ci·a·tions
Tissue makers
FibroBLAST!
-The most prominent cell in the PDL
-Blasts are Builders!
-Clasts are Destroyers!
The most abundant biofilm shaped species in oral cavity that are seen in health, gingivitis, and periodontitis are called:
Rods p 246
-Cocci are least "dangerous" (streptococcus)
-Rods most abundant (Actinomyces, P. gingivalis,P. intermedia, T. forsythia, F. nucleatum)
-Spirochetes of ANUG: T. denticola, T. socranskii, T. pectinovorum, T. vincentii
What type of stress is beneficial for your health?
Acute Stress! Yay!
HbA1C percentage for Grade C in AAP Staging and Grading

A type of periodontal disease that is characterized by changes in color, contour, and consistency of the peri-implant tissues, which can result in reversible tissue damage with homecare habits and professional care.
Peri-mucositis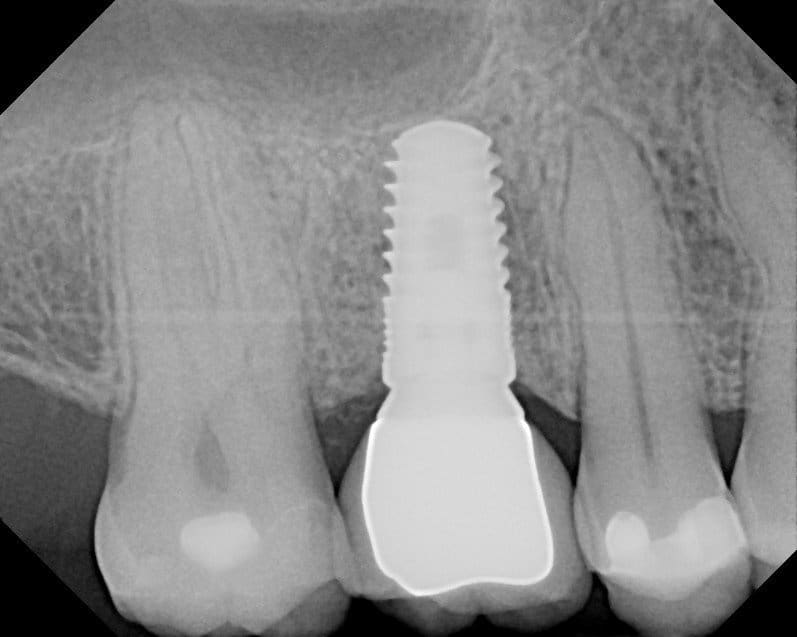
What is the most common local risk factor for periodontitis?
Subgingival calculus formation
-Biofilm ALWAYS attached to calculus
-Radiograph detectable
-Professional removal
The most ideal form of cementum is __________, because it is known as the "original cementum" and promotes new attachment after NSPT procedures.
Acellular cementum p. 42
-Original cementum
-Attaches tooth to bone
-Makes mostly up of Sharpey's fibers
2/3 of root
Interradicular fibers
The gingival fiber group that extends from the periosteum of the alveolar crest into the gingival connective tissue.
Alveologingival fibers p. 37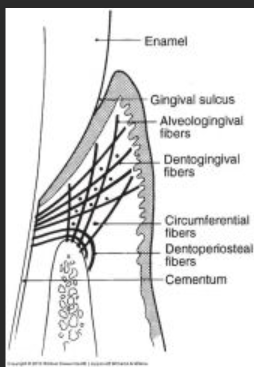
Define the cells of the PDL are capable of:
--Remodeling bone _________
--Breakdown of bone ________
--Cementum formation________
--Remodeling bone OSTEOBLASTS
--Breakdown of bone OSTEOCLASTS
--Cementum formation CEMENTOBLASTS
What Stage of Biofilm Formation does dispersal of microbes from the biofilm colony occur?
Stage 5 p. 250
-then starts process all over again
-Mushroom shaped
-Cell-to-cell communication
Is a form of gingivitis exaggerated by estrogen and progesterone, and has an increase risk of pyogenic granuloma.
