The German word for "Unified Whole" which is a principle that explains how we organize a whole.
What is Gestalt?
Example of selective attention: attention to a specific conversation at a noisy gathering is known as this effect.
*Attention can be drawn by the sound of a familiar voice, or the mentioning of your name.
What is cocktail party effect?
A researcher uses his friends and family to conduct a study on perceptions of objects during different times of the day.
What is sampling bias? Convenience sampling?
In depth look at children with hearing impairments and their development in one school year is an example of this type of research.
What is a case study?
According to a study, the less time spent looking on the internet the day before a test, the less tired students feel during the following school day is an example of what type of correlation.
What is a positive correlation?
The limbic system structure associated with emotions such as anger and jealousy
What is amygdala?
Completing the perception of a stimuli which relies on the how close together things are to one another.
What is proximity?
Occurs when we focus on one part of our visual field and miss or ignore others as it was not perceived.
What is inattentional blindness.
A participant who wants their actions and responses to be acceptable chooses to adapt their behavior and survey responses in a way that they feel is wanted by the researcher.
What is social desirability bias?
The relationship between mothers who breast feed their child and that child's emotional stability shows a coefficient score of .95 is this type of research.
What is correlational study?
Case studies specifically with a unique or small groups lack this fundamental thing about research. Makes it harder to apply the findings to a broader population.
What is generalizability?
The bundle of nerves in the brain which connect the two hemispheres.
What is corpus callosum?
Depth cues which require the use of two eyes.
What are binocular depth cues?
The depth cues which require only one eye.
What are monocular depth cues?
The influence on responses based on how the information is presented.
ex.)Which are you most likely to buy 90% lean or 10% fat ground beef?
What is framing?
A research wants to prove that pregnant women taking Tylenol will cause their children to develop autism need to conduct this type of research with at least one control group. (Will not happen because of ethical implications.)
What is an experiment?
