List at least two etiologies of Brown syndrome (six [6] found in Chapter 11) -- extra 200 points if able to name all.
BROWN(IE) BONUSES (+400): 1. How to clinically differentiate Brown from restrictive process? 2. Differentiate Brown from IO palsy? 3. Favored head posture? 4. Management(s)?
Periocular trauma, RA, sinusitis, tube shunts, scleral buckles, orbital tumors
BROWN(IE) BONUS:
1. Brown is relieved with globe retropulsion and worsens with proptosis. Opposite for restrictive process.
2. Victor Brown (V-pattern strabismus) whereas IO palsy is A-pattern. Also, no SO overaction in Brown.
3. Head posture -> chin up, face away from affected eye (maximally avoid elevation in adduction)
4. Management: Observation. Consider TO tenotomy if advanced (often combined with IO recession)
"Only nystagmus that" -- +100 each
Reverses direction depending on fixation?
Can present with a VF defect?
Two forms associated with Arnold Chiari malformation?
Associated with hypomyelinating leukodystrophies (e.g. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease -- chill, you didn’t know how to pronounce it either).
BONUS: What is the underlying cause of convergence-retraction nystagmus (but not actually nystagmus, ya know?)?
Reverses direction: fusion maldevelopment nystagmus (FMN) -> always has fast phase towards UNcovered eye
VF defect: see-saw nystagmus -> craniopharyngioma pressing on optic chiasm
Chiari malformation: downbeat and periodic alternating nystagmus (PAN)/ central vestibular instability nystagmus
Hypomyelinating leukodystrophies -> Spasmus nutans
Co-contraction of all muscles causes retraction, but MR has the strongest pull -- overpowers the LR --> convergence
“Which EOM” trivia -- fast-hitting.
- Most likely to cause the oculocardiac reflex?
- Cannot undergo resection?
- Most difficult to recover and why?
- Most frequently affected in pulled-in-two syndrome (PITS)?
- Most prone to adherence syndrome and why?
BONUS: For the final time, if Dr. Recko asks -- "How many rectus muscles can be operated on at once?"
Oculocardiac reflex: medial rectus
No resecting: inferior oblique
Most difficult recovery: medial rectus - no attachments to other muscles.
Pulled-in-two syndrome: inferior rectus
Adherence syndrome: inferior oblique. Proximity to orbital fat space.
BONUS: Two. Definitely less than three. Prostrate yourself before him and just accept what he says.
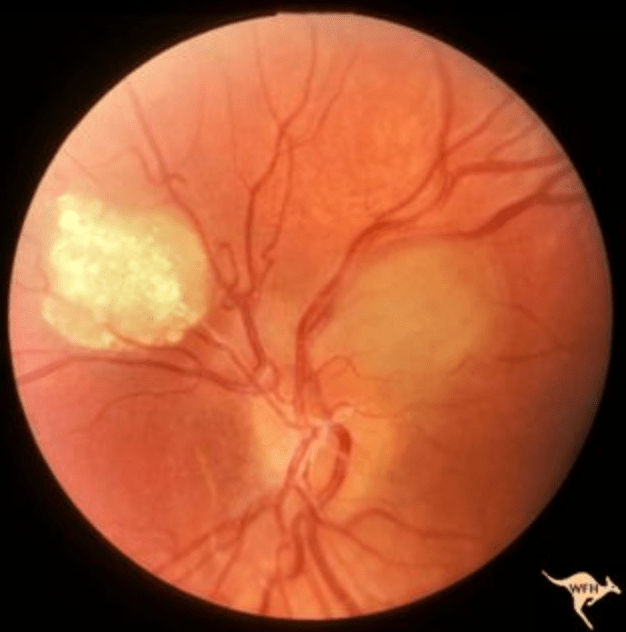
Assume this is part of a larger clinical picture. List at least two additional extraocular findings. If you list all five distinct, you can get up to +500 additional points.