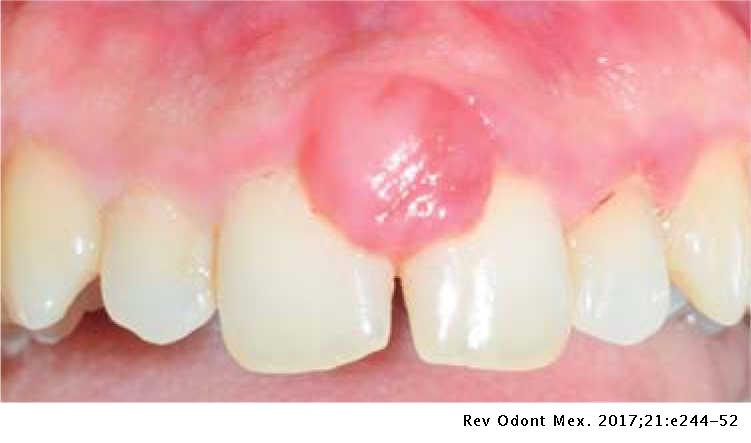
Pregnancy-gingivitis
-P. intermedia
-C. rectus
-gingivitis before pregnancy
What is Sequestrum?
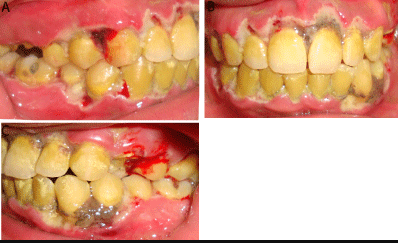
Necrotizing Periodontal Diseases:
Fetid odor
Hypersalivation
Ulcerated tissue, spontaneous bleeding
Death of the periodontium: BONE, tissues
Malaise, PAIN, fever, swollen lymph nodes
Fetid odor
Mineralized connective tissue that covers the root of the tooth.
Cementum (P. 12)
-Gives attachment to collagen fibers
-Cementum --> Sharpey Fibers --> PDL
-No blood supply or nutrients...gets it from PDL
1. What type of risk factor is presented by the arrows on the image below?
2. Estimate the % of RBL: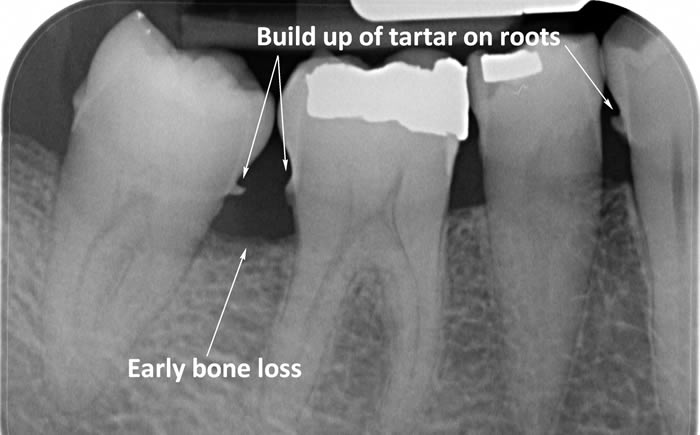
1. Local risk factors
2. 25% range
Ascorbic-Acid Deficiency Gingivitis can be remedied by which water-soluble vitamin?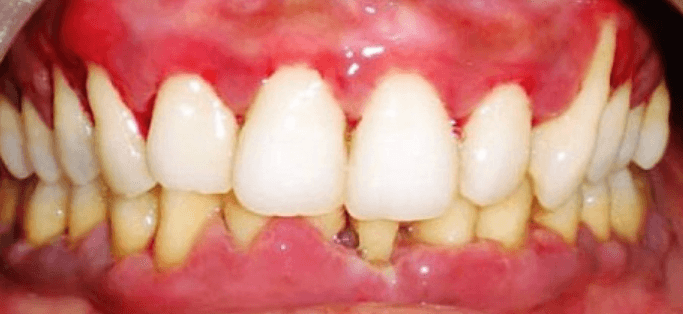
Vitamin C P. 370
-Cures Scurvy
-Water soluble
Epithelial cells that form the outer layer of the free and attached gingiva.
