Which drugs can be used to tx anxiety?
Drugs that increase GABA (ie BZD) or serotonin (ie buspirone)
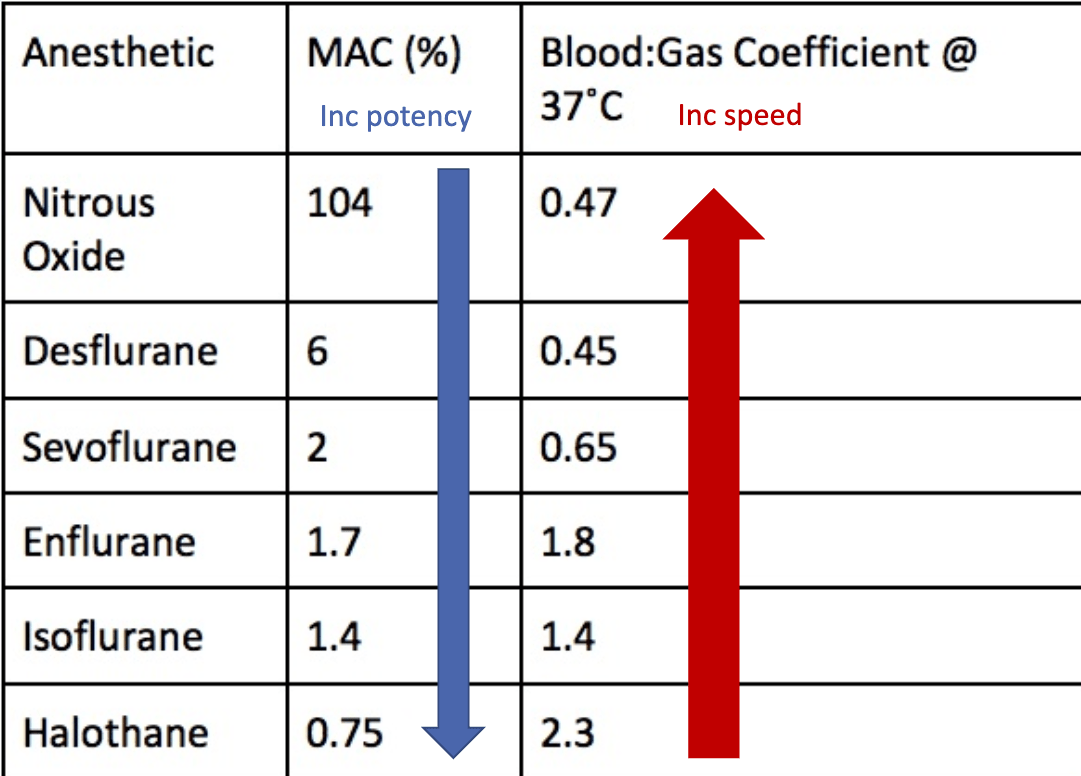
Which anesthetic has a high B:G and a low MAC? What does that mean?
Slow on and off- Low MAC: High B:G → HIGH POTENCY
Takes a while for effect, but longer duration (Halothane, Isoflurane)
Maintain anesthesia because longer-acting (maintenance)
Which drugs are teratogenic?
Phenytoin and Divalproex/valproic acid
Which group of people should not be given sumatotriptan? Why?
Patients with history of MI, CAD, etc (sumatotriptan causes coronary vasoconstriction) and don’t combine with ergots, SSRI’s or MAO inhibitors (it's a 5HT-1DR agonist--serotonin syndrome)
What type of symptom is akinesia in Parkinson Disease?
Negative; Akinesia- blank facial expressions, lack of blinking
Do opioids increase your heart rate?
Nope! They cause vasodilation but no reflex tachycardia since the baroreceptor responses are inhibited.
What are the MOAs of the drugs that reverse rocuronium?
Neostigmine (innactivates AChE) and suggamadex(encapsulates rocuronium in a water-soluble complex and inactivates it)
What are at least 3 signs of an anxiety attack, and which medications can be used to treat it?
