Where is the nasolacrimal duct opening located?
Under the inferior turbinate

Identify condition + how to treat
Complete punctual atresia
CDCR (conjunctivodacryocystorhinostomy)
How do newborns acquire infectious neonatal conjunctivitis
Through direct contact during passage through the birth canal (infections can ascend to the uterus so babies delivered by C section can still get infected)
Name the most common cause of preventable blindness in the world
Trachoma (C. trachomatis serotypes A-C)
What is the best test that correlates with dry eye disease severity in children
Fluorescein staining
What is the prevalence of congenital NLDO?
5% of newborns affected
20% in Down syndrome
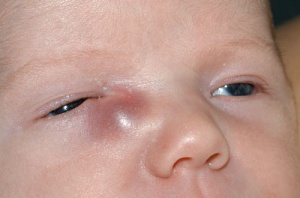
Diagnose + Treat
Congenital lacrimal fistula
Observe. If discharge present (distal NLDO can probe), can suture close if persists despite patent NLD
Describe the differences between Chlamydia and N. Gonorrhea ophthalmia neonatorum? (time to sx, ocular signs, systemic complications and treatment)
Chlamydia: inclusion conjunctivitis, onset 1 week, minimal/moderate filmy discharge, mild swelling, hyperemia, papillary reaction (follicular in adults), risk of pneumonitis/ OM, Tx= oral erythromycin x 14 days or Azithromycin x 3 days.
Gonorrhea: GNID, 3-4 days, copious discharge potentially corneal ulceration and perforation, risk of sepsis/ meningitis/ arthritis. Tx= systemic ceftriaxone and topical saline irrigation + top Abx if cornea involved.
Sexual abuse (cause with Chlamydia serotypes D-K)