Oral Epithelium p. 33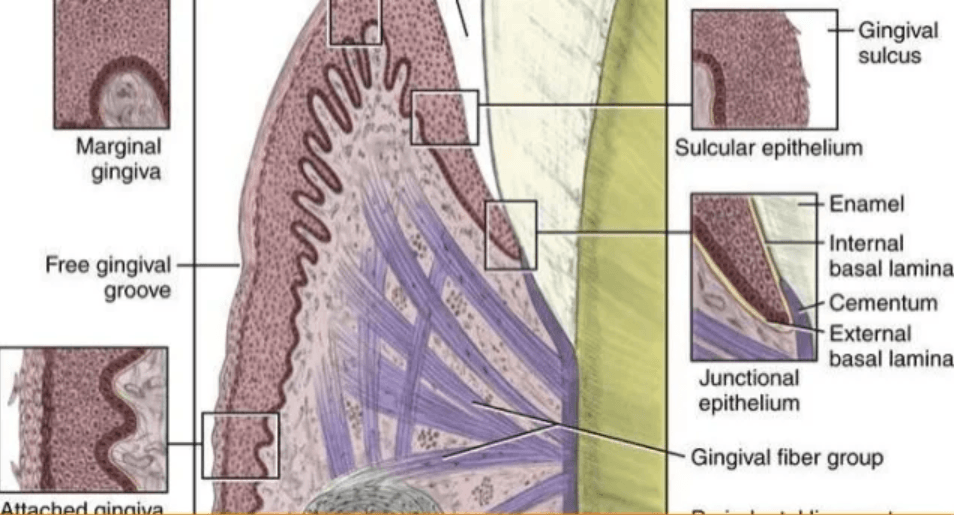
Obesity is related to a marked increase in plaque biofilm accumulation, attachment loss, BOP, deep pockets, and an increase in the proportion of which biofilm bacterium?
1) Tannerella forsythia
2) Streptococcus mutans
3) Candida albicans
T. forsythia p. 366
together with Porphyromonas gingivalis and Treponema denticola are primary pathogens in periodontitis
And, Aa...
The fluid that flows into the sulcus from adjacent connective tissue, slight in health and presence increases in inflammation.
Gingival Crevicular Fluid p. 425
CT-->PD
Houses Collagenase-->breakdown of collagen
Within minutes after cleaning, a film forms over the tooth surface known as ____________.
Acquired pellicle p. 247-248
-salivary glycoproteins
-free floating (platonik)
-Motile bacteria use flagella do overcome hydrodynamic fluid forces

What is the white formation on the attached gingiva with this patient experiencing Necrotizing Periodontitis?
Pseudomembrane
-Wipeable, ulcerated CT exposed
Bacteria: fusiform bacillus (rods that are motile) and spirochetes!
How many call layers are found in Oral Epithelium?