Acute symptoms: increased heart rate, sweating, trembling, panic, nausea, shortness of breath
Chronic symptoms: nervousness, restlessness, insomnia
Alprazolam (short-term)
Lorazepam (long-term)
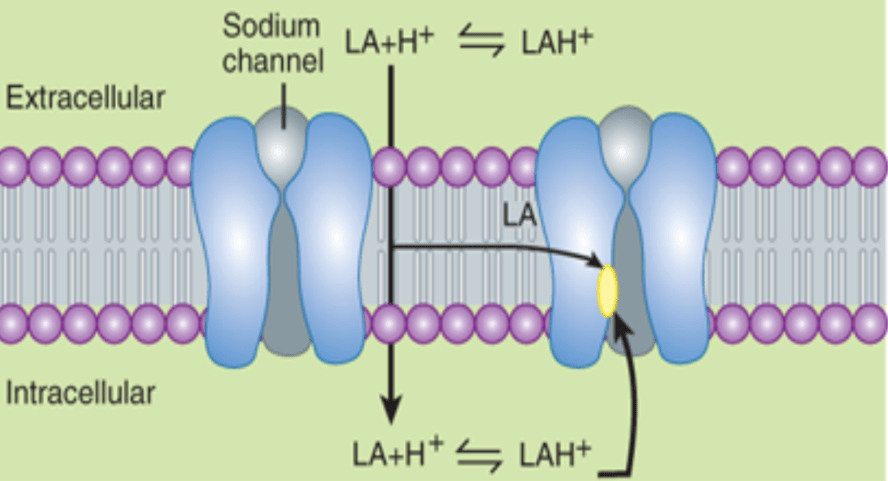
Why do some physicians combine bicarbinate with a local anesthetic? Be specific.
Most local anesthetics are NA+ channel blockers, and they do this by being unionized, so they can pass through the membrane. And once they are in the intracellular part, they become ionized so they do not pass through the membrane again and block the sodium channel.
Local anesthetics are weak bases, and combining them with bicarbinate (a strong base) makes it more likely that the local anesthetic will stay unionized = quicker for the anesthetic to pass through the membrane = quicker for there to be an effect.
Which drugs induce status epilecpticus?
Withdrawal from GABAergics (including use of flumazenil)
Where does ondansetron work in the body?
In area postrema (vomit center) eeeeeYUCK
Which drug is considered an "atypical antidepressant"?
Bupropion - DAT/NET blocker
Used to treat depression and to facilitate smoking cessation.
What do CB1 receptors do?
Inhibition of hippocampus = impaired memory
-Inhibition of signaling in dorsal horn = decreased pain
-Inhibition in area postrema = antinausea
-Inhibition of CNS excitement = anticonvulsant
-Psychosis in susceptible individuals
-Inhibition of pain pathways local and spinal antinociceptive
Before tracheal intubation, a pt is given an IV to cause flaccid paralysis. Now, the patient's body is rigid, hot, and their HR is climbing.
What should the pt be given?
Dantrolene - Prevents the release of Ca2+ ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of skeletal muscle cells to reduce muscle contraction.
Antidote for malignant hyperthermia
A patient follows up in your office after suffering from alcohol withdrawal and experiencing delirium tremens. You give him a 1st line medication, but warn him about the adverse effects.
What are the main AEs you emphasize?
Respiratory depression and tolerance/withdrawal/dependence
-Abrupt withdrawal may cause seizures, agitation, and anxiety!
Soon after being under general anesthesia for a BBL, the pt develops muscle rigidity, fever, and tachycardia. What is the MOA of this drug, and why is it an antidote for this condition?
Dantrolone
A ryanodine receptor antagonist that reduces Ca2+ release, which is needed since the inhaled anesthesia uses Ca2+ to cause these muscle contractions.
A 15-year-old woman comes to the ER with her mom after developing a painful rash on her abdomen and a fever. The pts mother states the symptoms started after the girl took medication to help her focus in class.
What is the MOA of the medication she took?