What is a special consideration in children with dry eye syndrome
Vitamin A deficiency
At what age should you probe if NLDO does not resolve spontaneously?
BONUS +100: what is the success rate of the initial probing if done at appropriate time?
12 months (90% of patients improved within 9-12 months)
80% or more
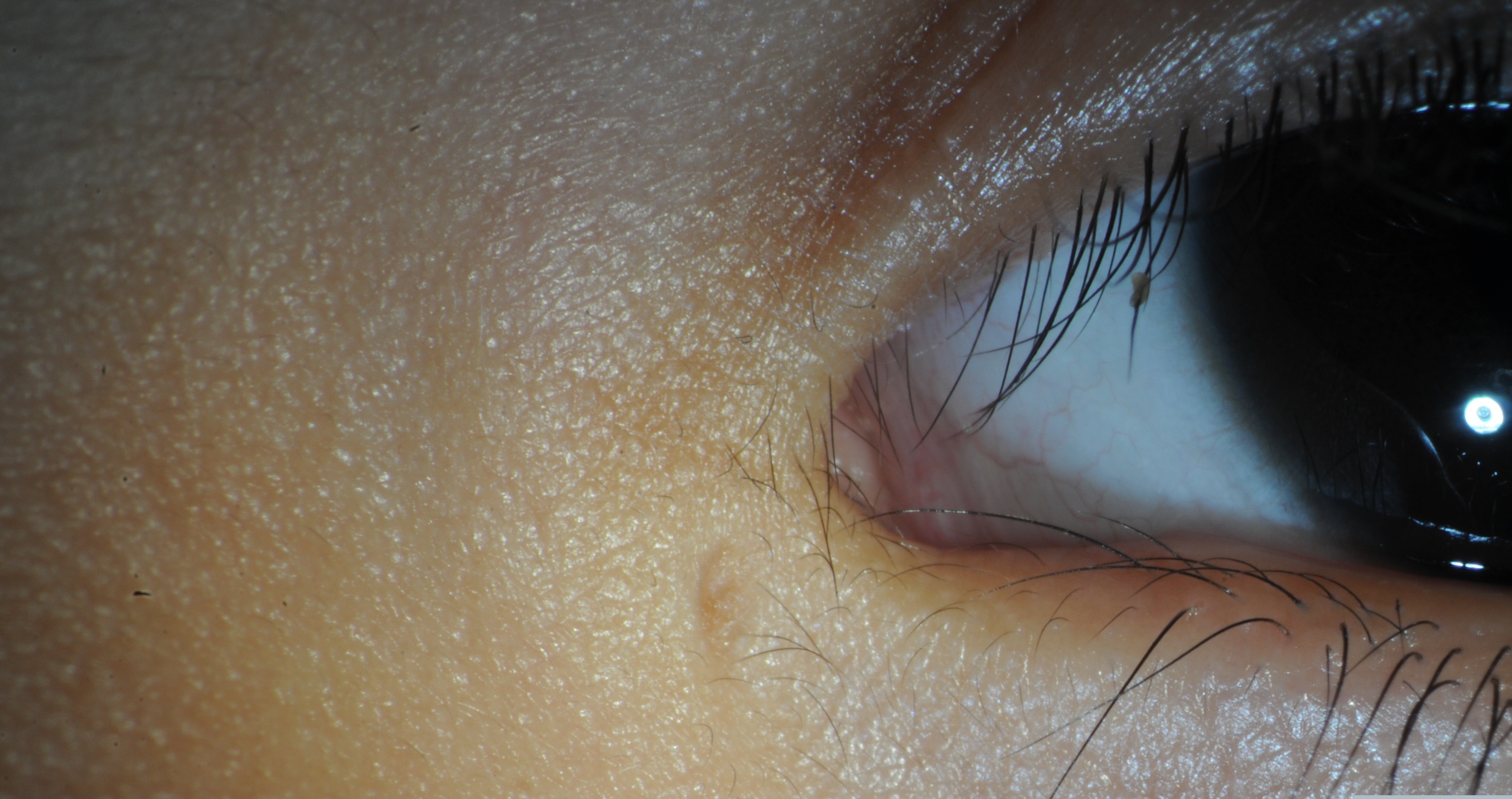
In this condition, which structure prevents decompression of the lacrimal sac
Valve of Rosenmuller.
List the 4 most common causes of bacterial conjunctivitis in school-aged children
Strep pneumo, Haemophilus sp., S. Aureus, Moraxella
How does molluscum contagiosum cause conjunctivitis? What kind of conjunctivitis
Type of hypersensitivity reaction for seasonal AK, perennial AK and the difference between them
Seasonal: type 1 to seasonal allergens in spring/ fall
Perennial: type 1 to ubiquitous household allergens (year long)
List all the structures your probe passes through when probing NLD
punctum, canaliculus, common canaliculus, valve of rosenmuller, lacrimal sac, nasolacrimal duct, valve of hasner


NLD probing alone is curative in what % of patient with Dacryocystocele
25%
Rest needs probing in combo w nasal endoscopy (BILATERAL) and intranasal cyst removal
What is Parinaud oculoglandular syndrome and name 3 organisms that can cause it
Unilateral granulomatous conjunctivitis associated with preauricular and submandibular lymphadenopathy.
Bartonella henselae (most common), Mycobacterium tuberculosis or leprae, Francisella Tularensis, Yersenia, Syphilis, Chlamydia.
