes and Eponyms
Potpourri
100

The name of the inheritance pattern for the disease responsible this radiograph.
What is autosomal recessive?
100

The name of this pathology
What is Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
100

This tumor, associated with a chromosome 11 deletion in children often presents with abdominal fullness and suspected constipation.
What is Wilms Tumor?
100

The name of this pathology
What is Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease?
100

This pathology usually presents with chronic cough and dysphagia.
What is a Double Aortic Arch / Vascular Ring?
200

Visually describing the findings below, this term implies a lung consolidation.
What is hepatization?
200

A poetic, floral buzzword, this is associated with a developmental anomaly that leads to recurrent UTIs/pyelonephritis.
What is the Drooping Lilly Sign?
200

Above is an intusussception caused by a small bowel hamartoma. There are also polyps in the colon and the stomach, and pigmentation on the patient's lips. Although these are not premalignant lesions, the patient will probably need to be followed for what risk?
What is an increased risk of malignancy?
200

This idiopathic, inflammatory, probably autoimmune pathology manifests with an acute febrile illness, mucosal inflammation and a rash on the hands and feet.
What is Kawasaki Disease?
200

The 6 week old infant above is experiencing nausea and vomiting caused by this acute abdominal pathology.
What is midgut volvulus with malrotation.
300

This is the most common microbiologic etiology for the pathology above causing edema of the epiglottis and the aryepiglottic folds.
What is Haemophilus influenzae?
300
This angle, when >50 degrees, indicates developmental dysplasia of the hip.
What is the Graf / alpha angle?
300

The gene often implicated in the following pathology.
What is RB1
300

The findings above are often associated with hepatoblastoma in this syndrome.
What is Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
300

Although unlikely to happen in infants >34 weeks, the vast majority of the pathology shown above typically occurs by what day of life?
What is day 4?
400


As this pathology developed in only hours, these rapidly developing findings are an indication for this often life saving treatment.
What is exchange tranfusion?
400

Of the two forms of this disease, this is most likely which form of what disease?
What is Intralobar Pulmonary Sequestration?
400
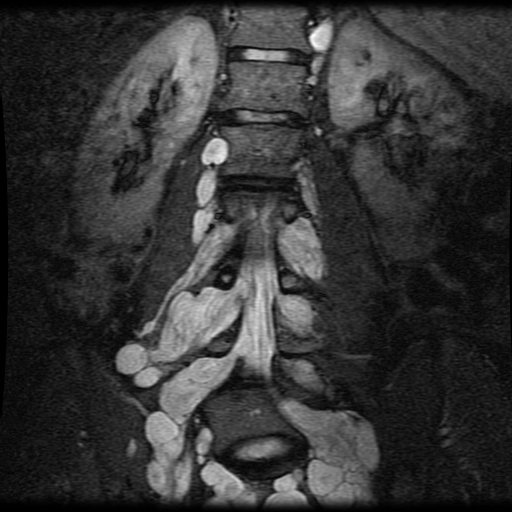
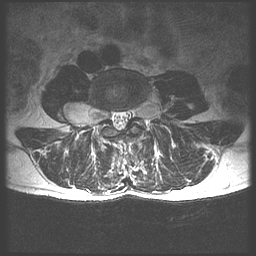
Typically involving the lumbar plexus or brachial plexus, these rope-like lesions have a 5% lifetime risk of malignant degeneration. What is the associated syndrome?
What is NF1
400

This is the syndrome comprised of the findings above and the absence of the parathyroid glands and thymus.
What is DiGeorge Syndrome?
400
This is the normal order of development of elbow ossification centers.
What is CRITOE (Capitellum, Radial head, Internal epicondyle, Olecranon, External epicondyle)
500
An 8 month old child presents with a diaphragmatic hernia, but his chest radiograph at birth was normal. He has a history of which type of pneumonia?
What is Group B Streptococcal Pneumonia?
500

Narrowed lumbar interpediculate distance is a differentiating feature of this disease.
What is achondroplasia?
500
This is the presumed etiology for early bone maturation in choriocarcinoma, hepatoma, and hepatoblastoma.
What is elevated beta-HCG?
500

This syndrome is characterized by malignant degeneration of the lesions above, retardation and genitourinary anomalies.
What is WAGR syndrome?
500

Although normal saline, ringer's lactate, and barium have been used in the past, Air contrast within this pressure range is used to reduce intussusceptions.
What is 80-120mmHg?