BONUS: What’s the most characteristic ocular finding in NF-2?
Retinal astrocytic hamartoma - TSC
Extraocular: subungal fibromas, Shagreen patch, cardiac rhabdomyoma, Ash leaf spot, adenoma sebaceum / facial angiofibromas, seizures (lameee)
BONUS: PSC or wedge-shaped cataract
THEOLOGY
+100 points for each Tim Keller book you can name (up to 1000 points)
Every Good Endeavor, Meaning of Marriage, Prodigal God, Counterfeit Gods, Freedom of Self-Forgetfulness, The Reason for God, The Songs of God, Prayer, King's Cross, Making Sense of God, Prodigal Prophet, Proverbs, Generous Justice
What is the typical cause of a minor upshoot or downshoot during adduction in patients with Duane retraction syndrome?
BONUS: For patients with Duane syndrome, what is the preferred surgical procedure to treat upshoots and downshoots?
Tight LR slips vertically
BONUS: Y-splitting of the tight lateral rectus muscle
Why is esotropia more prevalent in infantile nystagmus syndrome than exotropia? Looking for the physiologic reason tbhhh
BONUS: You have a patient with fusion maldevelopment nystagmus syndrome (latent nystag if you’re in the club). You cover the patient’s right eye. What eye movements are you expecting?
Convergence dampens nystagmus in INS. Pt’s overconverge to improve VA (nystagmus blocking syndrome) —> ET
—> patients “EAT UP” prism, as convergence increases when the prism tries to offset the ET.
BONUS: Slow drift toward right eye —> fast phase to left (Christian memory technique — eye wonders what’s going on with the cover, goes to check, and then occluded eye tells it to run away as fast as it can)
What is the management of a tear in Tenon capsule during strabismus surgery to prevent adherence syndrome?
BONUS: Walk me through how you'd generally think through a question asking how many mms needed for a resection/ recession? Bonus bonus if you have a memory tool.
Cut out the prolapsed fat, close the tear with absorbable suture
BONUS: LR always requires MORE mm because MR is the strongest muscle. Start at 15 PD and end at 50 PD. Because you’re taking more of the LR, smaller multiplier needed (usually no. mm x4 = PD). Not taking as much of the MR, so the multiplier is higher (usually no. mm x5-6 = PD)
3-4-6-9 rule for ET. Minimum no. mms and maximum for MR and LR. On your own for XT, tho.
You notice diffuse retinal hemorrhages during a NAT exam. The parents ask what visual consequences there might be. How would you explain the effects of NAT on visual development (assume nothing you say can be used against you in a court of law)?
BONUS: What percentage of AHT presents with retinal hemorrhages? Must be within 3%
Hemorrhages resolve without sequelae. Visual morbidity, however, is significant, seen in around ~40% of affected children. But this is from occipital / cortical damage and/or ONH damage.
BONUS: 80%
CINEMA
What is the word that was repeatedly being used?

BONUS: Can you name this animal?

"Inconceivable!"
"Rodents of Unusual Size"
Name the three types of Duane syndrome. How can you remember?
BONUS: Why doesn’t myasthenia gravis affect the pupils?
Type 1: Abduction deficit - 1 D (ET in primary)
Type 2: Adduction deficit - 2 Ds (XT in primary)
Type 3: Abduction and adduction - 3 Ds
BONUS: MG targets skeletal muscles whereas the pupil is controlled by smooth muscle
You have a patient with infantile nystagmus syndrome (congenital motor). His family abhors the idea of surgery -- sorry, Anderson K.
He has a right-beating nystagmus and prefers left gaze with right head turn. What are two options of prism correction that you can prescribe to help?
BONUS: 2 months later. Kiddo hates prism and comes crawling back for the ol' Anderson K(rueger) / Kestenbaum. What procedures are included to help this young kiddo?
