Diversity
This is a congenital foot deformity with the foot pointed down and inward, most common in males.
What is Talipes Equinovarus (Club foot)?
Recommended newborn breastfeeding intervals.
What is every 2-3 hours?
A baby with inspiratory stridor and respiratory difficulty is most likely infected with this organism.
Parainfluenza (croup)
This is the treatment for a heart condition that often presents with bounding pulses, hoarseness, and a machinery murmur at the L infraclavicular region.
What is indomethacin for patent ductus arteriosus?
These are lesions of capillary dilation usually found on the neck or forehead of infants.
What are nevus flameus (stork bites)?
Aside from family history, these are 2 major risk factors associated with developmental dysplasia of the hip.
What are females and breech birth?
One reason infants develop iron deficiency anemia; and one reason toddlers develop iron deficiency anemia.
What is breastfeeding and what is increased milk intake >20oz/day?
This condition is the early closure of skull sutures in babies.
What is craniosynostosis?
What is an Inhaled corticosteroid?
HgbF disappears and is completely replaced by HgbA by this age.
What is 12 months of age?
Newborn ear abnormalities and periauricular pits should prompt you to check this body system.
What is renal?
These 4 typically administered childhood vaccines are all Live attenuated vaccines.
Influenza, MMR, Varicella, Rotavirus
These two infections can lead to an increased risk of Reye Syndrome.
What is Influenza and Varicella?
This congenital heart defect often presents with a fixed split S2 on exam.
What is an Atrial Septal Defect?
These are blue/gray macular lesions on the sacral or gluteal areas of babies, most commonly of Asian or Indian descent.
What is Congenital dermal melanocytosis?
A patient is diagnosed with an supracondylar fracture after falling from a play structure. This is your management.
What is Assess NV status; Emergent orthopedic consult; Posterior long arm splint?
This normocytic anemia is seen in the first few years of life, usually following a viral infection.
What is transient erythroblastopenia of childhood?
This is a neurologic syndrome resulting from the deposition of unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin in the basal ganglia and brainstem nuclei.
What is Kernicterus?
Cryptorchidism should be corrected surgically in this age range.
What is 6-18 months of age?
The HEADSS Assessment stands for these areas evaluated with this adolescent assessment tool.
What is Home, Education, Activities, Drugs, Sexuality, Suicide/Depression?
An infant can pick up a cheerio with two fingers by this age.
What is 8 months?
Erythema toxicum classically presents and resolves in this time.
What is starts in the first few days of life and is gone by 1st week.
This condition classically presents with a rash once the fever has resolved.
What is roseola.
This heart defect can have rib notching and a differential blood pressure between the RUE and LLE.
What is coarctation of the aorta?
The most likely organism responsible for this rash.
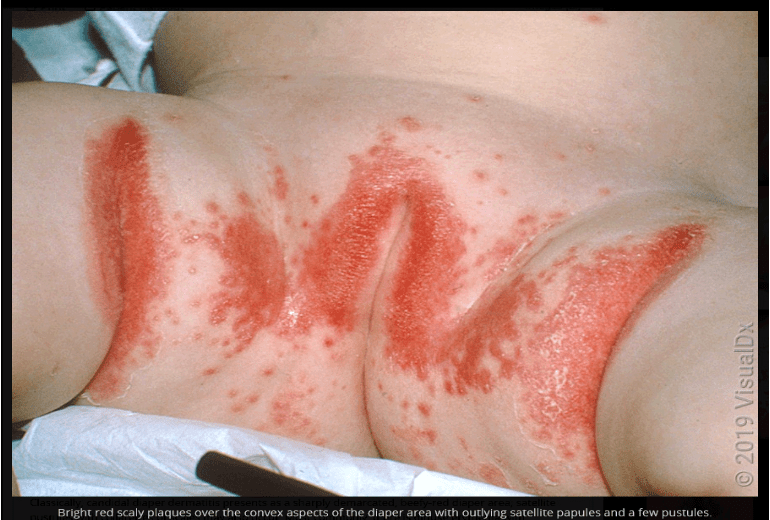
What is Candida?
