A patient is admitted with severe diarrhea and vomiting. Which electrolyte imbalance is the patient most at risk for developing?
*** Bonus Points ***
What is this electrolytes normal range?
What is Hypokalemia
Rationale: Severe diarrhea and vomiting can lead to excessive potassium loss, resulting in hypokalemia
This is when body fluid are located in excess within the blood vessels and begins to accumulate in the tissues. Ex: peripheral edema, acites, end-stage renal disease
What is Fluid volume excess.
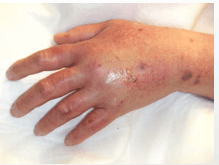
This common IV complication is known as:
What is infiltration?
This category of patients in triage is prioritized for care because their injuries are life-threatening but survivable with immediate intervention.
What is "red (immediate)"?
The Red category represents patients who need immediate care to save their lives, such as those with compromised airways, severe bleeding, or shock.
An arterial blood gas report indicates the client’s pH is 7.25, PCO 2 is 35 mm Hg, and HCO 3 is 20 mEq/L. Which disturbance would the nurse identify based on these results?
What is Partially Compensated Metabolic Acidosis
A nurse is caring for a patient with hyperkalemia. What assessment finding should the nurse expect to observe?
A) Muscle cramps
B) Increased urination
C) Cardiac dysrhythmias
D) Excessive thirst
Cardiac dysrhythmias
Rationale: Hyperkalemia can cause changes in the electrical conduction of the heart, leading to potentially life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias.
This is when the body is lacking fluid adequate levels of fluid within the blood vessels. Ex: dehydration, hemorrhage
What is Fluid volume deficit
This results from an infiltration of a vesicant, such as chemotherapy drugs. 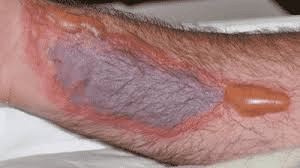
What is extravasation?
During a disaster, this nursing role involves rapidly assessing patients, assigning triage categories, and determining care priorities.
What is the "Triage Nurse"?
Rationale:
Triage nurses are responsible for initial patient assessments to ensure resources are allocated efficiently, particularly in mass casualty situations.
An arterial blood gas report indicates the client’s pH is 7.59, PCO2 is 27 mm Hg, and HCO3 is 17 mEq/L. Which disturbance would the nurse identify based on these results?
What is Partially Compensated Respiratory Alkalosis
A patient is admitted with severe pancreatitis and is found to have a serum calcium level of 7.2 mg/dL. Which intervention should the nurse anticipate for this patient?
A) Administer oral calcium supplements
B) Initiate intravenous calcium gluconate
C) Encourage increased dietary calcium intake
D) Provide supplemental vitamin D
Initiate intravenous calcium gluconate
Rationale: A serum calcium level of 7.2 mg/dL indicates hypocalcemia, which in severe cases requires prompt IV calcium replacement to prevent complications.
D5 0.45 NS is this type of fluid? What must be monitored while it is prescribed?
What is hypotonic and can be prescribed for mild dehydration and provide a source of calories. Blood glucose levels must be monitored.
Patient's IV is red, warm, and tender at the IV insertion site. Name this. 
What is Phlebitis?
This triage color is given to patients who have severe injuries or conditions that are incompatible with survival or require resources unavailable in a disaster situation.
What is the "Black (Expectant)" category?
Rationale:
Black is used for patients who are unlikely to survive given the resource limitations, allowing focus on those with a better prognosis.
An arterial blood gas report indicates the client’s pH is 7.38, PCO2 is 60 mm Hg, and HCO3 is 35 mEq/L. Which disturbance would the nurse identify based on these results?
What is Fully Compensated Respiratory Acidosis
A patient is admitted with severe vomiting and diarrhea. Which electrolyte imbalance is the priority to assess for?
A) Hypernatremia
B) Hyponatremia
C) Hyperkalemia
D) Hypokalemia
What is Hyponatremia
Rationale: Severe vomiting and diarrhea can lead to significant fluid and sodium losses, resulting in hyponatremia or low serum sodium levels.
This solution type moves fluid & electrolytes out of the cells, causing them to crenate (shrink). It is used to treat severe hyponatremia.
** Bonus 100 Points**
Name another condition it is used to treat?
What is hypotonic solutions?
Other uses:
Hypocholoremia - replaces chloride
Constipation - sodium phosphate enemas stimulate the bowel
The nurse is removing peripheral IV and must observe this.

** BONUS 100 points***
What is the potential complication?
What is intactness of tip?
Sepsis from foreign body in vascular space - blood stream infection
Patients in this triage color category have serious but not immediately life-threatening injuries that can wait for treatment until resources are available.
What is the "Yellow (Delayed)" category?
Rationale:
Yellow is assigned to patients whose conditions are stable for now but require eventual treatment, such as fractures or moderate head injuries.
An arterial blood gas report indicates the client’s pH is 7.45, PCO2 is 55 mm Hg, and HCO3 is 32 mEq/L. Which disturbance would the nurse identify based on these results?
What is Fully Compensated Metabolic Alkalosis
A patient with chronic alcohol use disorder is admitted with muscle cramps and tremors. Which electrolyte imbalance is the patient most likely experiencing?
A) Hypermagnesemia
B) Hypomagnesemia
C) Hypercalcemia
D) Hyperkalemia
What is Hypomagnesemia
Rationale: Chronic alcohol use can lead to poor dietary intake and malabsorption of magnesium, resulting in hypomagnesemia. Muscle cramps and tremors are common symptoms.
What is isotonic solutions and 5% Dextrose in Normal Saline
Name 4 physical assessment findings that may be affected by the administration of IV solutions that the nurse should assess.
What is: body weight, vitals, lung sounds, neck veins, cap refill, dependent edema, oral mucous membrane, LOC, urine output, IV site
This triage color is assigned to patients who are ambulatory and have minor injuries that do not require immediate medical attention.
*** BONUS POINTS***
How makes this category of patient most effective in a disaster situation?
What is the "Green (Minor)" category?
Rationale:
The Green category applies to "walking wounded" patients whose injuries are not life-threatening and can wait for care. Can often assist in care of others ie sitting with lost child, holding pressure on a wound.
A patient is admitted with severe pneumonia and arterial blood gas results show: pH 7.27, PaCO2 65 mmHg, HCO3 30 mEq/L. What acid-base imbalance is present, and what is the compensatory mechanism?
compensated respiratory acidosis, compensated by kidneys