This federal agency is in charge of ensuring the U.S. food supply is "safe, wholesome, sanitary, and properly labeled."
Who is the Food and Drug Administration (FDA)?
** Be able to differentiate the different food regulatory agencies, p. 442 Table 12-1.
Dates on food packages do not reflect food safety but alert to degree of freshness. This is the last date the food is at its highest quality.
What is best if used by?
*be able to differentiate best if used by; sell by; expiration date, & pack date.
Consumers should always follow this food safety label to minimize bacterial growth & cross contamination, especially with poultry.
What is the safe handling instructions?
 *RAW MEATS/POULTY (PROTEINS) REQUIRE SPECIAL HANDLING. IN STORES ARE GROUPED TOGETHER IN MOIST, NUTRIENT RICH ENVIRONMENTS=GROW MICROORGANISMS
*RAW MEATS/POULTY (PROTEINS) REQUIRE SPECIAL HANDLING. IN STORES ARE GROUPED TOGETHER IN MOIST, NUTRIENT RICH ENVIRONMENTS=GROW MICROORGANISMS
Honey should never be fed to infants under one year due to immature immune systems and their inability to fight off this bacterial spore.
What is clostridium botulinum?
* remember this can cause botulism- deadly toxin
This type of juice should be avoided in infants, children, and the elderly, as well as those with weakened immune systems due to risk of multiplying bacteria.
What is unpasteurized/raw juices?
* refrigerated pasteurized juices, reconstituted frozen juices, & shelf stable juices are generally safe.
Bacteria produce these poisonous chemicals as they multiply. These toxins can be absorbed into the tissues and cause harm from mild stomach pain to death. E.coli (escherichia coli) & salmonella are examples.
What are enterotoxins?
E. coli can cause severe bloody diarrhea & client present with severe abdominal cramps. Can lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome: lead to kidney and organ failure. Prevention includes sanitary food handling methods, cooking beef thoroughly, drinking treated water.
Salmonella- causes ever, V/D & can be fatal. prevention sanitary food handling, cooking foods (i.e. eggs/meat/shrimp) thoroughly, refrigerating promptly.
Staphlyococcus aureus- - cause N/V/D, abdominal cramps, fever. Prevention: sanitary food handling, cook thoroughly, refrigerate promptly. * most common cause of food intoxication!
Legislation developed to improve prevention of foodborne illnesses & support investigation into outbreaks. This law supports human and pet food supply, and also includes a Produce Safety Rule to regulate farmers.
What is Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA)?
* Also require verification that imported foods have been produced and handled in keeping with U.S. standards.
Ground meats should be cooked to this temperature and consumers should utilize food thermometers to check this, not visual inspections.
What is well done (internal temp. 160F)?
These are recommendations for safe handling picnic and leftovers. Name two.
What is:
-choosing foods safe without refrigeration (crackers)
-Thermal lunch bags
Well aged chesses
Freeze beverages
chill salads made with mayo- mayo is ok b/c acidity but chopped ingredients harbor bacteria.
Refrigerate within 2 hours; shallow 2 inch containers (chill quicker); toss at 4 days unless stuffying or grave- 2 days...
The use of these can protect crops from insect damage and increase potential yield per acre, but benefits should be weighed against risks.
What are pesticides (agricultural pesticides)?
* Pesticides only cause harm in adult humans at high doses- unlikely to occur.
Drawbacks:
accumulate in food chain; kill valuable pollinators (bees); kill pests (birds insects); pollute water/soil/air.
This fatal foodborne illness comes from a toxin produced by clostridium botulinum bacterium that can grow in anaerobic conditions. Difficulty breathing or swallowing, double vision, and weak muscles & paralysis can occur and requires immediate medical attention.
What is botulism.
