–Medications must be checked three times before administration:When is the first time?
Before medication is removed from the medication cabinet
–Can be pills, syrups, or other liquids
Oral Medication
–Sublingual medications
Held under the tongue to diffuse through the tissues and into the bloodstream
Gastr-
Stomach
Megal
Enlarged
Spasm
Involuntary Contraction
What angle is a SQ injection
45
§Actual length of the hollow needle
–Shaft
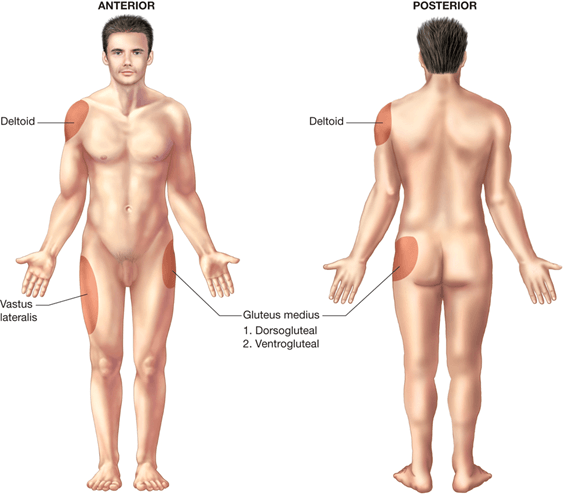
Sites for IM Injections
Equipment for dispensing liquid medication
Calibrated cups, spoons, droppers, syringes
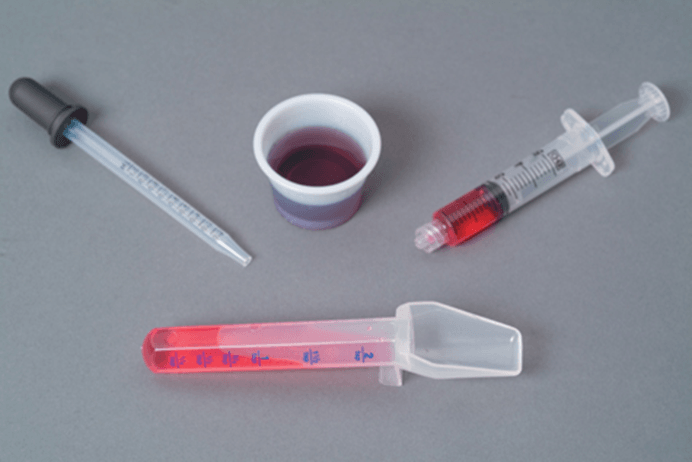
Oral Medication Equipment
Cardi
Heart
Itis
Inflammation
How is inhalation Medication administered
–Dispensed into the respiratory tract
–Absorbed quickly from the respiratory system into the bloodstream
–Equipment includes the metered-dose inhaler (MDI) and the nebulizer
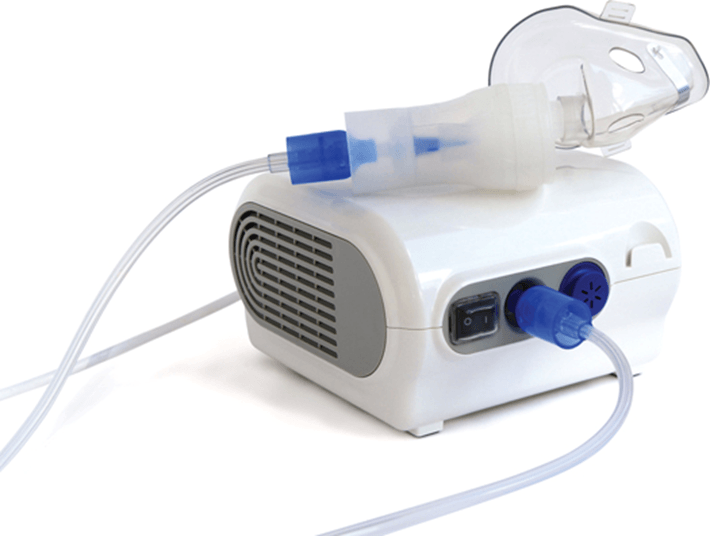
Inhalation medication equipment
IM injection
–Hilt
Connects the shaft to the hub
malacia
soft
Buccal medications
Placed between the patient’s cheek and gums for absorption through the tissues into the bloodstream
Medical assistants do not administer:
–Medications by intravenous (IV) fluids
–Chemotherapy drugs or narcotics
–Medications must be checked three times before administration: When is the second time?
Before medication is poured, drawn up into a syringe, or placed into a medication cup
Topical Medication Administration types
§Eye drops, eardrops, and nose drops
§Eye ointments
§Vaginal creams
§Rectal and vaginal suppositories
§Sterile douche solutions
§Sublingual or buccal tablets
Dermat
skin
What is IMPORTANT to remember when administering TOPICAL MEDICATION
Important to wear gloves
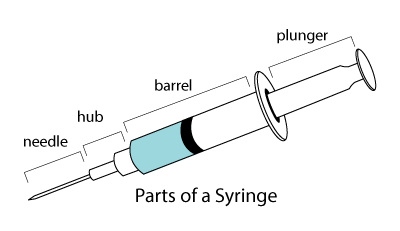
parts of a syringe
Hub
Connects the needle to the syringe
gingiv
gum
Plast
surgical repair
Enter
intestines
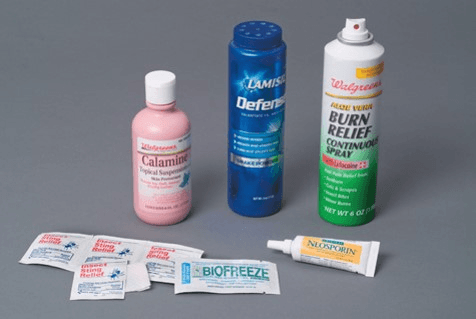
Topical Medication
Cerebr-
Brain
–A patch on the skin releases medication slowly over time.
