What is the safest process in use for administering medications in an acute care setting in the United States?
What is scanning?
This is the definition of pharmacodynamics.
What are the effects of drugs in the body and the mechanism of their action?
This is the definition of the term pharmacokinetics.
What is the movement of drugs within the body?
Refers to the dose required to produce a specific intensity of effect.
What is "potency"?
The nurse is passing 0900 medications which will be considered late at 0930. It is 0928. The patient tells the nurse "I never take a blue pill at home. Are you sure this is right?". This is the correct response.
What area is considered the primary expertise of nurses concerning medications in the acute care setting?
What is safe medication administration?
An important part of pharmacodynamics is associated with this, defined as... The ability of a drug or other chemical to be taken up by the body and made available in the tissue where it is needed
What is "Bioavailability"?
Sian receives flash burns after going into the sun with doxycycline in his system. He understands that this occurred because the antibiotic was deposited into his subcutaneous tissue where it interacted with sunlight. This demonstrates the way the drug _________ took place in his system.
What is distribution?
The science of dealing with the actions of drugs on the body.
What is "pharmacology"?
Example: A patient tells the nurse "Last time I took that medication it made me very sick to my stomach".
What is an adverse drug effect (ADE)
This route of administration provides for the greatest bioavailability of approximately 100% of the administered amount.
What is intravenous (IV)?
This is the function of a drug agonist.
This is the organ MOST associated with metabolism of medications by the human body.
What is the liver?
This is the maximum effect of which the drug is capable.
What is "efficacy"?
Example: The patient tells the nurse that when taking vancomycin his lips started to swell and he had trouble breathing.
What is an allergy?
These 3 vcommon routes of medication are considered parenteral.
What are IV, IM, SQ?
This is the definition of an antagonist.
What is to compete with other molecules and block a specific action or response at a receptor site?
Once a favorite breakfast food, this fruit fell out of favor when it was discovered that it can decrease levels of some of the CYP450 family of drug-binding enzymes.
What is Grapefruit? (Or sour orange juice).
The breakdown of orally administered drugs in the liver and intestines.
What is the "first pass effect"?
This is what the nurse tells the patient is the difference between the name brand medication he takes at home and the generic version supplied by the hospital.
What is the same chemically active ingredient in the same dose with differences in binding ingredients or sometimes flavor.
How many checks must each nurse engage in to ensure the right patient receives the right med at the right time via the right route?
What is whatever number is needed for the individual nurse to ensure they are giving the right med to the right patient at the right time via the right route, often considered to be 3 but can be more.
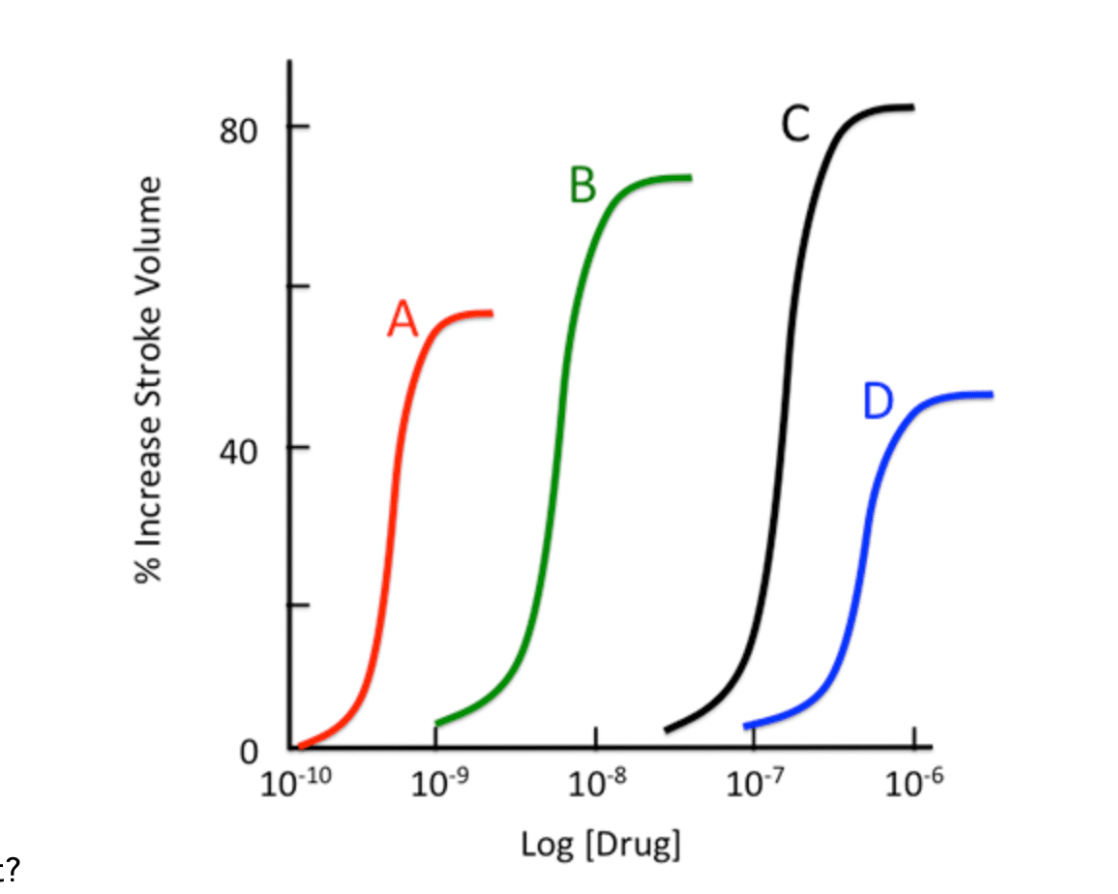
This letter represents the most potent drug on the graph
What is "A"
According to the text, this is the primary reason children receive lower doses of medication than adults.