This condition occurs when a child is jerked or lifted by the wrist/arm.
What is nursemaid's elbow?
Auer rods are seen in this condition.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
What is hydrocephalus?
A premature infant delivered at 28 weeks with grunting, tachypnea, retractions and ground glass with air bronchograms on CXR is likely deficient in this.
What is surfactant?
This history finding differentiates between B12 and folic acid deficiency.
What is neurological changes/deficits?
This supplementation is required for babies that are exclusively breast fed. (name 2)
What is Vitamin D and Iron?
This first sign of puberty in males occurs during this Tanner stage.
Enlargement of the testicles in Tanner stage 2
This condition can cause a "slapped cheek" appearance.
What is Erythema infectiosum or "Fifth disease"
Cyanotic at birth with "Egg on a string" or narrow mediastinum on chest xray.
What is transposition of the great arteries?
This is a reddish purple vascular nevus affecting the trigeminal nerve.
What is Port-wine stain of Sturge-Weber syndrome.
A painful limp in a teenage boy with external rotation of the leg is indicative of this condition.
What is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)?
This condition can present with neurologic deterioration, constipation, mental status changes and basophilic stippling on CBC.
What is lead poisoning?
What is Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
This organism is the most common source of cystic fibrosis lung infections.
What is Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
This is the mother's Rh status and second fetus' Rh status that could result in hydrops fetalis.
Newborns should regain this maximum body weight percentage loss by this time after birth.
What is 10% of body weight regained by 10 days of life.
Absence of a red reflex would be concerning for these two conditions.
What are cataracts and retinoblastoma.
The 5 Ts and 1 H of cyanotic heart disease.
What is: Truncus Arteriosus, Transposition of the Great Arteries, Tricuspid Atresia, Tetralogy of Fallot, Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return and Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome?
This lesion may have a serious associated condition that occurs when the V-1 branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved.
Nevus Flammeus (Port Wine Stain)
Sturge Weber Syndrome
This is your next step in management of a pediatric patient with a noted bucket handle fracture.
What is Call Child Protective Services?
This is the most common brain tumor found in children and this is it's most common location.
What is astrocytoma, infratentorial?
Risk of a condition that can present with a neural tube defect and a possible meningocele can be reduced by doing this.
What is Taking folic acid during pregnancy?
This diagnostic test is indicated in a 6 month old child who has had a febrile UTI.
What is renal ultrasound?
A thin upper lip, micrognathia, flat forehead, small eye slits, indistinct philtrum (lip) and flat mid face is often seen in this syndrome.
What is fetal alcohol syndrome?
These 3 interventions are performed within the first 24 hours of life.
These 5 vaccines are typically given at 2, 4 and 6 months of age.
What are DTAP, HIB, IPV, PCV, ROTAVIRUS vaccines?
Fever in the first 28 days of life requires a work up including these 4 diagnostic tests.
What is CBC, LP with CSF, Blood culture, Urine culture?
This most common cyanotic heart defect in children beyond infancy typically presents with these 4 components.
What is (TOF):
•Pulmonary stenosis
•Ventricular septal defect
•Overriding aorta
•Right ventricular hypertrophy
Children with this many cafe au lait spots (0.5cm before puberty, >1.5cm after puberty) must be evaluated for this possible associated serious condition.
What is neurofibromatosis type 1.
The classification of this injury.
What is Salter Harris III?
This malignancy can cause opsoclonus/myoclonus, Horner syndrome and periorbital ecchymoses.
What is neuroblastoma?
This sign indicating an upper motor neuron lesion characterized by extension of the great toe and fanning of the remaining toes is actually normal in children under this age.
What is 2 years of age?
Proteinuria >3.5g/24 h with hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia and edema would be seen in this umbrella condition.
A widely split S2 can be heard in this congenital heart defect.
What is atrial septal defect?