Transdermal patch
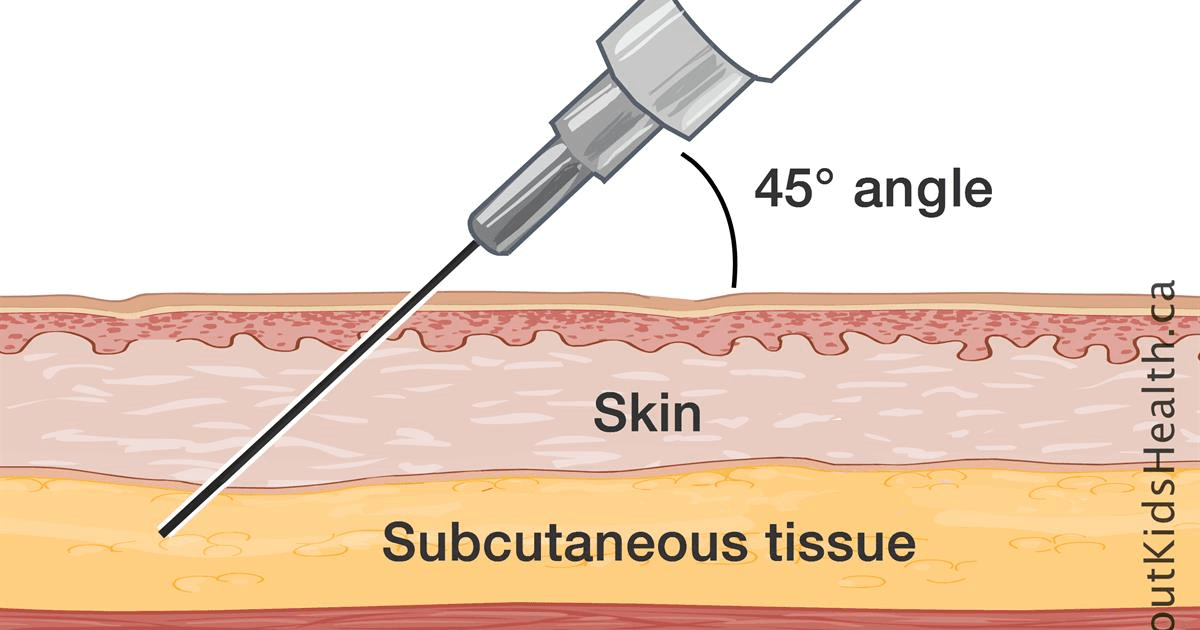
SQ injection
hepat
liver
Barrel
Holds the liquid in the syringe
rhin
nose
List the six rights to make sure of each time you administer a medication.
1.Right patient
2.Right medication
3.Right dosage
4.Right route
5.Right time
6.Right documentation
–Four additional rights to consider when you administer a medication:
1.Right patient education
2.Right to refuse (the patient’s right to refuse a medication)
3.Right assessment
4.Right evaluation
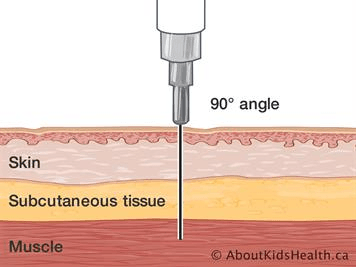
What angle is an IM injection
90
ectomy
surgical removal
–Medications must be checked three times before administration:When is the third time?
Before medication is returned to the cabinet
Osis
any condition
nephr
kidney
Flange
Prevents the needle from rolling on flat surfaces
blephar
eyelid
What is the medication calculation formula?
D/H X V
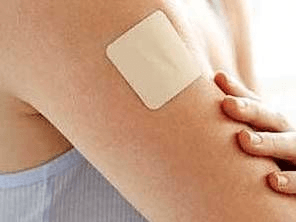
transdermal patch
path
disease
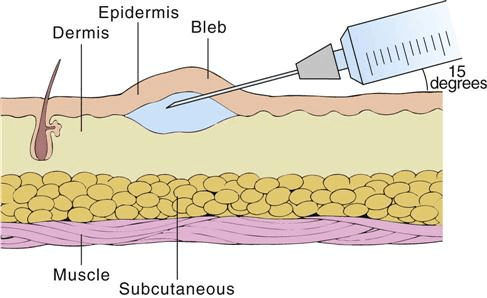
ID injection
List the parts of the syringe
shaft, hilt, hub, barrel, flange, plunger
MATH PROBLEM
What are the four types of injection routes
§Intramuscular
§Subcutaneous
§Intradermal
§Intravenous
–Plunger
§When pressed, expels medication from the syringe
§When pulled, gathers medication into the syringe
MATH PROBLEM