4 Layers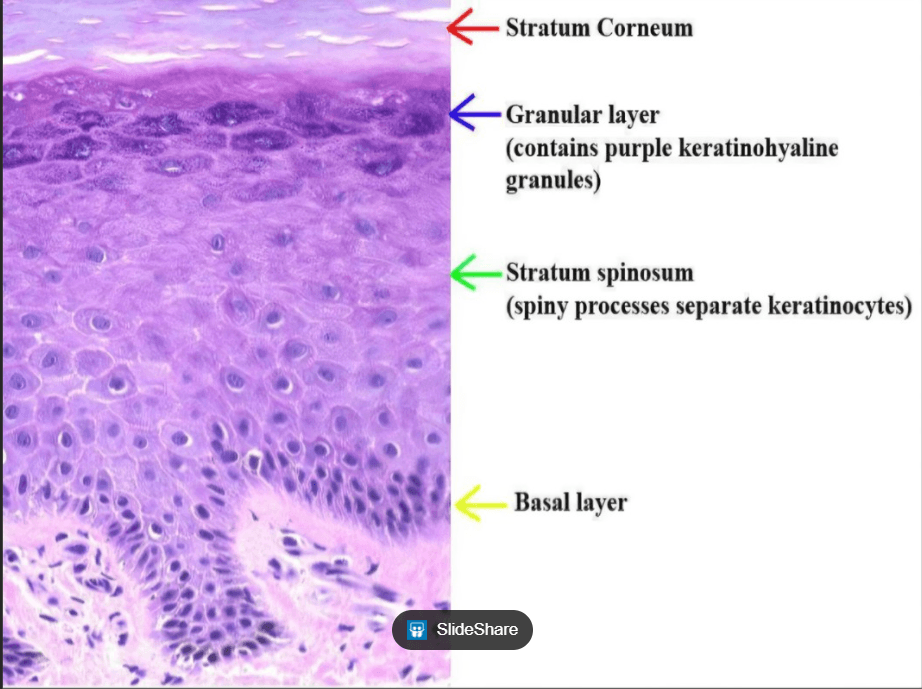
Oral mucosa consists of two layers, the surface stratified squamous epithelium and the deeper lamina propria. In keratinized oral mucosa, the epithelium consists of four layers:
- Stratum corneum (keratinized layer)
- Stratum granulosum (granular layer)
- Stratum spinosum (prickle layer)
- Stratum basale (basal layer)
Describe the tissue listed below.
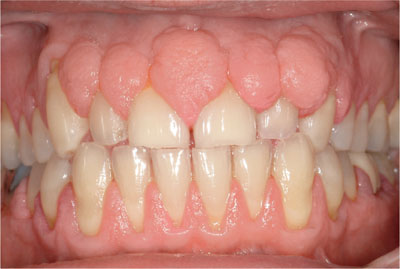
Gingival overgrowth
Gingival hyperplasia, medication-induced
Pallor
Fibrotic
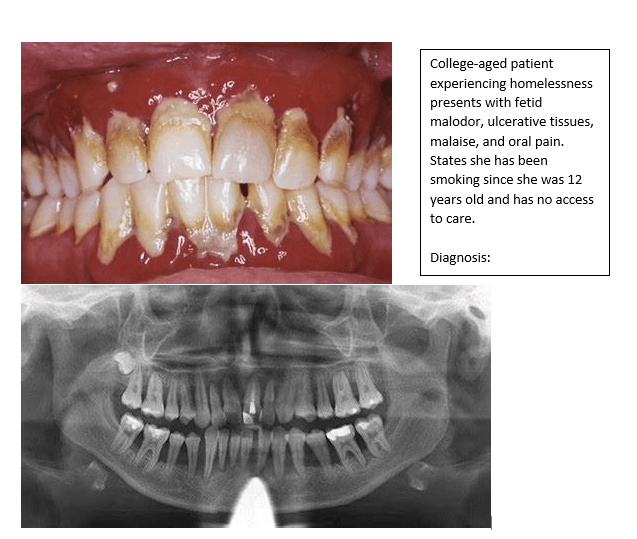
NUP
-Gingival descriptors:
-Risk Factors:
-Treatment:
A crown margin that is closer to 2 mm to the crest of the alveolar bone can result in resorption of alveolar bone, is called ______________ violation.
