What to give for Rickets
Adequate amount of vit D
Currant jelly-like stool
intussusception
What not to do with a suspected appendicitis
rub or put pressure on abdomen
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
Depends on symptoms: oral meds, lifestyle changes, weight loss, increased exercise
Common cause of UTI in children
Escherichia Coli
Aseptic necrosis of the head of the femur
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
When will surgery be needed for scoliosis
>40 degrees
Beriberi: severe lack; cardiac and neurologic symptoms
Thiamine deficiency
Common sources of lead poisoning in children
Lead-containing paint inside and outside older homes
Furniture and toys painted with lead-containing pain; vinyl mini blinds
Drinking water contaminated by lead pips or copper pipes with lead-soldered joints
Dust containing lead salts from lead paint; emission from lead smelters
Storage of fruit juices or other food in improperly glazed earthenware
If a patient drinks an unknown substance what should the parent never give them?
ipecac syrup
Ways to administer insulin
insulin syringe
pre-filled insulin pen
insulin pump
How do we test for UTI
Urine Culture
Malignant tumor seen in long bones
Osteosarcoma
What is the plate called that if fractured can cause permanent damage and stop the growth of the bone
Epiphyseal plate
Pellagra is deficient in
Niacin
Recurrent paroxysmal bouts of abdominal pain:
Colic
What teaching would might needed for a child diagnosed with Hirschsprung Disease?
Care for temporary colostomy
3 P's of Diabetes
Polyuria
Polyphagia
Polydipsia
Acute Glomerulonephritis
When should a brace be removed for scoliosis
Only for showers
Treatment for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Medications: NSAIDs, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, corticosteroids
Physical Therapy: used to improve strength and flexibility, exercise, use of heat-cold therapy, massage, electrical stimulation; exercise should not increase pain
Deficiency of protein, calories, and other nutrients #1
Severe deficiency of protein with adequate caloric intake #2
#1 Marasmus
#2 Kwashiorkor
Clinical manifestation: infant starts out eating well, gains weight, then starts vomiting occasionally after meals; vomiting increases in frequency and force and becomes projectile; emesis is sour, undigested food; obstruction mechanical issue, child still hungry; baby becomes irritable, loses weight, dehydration; alkalosis; constipation; scant urine; visible gastric peristaltic waves
What is the treatment for this disorder?
Pyloric Stenosis
Treatment: pyloromyotomy
Review ostomy care
PG 813
S/S drowsiness, lethargy, dry skin, flushed cheeks, cherry-red lips, acetone breath with fruity smell, Kussmaul breathing; nausea and vomiting; coma, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, rapid pulse, subnormal temperature and BP
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
What not to do with a pt with Wilms Tumor
Palpation of abdomin
5 Ps for pt with cast
Pain-any sign, exact location
Pulse-Check related locations for injured extremity
Paralysis-Check hand or foot function
Pallor-Check nailbeds of fingers or toes, capillary refill
Paleness-Discoloration, coldness
FIRST Clinical manifestations for Muscular Dystrophy
Difficulty standing and walking
Trunk muscle weakness
Trouble climbing stairs and running
Develop Gowers sign
Lordosis
Symptoms vary; common: urticaria, angioedema, pruritus, nausea, abdominal pain and cramping, repiratory symptoms; may appear quickly or have delay reaction
Food Allergies
GERD S/S
Clinical manifestations: vomits after eating, irritable,
hungry but may refuse to eat, aspiration after vomiting
may lead to apnea, wheezing, cough, pneumonia; failure
to thrive, lack of normal weight gain; in older child,
heartburn, nausea, epigastric pain, difficulty swallowing
Pinworm medication
Anthelmintics
Know the different insulins and the difference between short and long acting
NPH
Regular
Aspart
Glargine
Presenting symptom of edema around eyes and face in morning then shift to abdomen, lower extremities and ankles; anasarca develops, resp difficulty; edema shifts when child changes position
Loss of appetite, fatigue, irritability, malnutrition
Susceptible to infection with repeat acute resp conditions common
Something a patient with this syndrome should do daily?
Nephrotic Syndrome
Weighing on the same scale daily
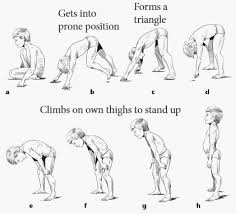
Gowers Sign
Different classifications of fractures:
Complete
Incomplete
Greenstick
Spiral
Closed
Open
Crushing