The broad term used for mental activities: thinking, knowing, awareness and understanding.
What is cognition?
What is cerebellum?
What is top-down processing?
Brain perceives depth by using parallel lines which appear to converge in the distance.
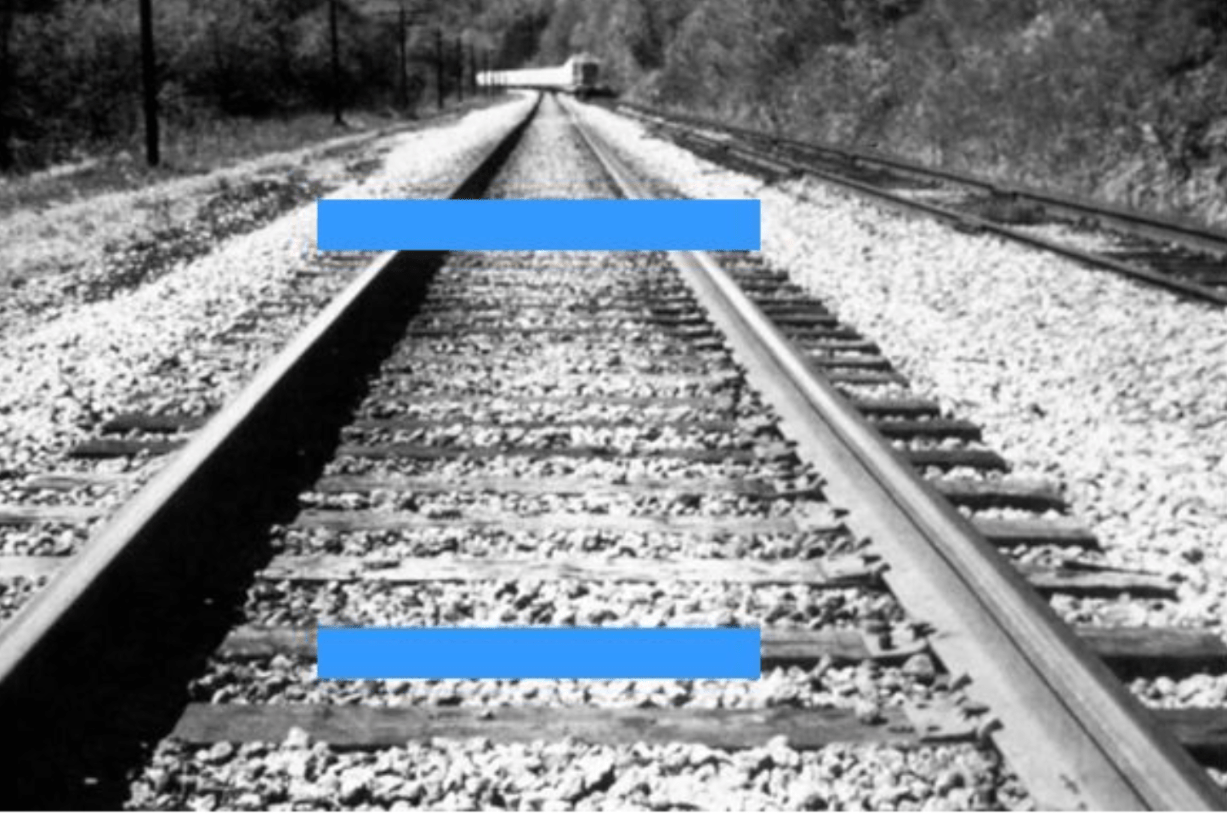

What is linear perspective?
This cognitive bias is the tendency to favor, search, and recall information that confirms your preconceived notions. Ignore contradictory evidence against your preconceptions..
This research method looks at two groups and analyzes how perception of authority figures affects behaviors and decisions. One groups consists of 18-24 year olds and the other group is 65- 71 year olds.
What is cross-sectional studies?
A monocular cue in which we perceive an object blocking another is closer than the other.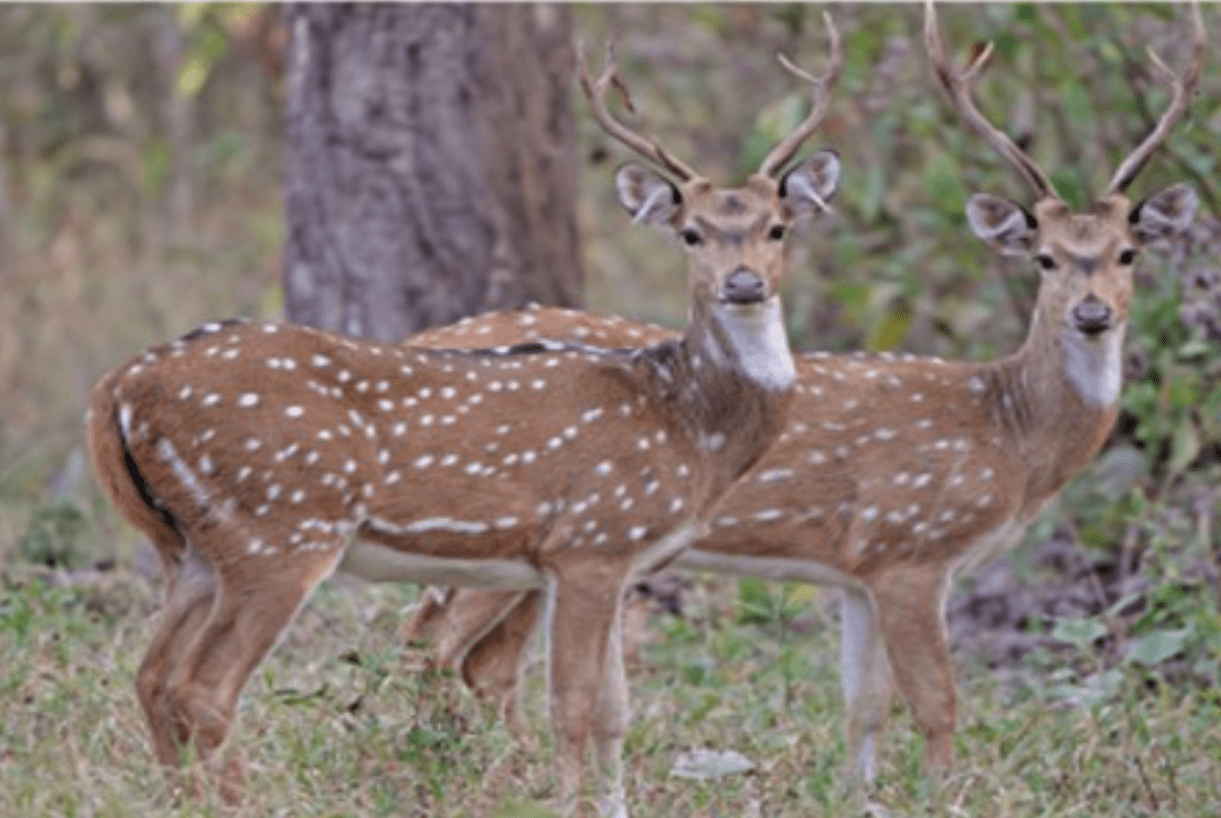
Spatial navigation, crucial for memory formation episodic and declarative memories.
What is hippocampus?
The 2 perceptions of motion.
1. Christmas lights turning off and on in a pattern.
2. Animations, flip books, and some still images where it appears as if things are in motion. 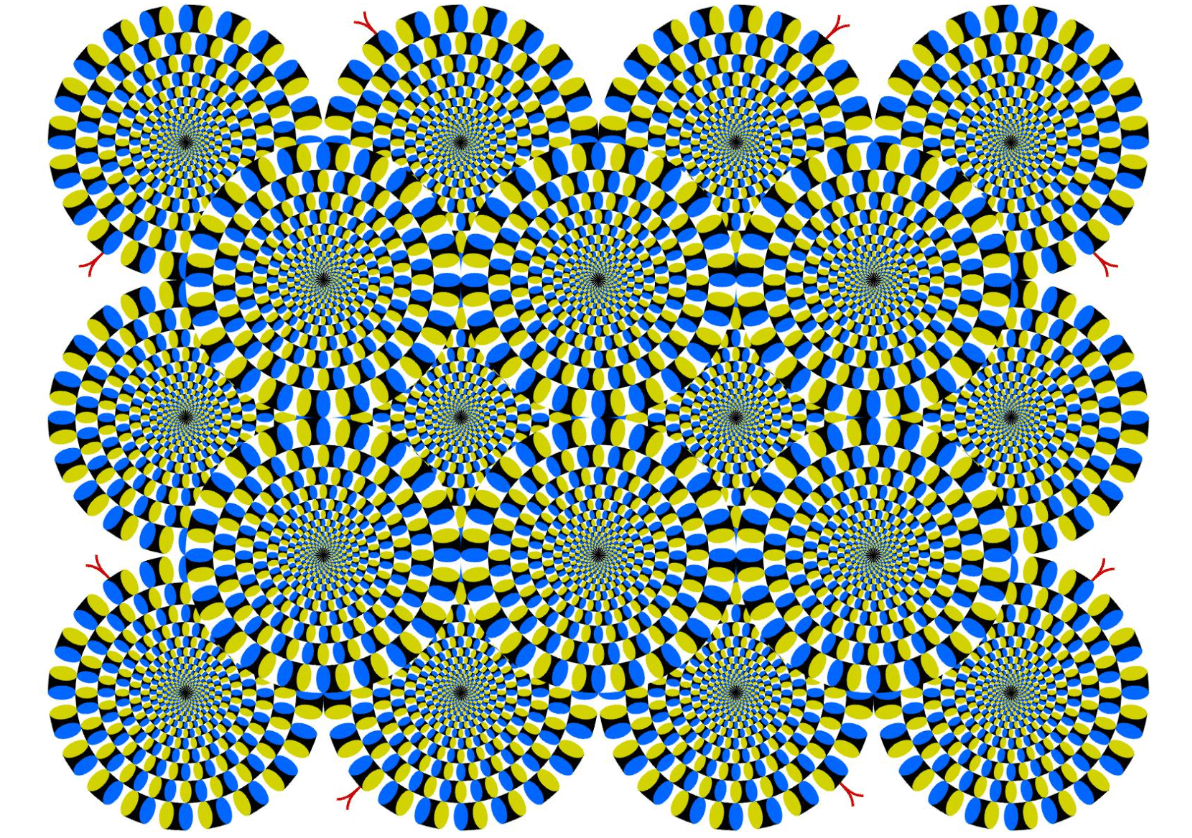
What are Phi phenomenon and stroboscopic movement?