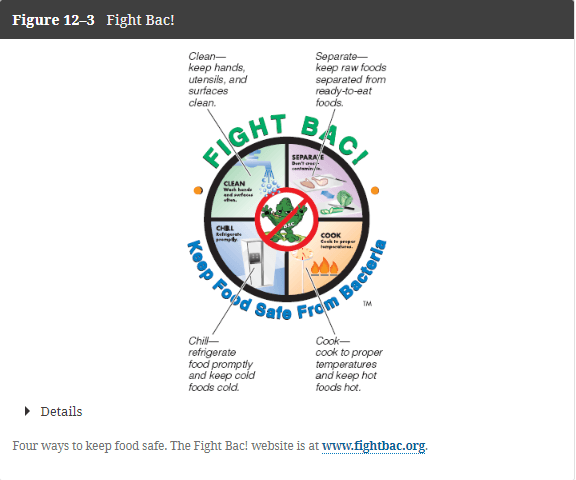
These are four practices to help prevent contaminating food. Additional recommendations include tossing food with a "off" odor or taste. "When is doubt, throw it out."
p. 447, *pathogens grow if there are nutrients available (i.e. glucose); moist & warm [40-140F] environment- a temperature greater than 140 F kills most harmful organisms.
This food accounts for 30% of the U.S. Salmonella infections. This is one reason this item is washed and sanitized before packing, while some being pasteurized. Consumers should always cook this item thoroughly and never eat raw.
What are eggs?
This process can improve the quality/safety of food and uses ionizing radiation with gamma rays to reduce insect infestation or microbial contamination. AKA "cold pasteurization"
What is irradiation?
Additional info on irradiation:
- does not sterilize
-approved doses does not change taste, texture, appearance
-some vitamins can be destroyed but no greater than other methods
-biggest concern with radiation is workers and their use of radioactive materials- food industries address safeguards.
These are used to promote growth or increase milk production and are FDA approved. Overuse in humans can pose a serious threat to treatment of infections in the future.
What are antibiotics?
antibiotic resistant bacteria develops
* hormones are also used in meat/milk: growth hormone
* arsenic is found in the earths crust but also administered in small amounts to poultry flocs to kill parasites.
These are our most vulnerable populations (5) harmed from foodborne illnesses.
*name all five
Who are pregnant women, infants, toddlers, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems.
Cleaning, and clean hands is one practice that consumers should remember. This is how to wash your hands: water, soap, lather, scrub for this long_____,rinse, and dry!
What is 20 seconds or singing "Happy Birthday" twice?
Consumption of this raw protein is thought to be safe, however dangers are increasing. Only cooking will kill all worm eggs, bacteria and other microorganisms. This item is often made from acidified rice and held at cold temperatures to help decrease the risk.
What is seafood/sushi?
Another term for vacuum packaging that reduces oxygen, inhibits growth of oxygen dependent microbes, prevents discoloration of cut vegetables & fruit, prevents spoilage of fats, and slows ripening of fruits/vegetables.
What is Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP)?
This heavy metal has been found in waters where aquatic bacteria metabolized it into a nerve poison and people who at these fish were ill especially those pregnant, lactating, or in childhood.
What is mercury/methylmercury?
This process is used by dairy farmers to kill pathogens in milk. A flaw in this system can lead to outbreaks of illnesses.
What is pasteurization?
* treatment of milk, juices, or eggs with heat high enough to kill certain pathogens commonly transmitted through foods- not the same as sterilization.
pasteurized products still retain bacteria that can cause spoilage.
These are the three additional practices consumers should remember to protect themselves from foodborne illnesses.
What is:
1. Keep raw foods separated to prevent cross contamination ( separate cutting boards; clean hands between handling; use clean dishes throughout cooking...)
2. Cook foods long enough to reach a safe internal temperature. * Foods kept at 140F until served; meat well done to decrease risk; foods should be refrigerated within two hours at max- or throw it out!
3. Chill- cold foods should stay cold!* safe refrigerator temp: 40F & freezer 0F; thawing meat in a refrigerator; marinate in refirgerator
It is recommended to scrub vegetables with a brush to dislodge bacteria and rinse with vinegar to cut through/remove this that car harbor microbes.
What is biofilm?
This natural toxin turns potatoes green and should be peeled away or eaten in moderation.
What is solanine?
This additive is a sweetener made from amino acids: phenylalanine & aspartic acid, however should not be given to children with phenylketonuria disease (PKU).
What is aspartame (nutrasweet/equal)? *is found in diet soda
Splenda is sucrose with Cl atoms and isn't digested or absorbed. aspartame is digested and absorbed.
* We discussed BPA previously- recommend to review.
* additional notes: what type of containers should be avoided/not used in the microwave?
avoid: plastic margarine tubs, single use trays. Use glass containers or ceramic or plastic if identified as microwave safe.