The firms in perfect competition are known as:
Price Takers
Which curve represents marginal ATC?
A= MC
B= ATC
C=AVC
The Monopolist will keep producing quantity until
MR=MC
A company utilizes a dynamic pricing strategy on their website, where prices fluctuate based on each individual's browsing behavior and purchase history, effectively charging customers differently according to their presumed willingness to pay. What form of price discrimination does this represent?
First, second or third degree?
First Degree
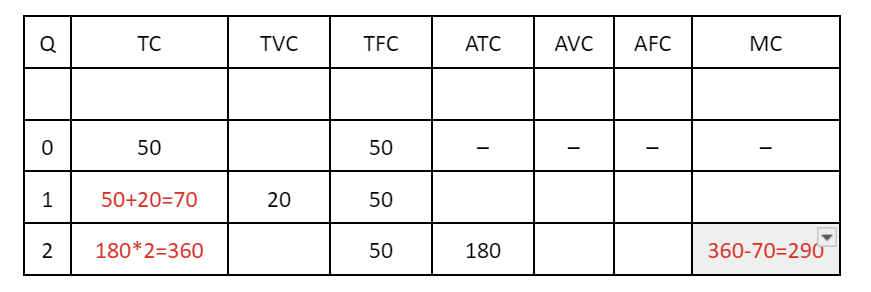
Given the following cost function, what is the total variable costs?
TC(x) = 30x2+5x+100
30x2+5x
Which area reflects deadweight loss in monopoly?
def
Which of the following is a key factor in the formation of a monopoly?
Barriers preventing potential competition from entering the market
An inelastic supply curve for the market
A new invention
All firms are price takers
Barriers preventing potential competition from entering the market
Which of the following describes third-degree discrimination?
A supermarket has a 'buy one, get one free' offer on a brand of pasta.
A clothing retailer charges more for the latest fashion trends compared to out-of-season items.
An amusement park provides a lower entry fee for children under 12 years old.
An electronics store offers a discount on the previous model of a smartphone after the release of a new model.
C
What are the 4 characteristics of perfect competition?
1. price taker
2. Free entry and exit (no barriers)
3. Identical good
4. Many buyers and sellers
In the short run, if a perfectly competitive firm has production costs summarized by the cost curves below, what price range will it produce more than zero units?
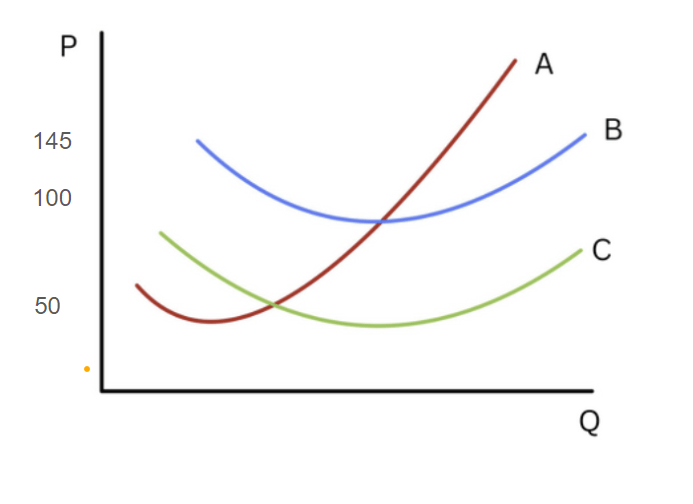 a. 50 +, b. 100+, c. 145+
a. 50 +, b. 100+, c. 145+
Anything above 50. The firm starts losing value but is still operational, which means produces some units.
ne utility company is allowed to provide electricity to a city. This is due to the government only allowing one company to provide this service, This is an example of what type of monopoly?
Natural monopoly
Resource monopoly
Legal monopoly
A patent
Legal monopoly
What's the definition of arbitrage?
Traders can exploit price differences for identical products. Buy low and sell high especially due to low transportation costs between the two markets.
Which costs exist in the long run?
Variable costs
Fixed costs
Variable and Fixed Costs
Variable costs.
In the long run, a firm can decide to change its fixed costs, by moving to a bigger or smaller facility for example (altering the rent costs). The firm has the time and flexibility to adjust all aspects of production to the level of output that it seeks to achieve.
which graph represents long-run equilibrium for a perfectly competitive firm?
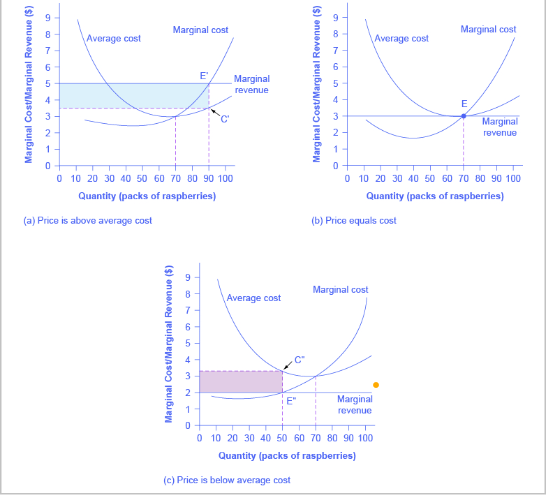
B
Which of these relations is always TRUE for monopolies?
P< MR
P > MR
P > AC
tR < TC
P > MR
What's more beneficial? Sell at high, low, bundle high, boundle low?

Bundle at $22.
Why? 2*22=44 > 15+12=27 which is a single high
but since we also want to incentivize the buyers to go for the deal, we don't want to overprice at $25 for a 2*25= $50 total
CALCULATE A
How much will a monopolist charge if they are setting MC = MR?
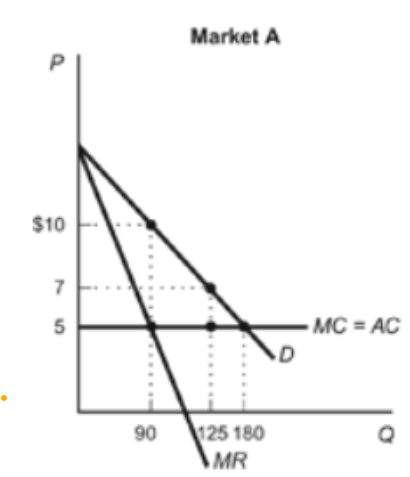
$10
Method: you want to find the point of intersection of MC=MR. Then, you want to go up on the same line (at Q=90) until you get to the Demand curve "D". What's the corresponding price there? 10!
How do monopolies affect economic welfare?
(a) Producer surplus increases at the expense of consumer surplus; no deadweight loss
(b) Consumer surplus increases at the expense of producer surplus; no deadweight loss
(c) Producer surplus increases at the expense of consumer surplus; there will be deadweight loss
(d) Consumer surplus increases at the expense of producer surplus; there will be deadweight loss
C
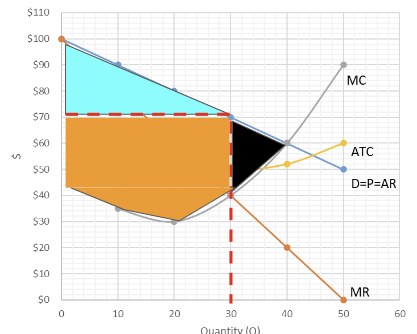
How does perfect price discrimination affect market surplus, when compared to a standard monopoly model?
Deadweight loss does not occur as the firm is receiving all possible gains from trade