What is relative clarity?
"I knew it all along" effect. People perceiving they knew about something after it was revealed is this type of bias.
What is hindsight bias?
Multiple studies are compiled on a specific topic is known as this type of study. Used to synthesize research findings and determine statistical significance and effect size particularly in the field of psychology.
What is meta-analysis?
Part of neuron communicating with each other via action potential, reuptake, and refractory period. Also called chemical messengers.
What are neurotransmitters?
Located in the midbrain and associated with sensory processing.
What is thalamus?
A monocular cue in which size of objects are small when far away and large when near.
What is relative size?
What is perceptual set?
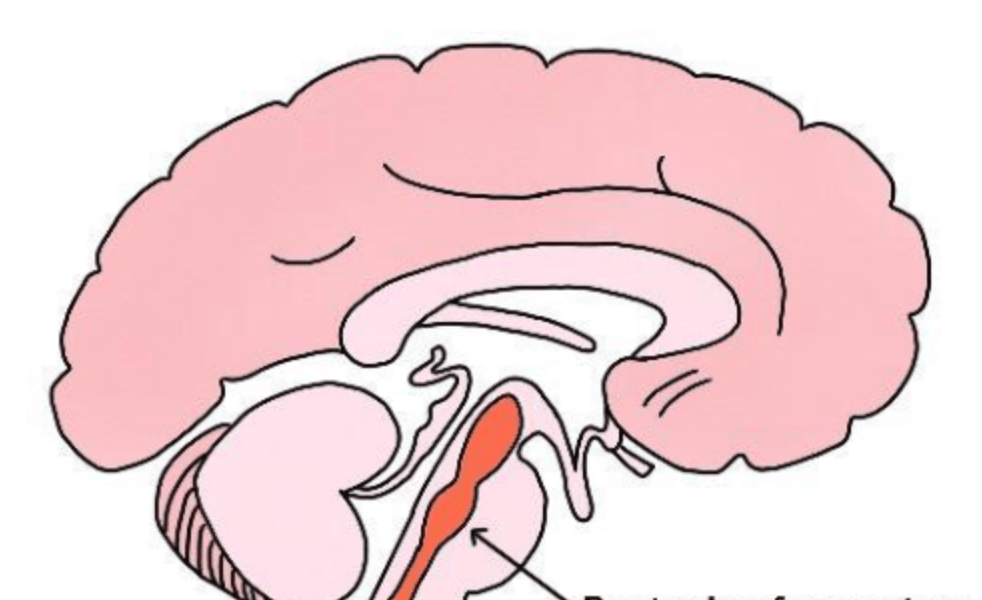 Part of the brain that regulates consciousness, awareness, arousal and sleep-wake cycles.
Part of the brain that regulates consciousness, awareness, arousal and sleep-wake cycles.
What is reticular formation?