1. Shift the perceived object to the LEFT to reduce head turn (image goes to APEX, light goes to base) —> Base IN OS, Base OUT OD.
2. Base OUT prism OU to stimulate convergence —> improves vision.
BONUS:
Left LR recession, Left MR resection.
Right MR recession, Right LR resection.
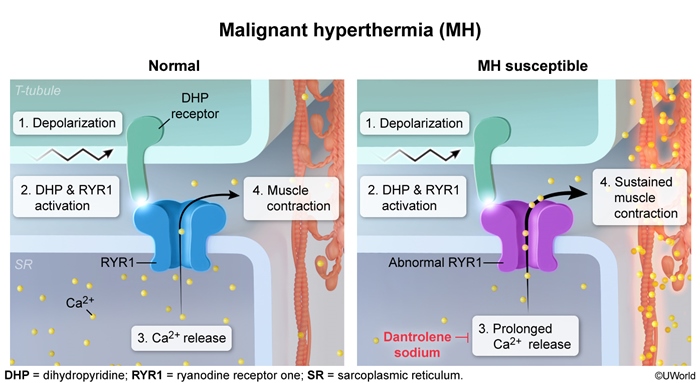
What should you suspect if you have a child undergoing general anesthesia for strabismus surgery who has an unexplained elevated end tidal CO2?
BONUS: Explain the pathophysiology.
Malignant hyperthermia
BONUS: Defect of calcium binding by the sarcoplasmic reticulum of skeletal muscle.
What are the classic lens findings in Alport syndrome and Lowe syndrome?
BONUS: What percentage of Lowe syndrome patients develop glaucoma? What percentage develop corneal/ conjunctival keloids?
BONUS BONUS: What specific systemic disorder is associated with oculocerebrorenal syndrome (Lowe)? What does this lead to?
Alport = ANTERIOR lenticonus. Lowe syndrome = POSTERIOR lenticonus / congenital cataract in most patients
BONUS: 100-50-25 rule. 100% classically have cataracts, 50% glaucoma, 25% keloids
BONUS BONUS: Fanconi syndrome (proximal renal tubulopathy) -> aminoaciduria, metabolic acidosis, rickets
TRAVEL
Name this European city that inspired JK Rowling to write Harry Potter.

BONUS: What is the name of this delectable dessert first originating in the city above?

Edinburgh
Sticky toffee pudding
You have a 16-year-old patient in your room who was recently involved in an MVC. She claims she cannot abduct her left eye. To the contrary, she has Duane syndrome. She refuses neuro-imaging and demands to know three findings that would differentiate Type 1 Duane syndrome from CN VI palsy. You offer the following:
BONUS: She says you're still wrong and changes her mind. She accepts the invitation of an MRI Brain. What might this find?
Globe retraction on attempted adduction. Small ET in primary position (< 30 D) and orthotropia with only a small face turn. Small XT on right gaze to affected eye
BONUS: Absent CN VI nerve +/- hypoplastic lateral rectus muscle
What are the distinct waveforms seen in congenital sensory nystagmus? When is each seen (plz be specific)?
BONUS: It's written that FMNS presents when one eye is occluded. So explain how FMNS can be present with both eyes open. Speak up for yourselves!
Waveform depends on visual acuity:
20/60 – 20/100: Jerk
20/100 – 20/200: Pendular
<20/200: ‘Searching’
BONUS: If the non-fixating eye is suppressed / amblyopic, then can see FMNS even when no disruption to binocularity
What general type of strabismus surgery is employed when a muscle exhibits no force generation (e.g. paralytic CN VI palsy)?
BONUS (+300): Name three complications that can result from perforation of the sclera during strabismus surgery?
Transposition procedure
Need to move some EOM buddies over to help the inactive muscle
BONUS: Retinal detachment, endophthalmitis, chorioretinal atrophy/ scarring
Please list a pediatric differential diagnosis for Bull’s Eye Maculopathy (don't have to be perfect - at least 4-5 will do)
BONUS (+600): strong work there. ___ was a tough one. Speaking of which, how would you differentiate ___ from Stargardt disease in a young patient?