Biologic Width
-iatrophic from DDS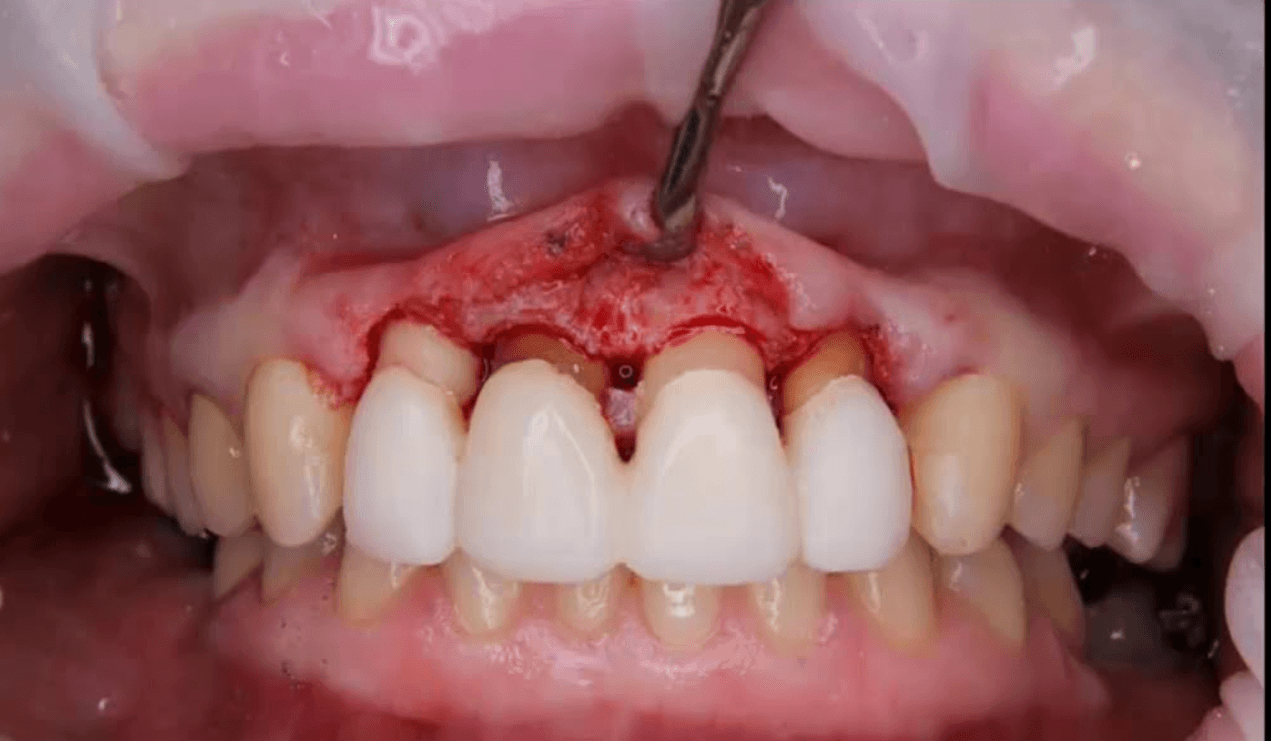
_____________ epithelium faces the tooth surface without being in contact with the tooth surface.
Sulcular P. 29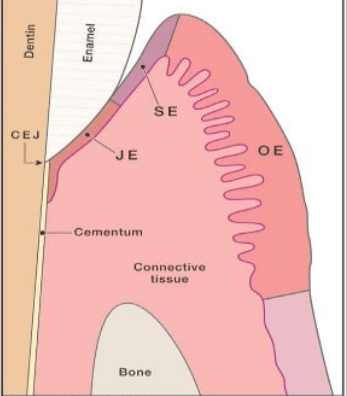
In the absence of disease, Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) facilitate in normal turnover of the periodontal tissue matrix. Increased MMP levels cause extensive _______ destruction of the periodontal tissues.
Collagen P 284
-Without collagen, tissues of gingiva, PDL, and supporting alveolar bone degrade
1. Localized, painful, rapidly expanding lesion that involves marginal or interdental papilla and does not involve the underlying periodontium
2. Localized accumulations of pus within the wall of a periodontal pocket
3. Occurs around a partially erupted tooth.
4. Results from pulp infections
1. Gingival
2. Periodontal
3. Periocornitis
4. Periapical
Bacteria: S. viridans
P. gingivalis, P. intermedia, F. nucleatum
Tx: debridement, drainage, systemic antibiotics, perio surgery, endo surgery
Bacterial biofilm, Identify the characteristics:
Make a column for HEALTH vs DISEASE
Anaerobic cocci P. gingivalis
Gram - Blue Stained Streptococci
Gram + spirochetes T. denticola
Supra. plaque S. Mitis Red stained
Rods Aerobic A. odontolyticus
flagella Red stained T. forsythia
Non-motile Sub. plaque Motile
HEALTH: Gram +, Aerobic, Non-motile, cocci, RODS, S. mitis, Streptococci, Blue/purple, supra plaque
Disease: Gram -, Anaerobic, Motile, RODS, spirochetes, T. denticola, T. forsythia, P. gingivalis, Sub plaque, pink stained, Flagella
Adverse pregnancy outcomes that have been associated with periodontitis include preterm birth, low birth weight, and _____________.