Blocking the T-type Ca2+ channel current in thalamic neurons (Ethosuximide for absence seizures)
SE: significant GI distress may occur, drowsiness, dizziness, SJS, bone marrow depression
Your veteran pt tells you the new medication for his dreams is working, but "the little guy is too excited" to the point that it's painful.
What is the MOA of the drug you gave him?
Prazosin – alpha 1 AR antagonist
-Used for hypertension, and off-label for BPH and PTSD-associated nightmares
-Blocks smooth muscle contraction (periphery) and trauma-induced hypervigilance in CNS
-AE’s: orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, priapism
EPS: Akathsia, tardive dyskinesia, parkinsonism, and dystonias
AE for conventional antipsychotics (haloperidol and chlorpromazine)
You find someone on the sidewalk barely breathing and losing consciousness. After inspecting them and finding a used needle next to their body, you administer a medication intranasally. When the person wakes up, they immediately become agitated.
Why should you stay?
The t1/2 of naloxone is short, so you’ll have to watch for re-emergence of respiratory depression!
What is one reason why we see the main AEs of the non-depolarizing agents (tobocurarine and rocuronium).
Histamine release
Histamine is a potent vasodilator-->dec venous return-->dec CO-->dec BP-->hypotension
Histamine release causes bonchospasm and itching (minor)
You see someone in Dollar General scratching at their skin and gulping down water. You go into the other aisle and hear a sudden thud. When you go back to the aisle, the person is on the ground, gasping for air! You find a half-empty bottle of a med you remember from your last exam and quickly take action.
What is the class of drug and its antidote?
Z-drugs and flumazenil!
Z-DRUGS
-MOA: GABAA receptor agonists.
-Examples: Zolpidem, Zaleplon, Eszopiclone
-Uses:
• Short term hypnotic (though eszopiclone is indicated by FDA for use > 7 days)
-Reversed with flumazenil (but also be careful of status epilepticus)
A 59-year-old woman is brought into inpatient care to monitor her condition while she's in a coma and under ventilation. After the third month, the pts legs began to swell, and her labs showed high amount of CK in the urine and blood. What is this pt suffering from?
Propofol infusion syndrome – acidosis, rhabdomyolysis, renal failure limits infusion rate in chronic use (e.g., ventilator patients)
A pt comes into your office inquiring about medications she can take for her partial seizures, but she's trying to keep her waist "skinty".
What is the medication and what do you encourage her to do when she takes it?
Topiramate!
Enoucrage fluids because it is partially renally cleared.
A 15-year-old pt sees her psychiatrist because she feels more helpless and useless recently. She has a history of suicidal thoughts and hurting herself. The physician wants to prescribe her a medication, but stops herself because of an AE that is seen in her age group.
What is the group of medications?
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Uses: depression, GAD, PTSD, OCD, panic disorder, PMDD and bulimia.
MAO = Block SERT. Fluoxetine is also 5-HT2C receptor antagonist
Adverse effects: weight gain, sexual dysfunction, nausea (usually remits), insomnia, anxiety, suicidality (boxed warning)
Discontinuation syndrome: dizziness, fatigue, nausea, agitation, insomnia, myalgia, tremor, anxiety.
A 69-year-old woman follows up with you on the new medications you prescribed her. She says she still has her Parkinson's symptoms, and the meds haven't helped at all. You decide to add another medication that will work along with the other two to help her condition.
What is an AE of the new drug?
Serotonin syndrome if combined with serotonergic drugs like SSRI’s!
The pt was already given L-DOPA and carbidopa, so to prevent further degradation in the brain you can prescribe a MAO-B inhibitor
Sasha is trying a new OTC medicine to help with her period cramps. After an hour of having no effect, she takes two more pills. Then, thirty minutes later, she takes two more. Her brother finds her in the bathroom, breathing slowly, in and out of consciousness, and with pinpoint pupils.
List the four possible drugs and their form.
Extended-release PO Morphine, Hydromorphone, Oxycodone, or Oxymorphone.
