Characterized by yellowish, greasy, scaly, or crusted patches on scalp in NB and older infants
Excessive sebaceous glands
Seborrheic Dermatitis
(cradle cap)
What is an infection that is contracted while in the hospital
Nosocomial (health care-associated) infection
Examples of STI prevention/education
Prevention most effective tool against STIs
Abstinence
Condoms
Adolescents must be taught all aspects of consequences
Characteristics of autism spectrum disorder
Inability to communicate with others
Inability to relate to others
Limited activities and interests
What should someone do if they are on a antidepressant therapy and have a loss of interest
Notify the physician immediately
Nursing care for Diaper dermatitis (diaper rash)
Remind family prevention is best treatment; teach proper hygiene; caution on use of commercial wet wipes; avoid use of powder
What are the 3 types of pediculosis (lice)
How is lice spread
S/S
Pediculus humanus (head), Pediculus humanus corporis (body), and Pthirus pubis (pubic)
Passed by direct or indirect contact
S/S nits attached to hair, not easily removed, nits hatch in about 1 week, severe itching
Vaccination Education
Are used to prevent serious disease and infection
Possible characteristics: impulsiveness, easy distracted, excessive fidgeting or squirming, difficulty sitting still, difficulty playing quietly, problems following through on instructions, despite being able to understand them, inattentiveness when being spoken to, frequently losing things, lack of organization, going from one uncompleted activity to another, difficulty taking turns, interrupting, frequent excessive talking, blurting out, engaging in dangerous activities without considering the consequences
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Most common substance used by teenagers
alcohol
S/S and cause of Candidiasis
Caused by CANDIDA ALBICANS
S/S mouth has white coating and looks like milk curds
What is the cause for Rocky Mountain spotted fever
tick bite
Which age group has the highest incidence of STIs
adolescents
Therapeutic Response for a child being bullied
Make sure the child knows not to blame self for being bullied
4 stages of substance abuse
1. Experimentation, learning the mood swing
2. Seeing the mood swing
3. Preoccupation with the mood swing
4. Using to feel normal
Name the highest sebaceous glad activity areas
Face
Upper Chest
Back
Scalp
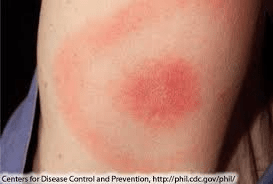
Lyme Disease (Bulls-eye rash around the bite)
S/S of Koplik Spots
Fever, Cough, Coryza (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose), tiny grains of white sand with red rings inside of child's mouth
PG 900
What are 3 classifications of anxiety noted in children
Generalized anxiety disorder
Separation anxiety
Phobias
Characteristics of a patient with Anorexia Nervosa
Always trying to please everyone; families over-involved with child's life; depression and anxiety disorders common; deny weight loss; adhere rigid program of exercise; obsessive-compulsive traits common; deny hunger; often suffer from fatigue
S/S Acne Vulgaris
Caused by increased hormonal levels (especially androgens); hereditary factors: irritation and irritating substances; growth of anaerobic bacteria
Sebaceous glad secretes sebum which gets blocked leading to infection, inflammation and papules, pustules, and nodules
Burn Causes
Thermal or heat burns (contact made with heat source or fire)
Electricity
Chemical
S/S and transmission of Infectious Mononucleosis
Adolescents and young adults most susceptible. Transmitted through saliva also known as "kissing disease"
S/S variety of symptoms, mild to severe; fever, sore throat with enlarged tonsils; thick, white membrane covering tonsils; palatine petechiae; swollen lymph nodes; enlargement of spleen; extreme fatigue, lack of energy; headache, abdominal pain, epistaxis
Risk factors for children dealing with depression and suicide
Family hx of depression, family dysfunction, loss of loved one, traumatic life events, injury, chronic conditions, emotional, physical and/or sexual abuse
Binge eating followed by purging
Behaviors include: immediately going to bathroom after eating, not eating in social settings, chewing gum or breathe mints, drug abuse, alcoholism, stealing, promiscuity, other impulsive activities
Bulimia Nervosa