pre-eclampsia p. 761
-#1 cause of neonatal death, PDD is modest association.
-Additional risk factors: tobacco smoke, alcohol use, obesity, and DM
What type of bony defects are ideal for bone grafting procedures for periodontal regeneration?
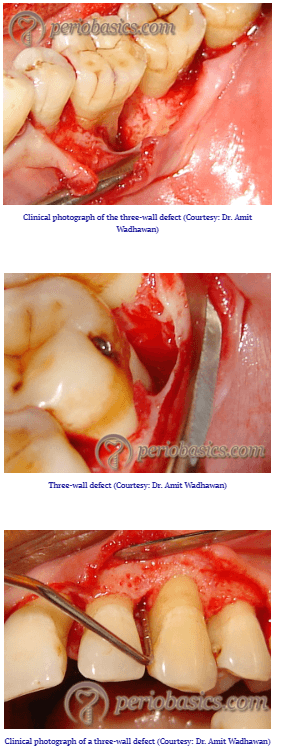
Used in INFRABONY defects and Class II furcations!
Autografts - Donor bone from self (tori, max. tuberosity, hip, sternum)
Allografts - another person of the same species
Alloplasts - synthetic bone materials (hydroxyapatite or ceramics)
Xenografts - bovine, porcine
What is dehiscence?
Self-inflicted
Orthodontics
Anatomy
Occlusion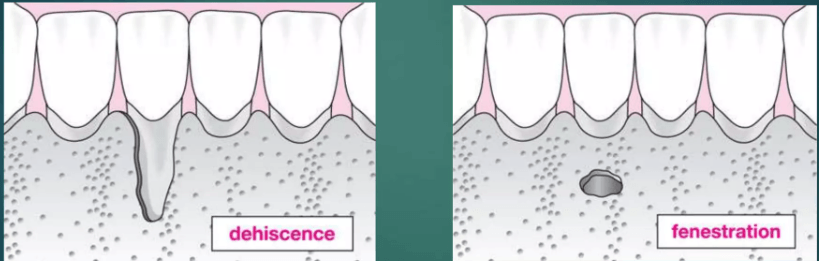
List three local risk factors in this image: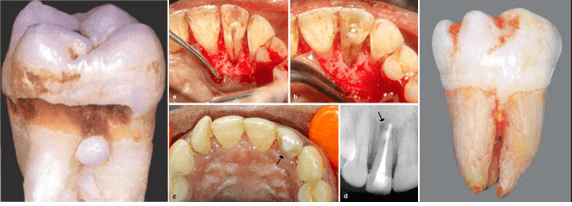
Enamel Pearl
Palatogingival Groove (Most prominent on??)
Cervical Enamel Projections
True or False.
1) Second hand smoke does not put patients at risk for periodontal disease than those who do not smoke.
2) Waterpipe smoking is just as detrimental as tobacco smoking, and contains 40x more nicotine than cigarettes.
1) False. It does!
2) True. Don't do it!
What is the largest PDL fiber group that extends coronally to the bone, withstanding masticatory stress in vertical direction.
Oblique fiber group
What proinflammatory cytokines are released from adipose tissue?
IL-1, IL-6, TNF-alpha p. 366
With adipokines, reactive oxygen species all affect PDD directly
PMNs can move through capillary walls and into the tissue. They are attracted to bacteria by a process called ___________.
