Damage to the L2 nerve root would cause weakness in this joint movement
What is hip flexion?
These two nerves are comprised from nerve roots C5 and C6
What are the axilla and the musculocutaneous nerves?
Damage to this LE peripheral nerve will result in weak hip flexion and knee extension
What is the femoral nerve?
This ULNT is assessing irritability of this UE nerve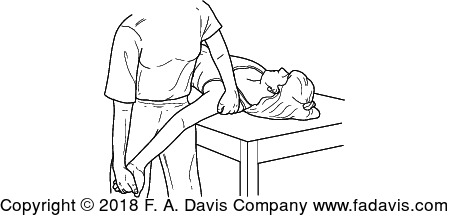
What is the median nerve?
This level of Seddon's nerve injury is characterized by: •segmental demyelination, •Action potentials slowed or blocked, •No muscle atrophy, just temporary sensory problems, •Result of mild ischemia, •Recovery usually complete
What is neuropraxia?
Reduced light touch to the deltoid region indicates dysfunction at this nerve root level
What is C5?
Damage to this nerve will likely result in weak elbow flexion and supination
What is the musculocutaneous nerve?
This LE peripheral nerve can be damaged during labor from the weight of the uterus and may result in weak hip adductors
What is the obturator nerve?
This ULNT is assessing the irritability of which nerve?
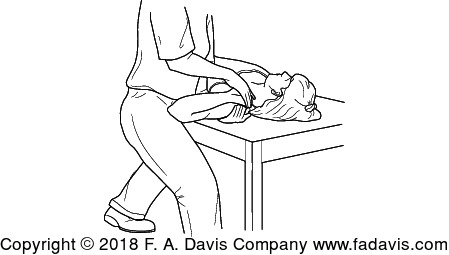
What is the ulnar nerve?
What is the return to function phase or chronic phase?
Compression of the T1 nerve root will likely cause weakness of this joint motion
What is finger abduction?
This nerve can be damaged as it becomes entrapped within the cubital tunnel, or at the tunnel of Guyon
What is the ulnar nerve?
This is the largest nerve in the body
What is the sciatic nerve?
This ULNT is assessing the irritability of which nerve?

What is the sciatic nerve?
Name one desensitization exercise that can be used to facilitate return of normal sensory processing for injured nerves
What is textures, vibration, etc.
Decreased sensation along the index and middle finger would likely correlate with weakness of what joint motion?
What is elbow extension and wrist flexion?
Damage to this nerve will result in carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms
What is the median nerve?
This nerve may become damaged as it passes around the fibular neck, causing weakness in both ankle DF and EVER
What is the common fibular nerve (or common peroneal nerve)?
This ULNT is assessing the irritability of what nerve?

What is the femoral nerve?
What is the FIRST symptom of return of nerve function?
What is pain and hypersensitivity?
What is ankle dorsiflexion?
Damage to this nerve up near the glenohumeral joint will result in weak elbow extension
What is the radial nerve?
This nerve passes under the posterior medial malleolus before it enters the sole of the foot and splits into two separate nerves
What is the posterior tibial nerve?
This ULNT is assessing the irritability of what nerve?
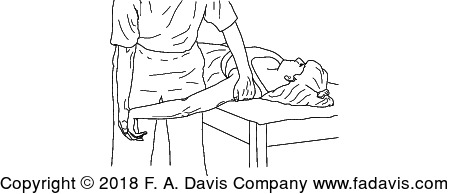
What is the radial nerve?
This condition is marked by marked pain and hyperesthesia that does not correlate to the original level of injury, decreased motor function, and autonomic nervous system changes
What is CRPS? complex regional pain syndrome