How are conjunctival papillomas managed
observation, if too big and irritation oral CIMETIDINE
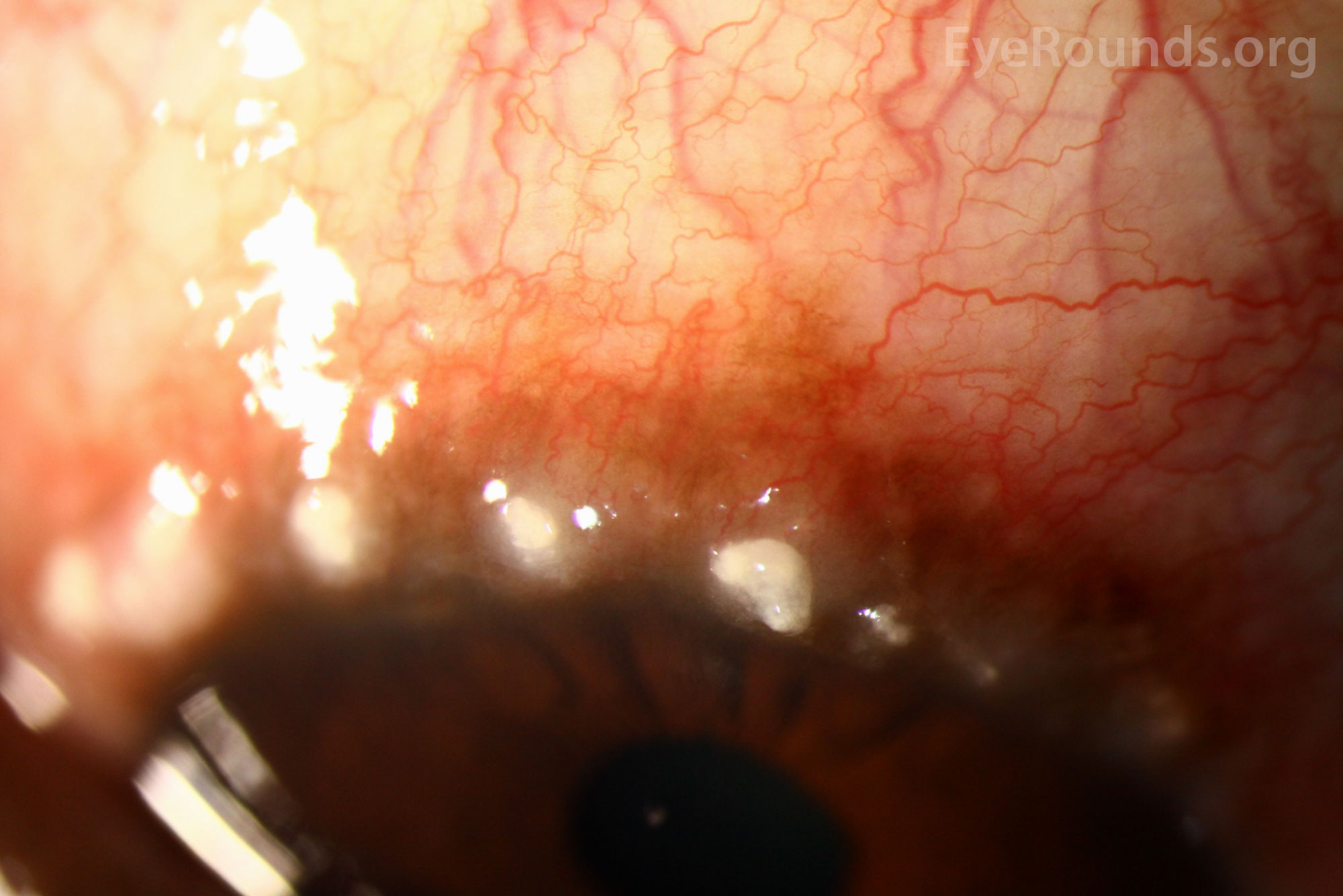
Name this and where do you typically see those
Limbal form of VKC (thickening and opacification of limbus) Horner trantas dots- raised whitish center filled with eosinophils and epithelial cells
What does DCR stand for and what does it entail?
Dacryocystorhinostomy- new opening created between lacrimal sac and nasal cavity
Differential diagnosis of dacryocystocele (name all 3)
Hemangioma (vascular appearance), Dermoid cyst, Encephalocele (later 2 are ABOVE medial canthal tendon)
Name the 4 types of adenoviral diseases
Double points if you can name ALL serotypes
- epidemic keratoconjunctivitis (serotypes 8,19,37, subgroupD)
- pharygoconjunctival fever (3,7)
- Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (11,21)
- Acute follicular conjunctivitis (1,2,3,4,7,10)
Describe the typical course of EKC (with durations)
Acute follicular conjunctivitis followed by diffuse superficial keratitis, followed by focal epithelial lesions. After 11-15 days sub epithelial opacities begin. epithelial component fades by day 30 but subepi opacities can remain for up to 2 years.
Most common cause of SJS/TEN in children
Medications: anticonvulsants and sulfonamides
Infections: Mycoplasma or herpes simplex