Chemotaxis P. 266
-PMNs are short lived cells, and part of the "first responders" with Mast Cells and Macrophages
-PMNs are AKA Neutrophils, a leukocyte
Protective substance that that protects biofilm microbes from phagocytosis and antibiotic treatments.
Extracellular Protective Matrix p.248
-Phagocytosis - engulfing
-Results chronic diseases like periodontitis
List the 10 Periodontal and Oral Manifestations of HIV infections.
P 321
Hairy Leukoplakia -->UNIQUE!
candidiasis --> FUNGAL!
herpes labialis
recurrent intraoral herpes simplex
herpes zoster
recurrent aphthous ulcers --> OUCH!
Kaposi Sarcoma --> UNIQUE!
Necrotizing PDDs
Linear Gingival Erythema --> 2-3MM band, intense erythema in free gingiva, exaggerated
Periodontitis
What is the disorder characterized by the presence of abnormally few numbers of neutrophils in the blood, leading to increased susceptibility to infection?
Neutropenia P. 322
-Higher plaque scores, gingival bleeding, inflammation, and alveolar bone loss reported
-Increase risk of infection in general...
- PMNs = Neutrophils = RAPID RESPONDERS
-Cyclic Neutropenia = congenital
- Associated with leukemia, drug-induced, radiation-induced, idiopathic (unknown)
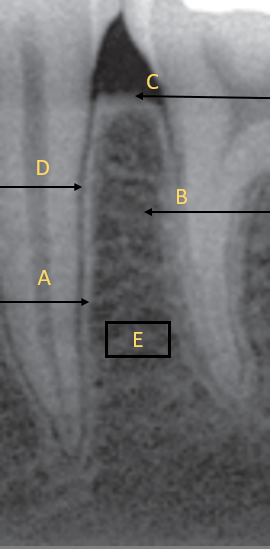
A: Lamina dura
B: Cancellous bone
C: Alveolar Crest
D: PDL
E: Bone Marrow (blood vessels, nerves!)
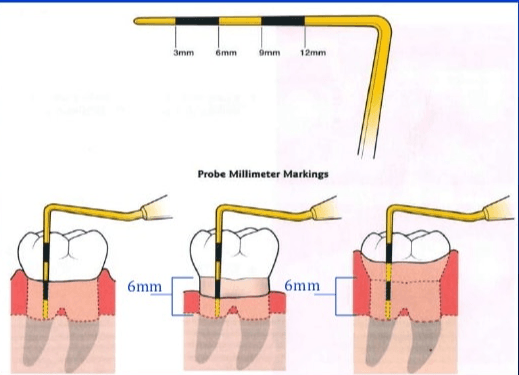
How do you measure CAL?
_____________ occlusal forces result from tooth-to-tooth contact when not in the act of eating.
Parafunctional occlusal forces p. 361
-Clenching/bruxism
Functional occlusal forces - mastication
Primary Occlusal forces?
Secondary Occlusal forces?
What bacteria are considered "Red Complex"
Name a bacterium binds Primary and Secondary colonizers?