A 20-year-old woman comes to your office with complaints of "bedroom eyes" and struggling to swallow her food and drinks. You tell her the medication you're prescribing, but she wants you to explain it fully.
How would you explain it?
AChE breaks down ACh-->less muscle contractions/function
Add in neostigmine-->neostigmine blocks AChE-->inc conc and duration of ACh-->improve muscle contractions/functions
A 30-year-old male is brought into the ER by his friends, who found him having a seizure in his room. The resident on call was too busy thinking about the new MJ album and just prescribed him a med. Later, the pt starts screaming in pain while clutching his stomach and vomiting. This lasts for 2 days, then the pt passes.
What is the MOA of the given med?
Barbiturates!
MOA: Increase duration of Cl channel in open state – increase affinity of GABA for GABAA receptor AND have inherent activity in the absence of GABA, causing CNS Depression.
Uses:
• Phenobarbital (C IV) is generally used only as anticonvulsant
• Thiopental (CII) for anesthesia induction
-Barbiturates are CYP450 enzyme INDUCERS causing a lot of drug interactions
-Barbiturates is contraindicated in acute intermittent porphyria
A 70-year-old man comes to the dentist after developing a dull ache in his left molar. The dentist tells him that he has a severe cavity and the tooth needs to be extracted. The pt asks the dentist not to use "that other stuff" when numbing him because it makes his heart race. The dentist agrees and numbs the patient. A few days after the procedure, the dentist receives a call saying the pt is in the hospital because of his liver!
What went wrong?
The pt has either a hepatic disease or reduced hepatic perfusion, and is now suffering from an accumulation of amides (local anesthetic not safe in pts with hepatic diseases).
Also, the "other stuff" the pt is referring to is epinephrine, which slows absorption so the anesthesia doesn't travel throughout the body ie. the liver.
A 30-year-old woman follows-up in your office on her new focal seizure medication. Her condition has improved! Success! She then tells you that she is trying for a baby with her partner and the stress is showing in her bleeding gums. This news makes your eyes nearly come out your skull, and you quickly tell her to dioscontinue the medication.
Explain the metabolism of the medication.
The drug the pt was taking is phenytoin.
It starts as first order metabolism, then turns into zero order metabolism.
You're a resident doctor making your rounds in the ICU. When you walk in to see your first pt (PMH of anxiety and depression), you notice their eyes are moving rapidly, they're diaphoretic, and have hyperthermia. You find out that one of the patients' friends gave them something that was prescribed to them for depression.
What is the name of the drug from this group that the friend gave the pt?
Phenelzine, MAO-A selective inhibitor
The pt is suffering from serotonin syndrome.
A pt follows up on her new medication in your office. She is lively and excited to talk to others again, and doesn't have anymore "outbursts" or "visions".
What do you do to check for a certain AE?
This AE is neuroleptic malignant syndrome, specifically, lead pipe rigidity.
You can try flexing the pts forearm to see how easy it is. If it is not easy and the muscles seem to want to stay straight, she may have lead pipe rigidity.
Justin is in Florida with his friends for spring break. While he is chillin' on the beach, he gets a deep pain in his stomach, matching his usual chronic pain episodes. He left his usual medication at home, so his friend, who needs only a little pain relief, gave him some of his medication. Later, Justin is in his hotel room, writhing in pain.
What happened? Why?
Justin is suffering from withdrawal symptoms because he usually takes a full agonist for his chronic pain and his friend gave him a partial agonist.
You are a doctor in charge of teaching OMS-III students. You are showing them how to perform an endotracheal intubation, and in the middle of your explanation, the pt starts twitching. The students appear frazzled--even after the pt relaxes, so you begin to explain what happened.
How would you explain this?
Pt was administered succinylcholine for the endotracheal intubation. There are two phases on how it works.
-Phase 1: Open Na+ Channel -->Strong depolarization -->Transient twitching of muscle (Fasciculations)
-Phase 2: With time, continuous Depolarization gives way to gradual repolarization as the Na channel closes or is blocked.