Cone dystrophy
Cone-rod dystrophy
Ciliopathies
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL)
LCA
Spinocerebellar ataxia VII, Cohen syndrome (?)
Stargardt disease (honestly not sure why they included this)
BONUS: NCL has...
- electronegative ERG early on in disease course
- OPTIC ATROPHY
- rapidly progressive course
- more noticeable bull’s eye maculopathy
- Also, withdrawn/ inattentive behavior/ sleep probs
MUSIC:
What southern city is widely considered the epicenter of hip hop? There are a couple others that can be accepted as well if an explanation can be given.
BONUS: Name at least two artists from the city in question. +50 more points up to additional 400 points.
Atlanta, GA
OutKast, TI, 2Chainz, Lil Nas X, Young Thug, Ludacris, Young Jeezy, Future, Gucci Mane, Lil Jon, B.o.B, Migos, Yung Joc,
Alternatively Houston (Travis Scott, Megan Thee Stallion, Bun B / UGK, Paul Wall)
Part 1 - Name this syndrome (+250)

Part 2 (unrelated): What 2 syndromes are associated with Duane syndrome (+250)
BODACIOUS BONUS: What does ___ syndrome entail?
Part 1: Mobius syndrome
Part 2: Goldenhar syndrome, Wildervanck syndrome
BODACIOUS BONUS: Sensorineural hearing loss and Klippel-Feil anomaly with fused cervical vertebrae
What are the 4 drugs/drug classes associated with acquired vertical nystagmus?
BONUS: What are the 3 common causes of opsoclonus in children?
NOTE: I promise the other questions in this category are more fun!
Codeine
Lithium
Anxiolytics
Anticonvulsants
BONUS:
Acute cerebellar ataxia
Viral encephalitis
Paraneoplastic syndrome of neuroblastoma
What complication of strabismus surgery can occur when performing inferior oblique anteriorization? Why?
BONUS: What method of SO weakening is used to preserve the torsional action of the muscle?
Anti-elevation syndrome - restricted elevation in abduction.
If both poles of IO are anterior to insertion of inferior rectus, then contraction depresses the globe.
BONUS: Tenectomy/ tenotomy of only the posterior 75% of the tendon
Please list the INHERITED causes of a combined pigmentary retinopathy and early-onset hearing loss clinical picture. Ahem. I SAID PLEASE LIST --
BADDIE BONUS (up to +1000): all the ciliopathies have pigmentary retinopathy + renal dysfunction. Can you name the four ciliopathies and name distinctive findings of each if present? Note: one syndrome lacks a distinction (eternal respect earned if correct).
Usher syndrome, Alport syndrome, ciliopathies, peroxisomal (e.g. Zellweger), mitochondrial (e.g. Kearns-Sayre)
BADDIE BONUS:
Joubert: molar tooth sign on MRI - thickening superior cerebellar peduncles, oculomotor apraxia, developmental delay (kinda weak)
Bardet Biedl - polydactyly, hypogonadism (and obesity + intellectual disability)
Senior Loken - Just pigmentary retinopathy + renal dysfunction
Alstrom syndrome - Cardiomyopathy (and obesity)
CLASSIC LITERATURE:
Name at least three (3) John Steinbeck novels. Which novel did he consider to be his Magnum Opus (I know we got this, fam)?
BONUS (+250 each): What biblical story was explored in his Magnum Opus? What word was focused upon?
Magnum opus: East of Eden
Of Mice and Men
Grapes of Wrath
Cain and Abel
"Timshel" = thou mayest
Then the Lord said to Cain, “Why are you angry? Why is your face downcast? If you do what is right, will you not be accepted? But if you do not do what is right, sin is crouching at your door; it desires to have you, but you must rule over it."