What is developing (not yet fully developed) liver function?
An unintended pharmacological effect that occurs when a medication is administered correctly
What is "Adverse Drug Effect (ADE)"?
These are not regulated by the FDA and may not have been rigorously tested in the manner of other substances.
What are herbals and supplements?
Besides following physician orders, this is one way nurses ensure medication is administered via the "right route" for the post stroke patient.
What is evaluate the patients ability to swallow prior to administering PO medications.
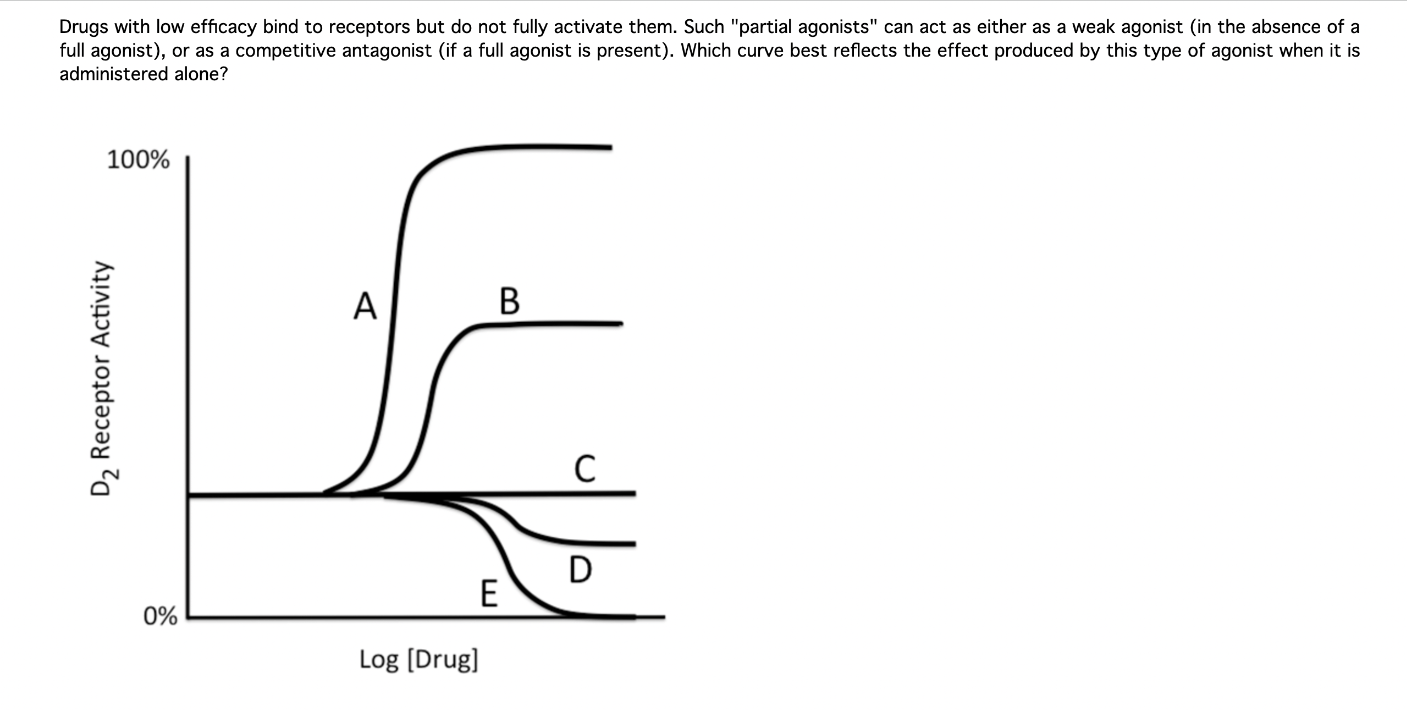
What is "B".
Examples of partial agonists (drugs that have both agonist and antagonist properties, or antagonists with "intrinsic activity") include the atypical antipsychotic aripiprazole (a D2 partial agonist), and the beta-blocker pindolol.
These are the 4 main parts of pharmacokinetics in order.
What are absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion?
Digoxin is a drug that has been used to treat systolic heart failure for over 200 years. It has a therapeutic index value of 2. This is the number of daily doses of digoxin will the average patient have to take at one time to have a 50:50 chance of developing toxic side effects
What is "2".
Drugs with low therapeutic index values (e.g. digoxin, most general anesthetics & cancer chemotherapy drugs) have to be used with great caution. This contrasts with most Over-The-Counter (OTC) drugs which have TI values of 10 or more
Ginger teaches Sage, her teenage patient who has been given rifampin for TB, that the use of this type of antibiotic can decrease the efficacy of her birth control pills. This is the reason.
What is drugs are biotransformed (metabolized) by intestinal bacteria and reabsorbed? If intestinal bacteria are impacted by an antibiotic this process is impaired.