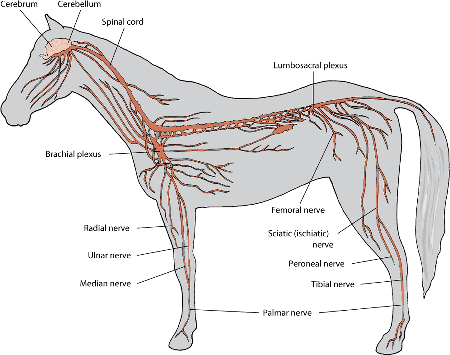
The radial nerve branches off this big nerve structure
ventral nerve roots of T1 of the brachial plexus (originates from C6-T2)
Nerves regenerate at this rate
1 inch/month
This common symptom of radial nerve paralysis is characterized by
Dropped elbow and inability to extend leg ("knuckling over")

To prevent further injury, this supportive measure is often used to help the horse stand and move.
A splint
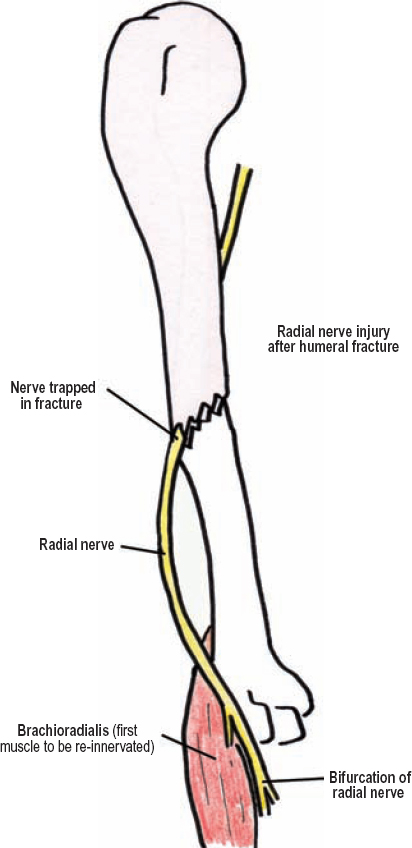
The radial nerve can be injured at this anatomical location, often leading to radial nerve paralysis
Mid-humeral region
This type of muscle fiber is primarily affected by radial nerve paralysis, leading to muscle atrophy.
Skeletal muscle fibers
This visible sign in the forelimb muscles can be an indication of chronic nerve damage.
Muscle wasting/atrophy
Horses with radial nerve paralysis may benefit from this type of supplement to support nerve health.
Vitamin E!
What is the function of the radial nerve?

Innervates extensors of the elbow, carpus, and digits
In cases of nerve injury, this process involves the degeneration of the nerve distal to the site of injury.
Wallerian degeneration
How does a grade 4/5 lameness present in a horse?
Lameness is obvious at the walk.
Initial treatment often involves this basic intervention to reduce swelling and pain.
Anti-inflamatories
Deep brachial artery
What can cause radial nerve damage?
hyperextension of the forelimb, excessive abduction of the shoulder, fractured humerus, and prolonged lateral recumbency
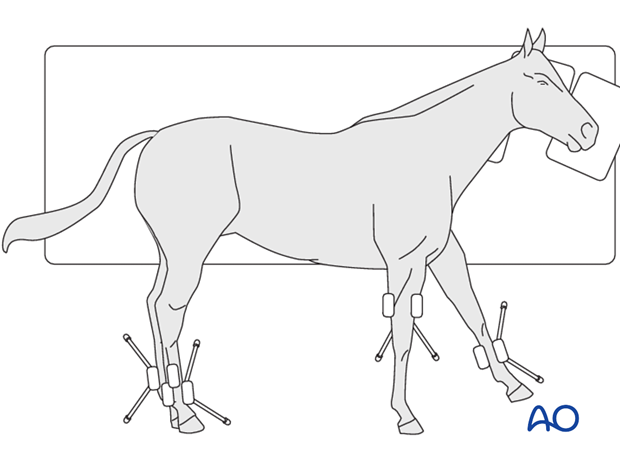
What position should you place a horse in lateral recumbency while under GA to reduce compression on the radial nerve?
front leg on the down side should be extended cranially to relieve pressure on triceps mass
What is the prognosis for a horse that shows improving voluntary movement of the affected limb and still has pain reception intact?
A good prognosis =)
The radial nerve sits in this structure of the humerus.
musculospiral groove of the humerus

nociception (pain), voluntary movement of forelimb, ability to bear weight (must progress in the healing process)
Alongside the neuropathy from compression of the radial nerve, what other abnormality might occur with prolonged pressure on the should in lateral recumbency?
ischemia of the triceps musculature

What are the mg/kg doses for phenylbutazone?
2.2 mg/kg or 4.4 mg/kg