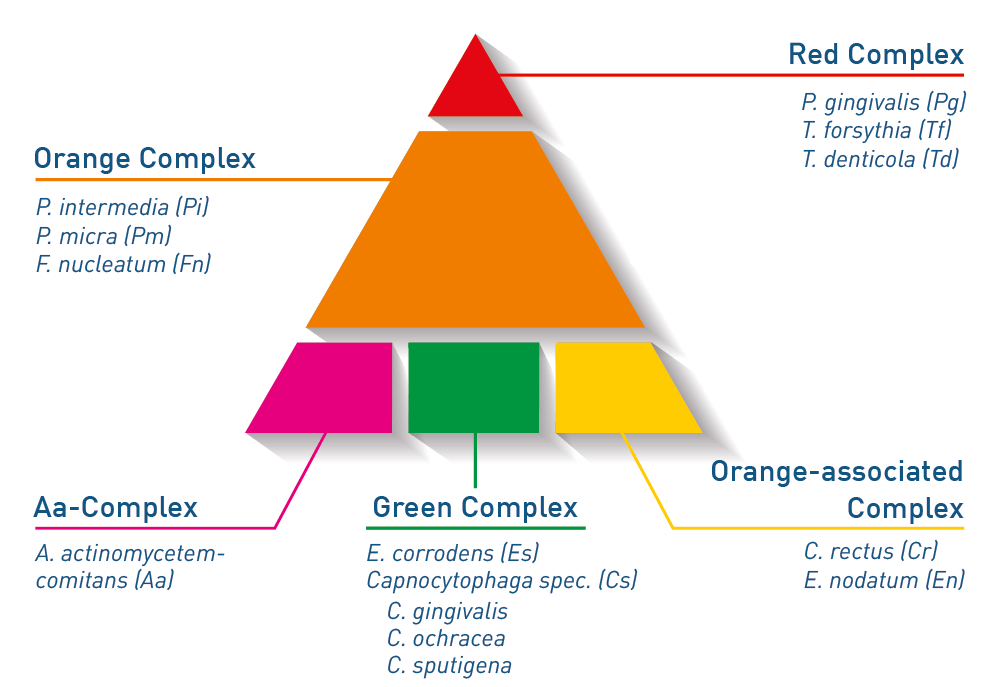 P. gingivalis
P. gingivalis
T. forsythia
T. denticola
Aa is not good either
P. intermedia in pregnancy gingivitis
The double-ended sticky tape? F. nucleatum
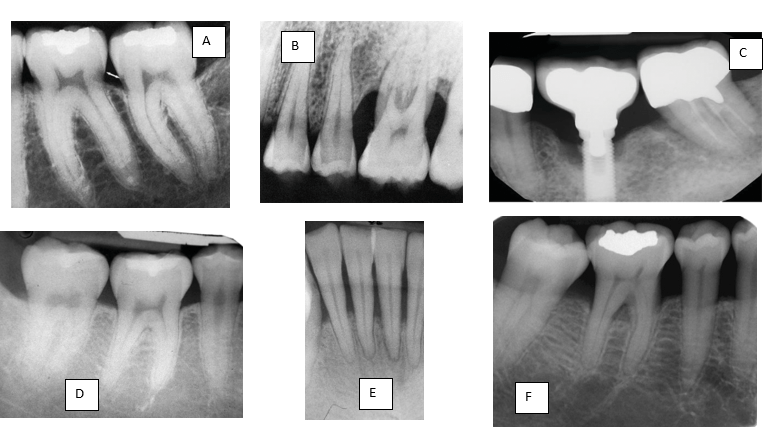
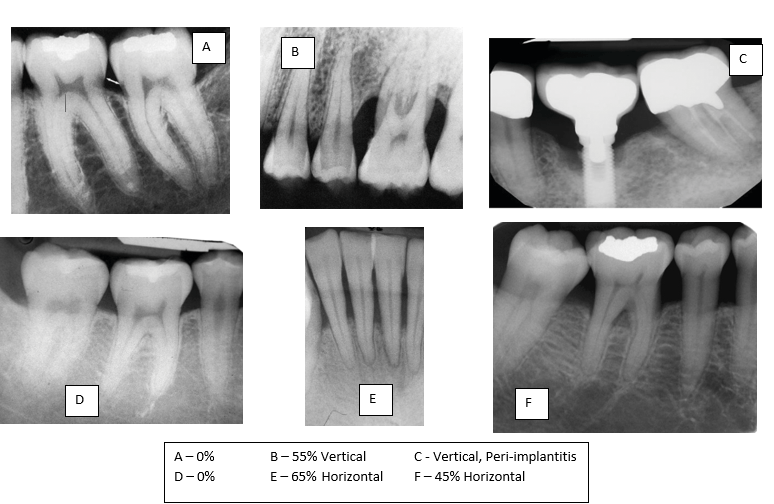
Two early radiographic signs of periodontitis are crestal irregularities and triangulation of the periodontal ligament space - as well as bone loss levels. Label the type of bone loss exhibited in the photographs below, including your estimated RBL % (or implant condition).