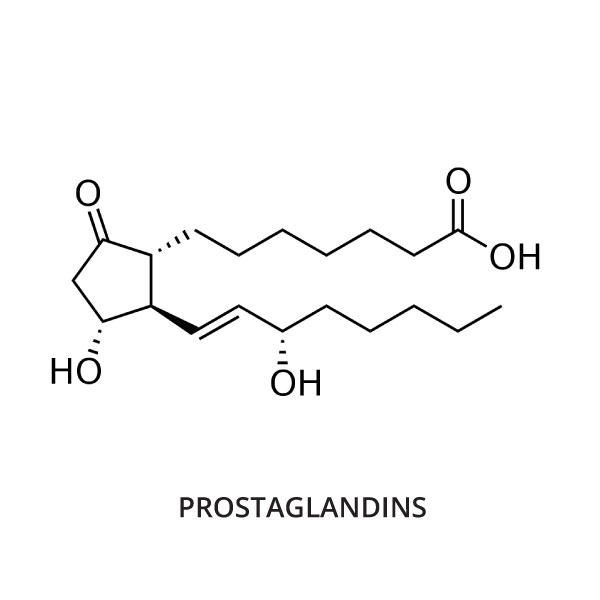
This lipid molecule is a derived from arachidonic acid and is the cause pain recognition, fever and vasodilation.
Prostaglandin
This plant is the source of the analgesic morphine.
Opium poppy (Papaver somniferum)
This enzyme is the target of penicillin and also known as penicillin-binding protein.
Transpeptidase enzyme
This common catalase-positive and coagulase-positive gram-positive bacterium produces beta-lactamases that destroys penicillin.
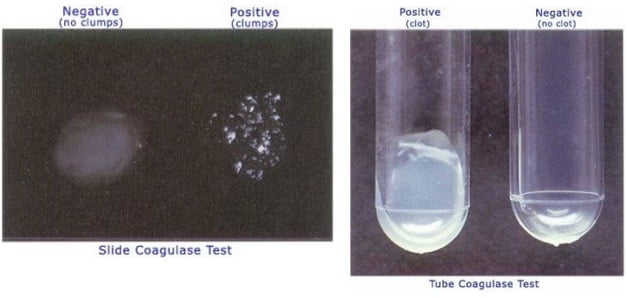 Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus
This intravenous cephalosporin is usually given for surgical prophylaxis.
Cefazolin
The condition below is seen in the rapid administration of this drug.

Vancomycin
This organ produces proteins that act as suicide bomber that create pores in the membrane of bacteria.
Liver

This process happens when the nerve endings are sensitized by the products of damaged cells, leading to pain that is unproportional to the stimulus.
Hyperalgesia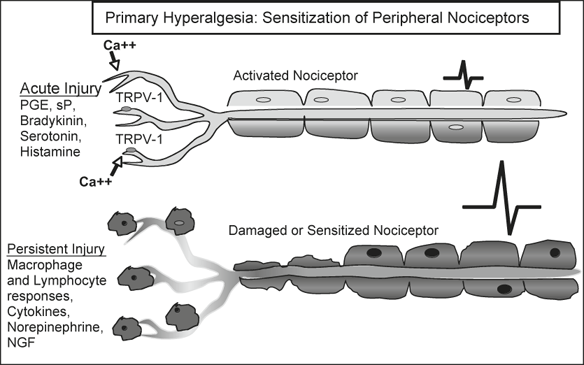
This opioid receptor is the main receptor that endorphin most avidly binds to.
Mu receptor
This antibacterial drug is a detergent that creates pores on the cell membrane.
Daptomycin
This gram-negative double-walled cell component prevents the penetration of drugs into the cell wall, leading to its natural resistance against older penicillins.
 Outer membrane
Outer membrane
This antibacterial is the best drug to give to a patient inflicted by Listeria, severe Leptospirosis and Syphilis.
Penicllin
This class of antibacterial drugs are contraindicated among pediatric (<19 years old) due to severe cartilage damage.
Floroquinolones
This enzyme is found inside the granules of neutrophils and is responsible for the production of bleach.
Myeloperoxidase
This NSAID has anti-platelet activity and a maintenance medication for patients who had myocardial infarction.
Aspirin or Acetylsalicylate
Fentanyl 
This is the target enzyme of vancomycin.
Transglycosylase enzyme
This bacterial endotoxin causes massive immune response in the body, leading to sepsis and septic shock.
Lipopolysaccharide
This is the drug of choice for a patient suffering from meningitis due to its therapeutic effects and removal of carrier state.
Ceftriaxone
The proliferation of this bacterium that causes watery diarrhea is caused by the usage of antibiotics.

Clostridioides difficile
This immunoglobulin complexes up to 10 pathogens and a marker of acute infection.
Immunoglobulin M
This drug is a powerful hormonal drug that inhibits the cleavage of arachidonic acid from the membrane.
Glucocorticoids
This partial opioid antagonist is used as a cough suppressant and is currently marketed as an over-the-counter drug.
Dextrometorphan
This powerful antibacterial makes the prokaryotic ribosome misread the mRNA, leading to aberrant protein and cell death.
Aminoglycosides
This gram-negative bacteria often found in the environment and hands of healthcare workers is highly resistant to common antibacterials and the usual cause of hospital acquired infection.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa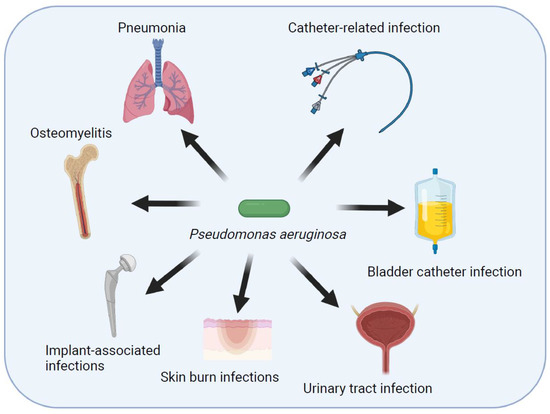
This combination of two antimicrobial drugs should be given in a patient presenting with urethritis or cervicitis ("tulo")
Ceftriaxone and Azithromycin or Doxycylin
This antibiotic can cause neuromuscular blockade commonly seen in curare or rocuronium.
Aminoglycosides
This immune tissue found in the ileum prevents infections coming from the alimentary canal.

Peyer's patches
This biologic (antibody) disease-modifying anti-rheumatoid drug attacks the inflammatory interleukin-6.
Infliximab
This partial opioid agonist is given for breakout pain for cancer patients.
Hydrocodone/Oxycodone/Dihydrocodeine
This enzyme is the target of Sulfa drugs or Sulfonamides
Dihydropteroate synthase enzyme
This extracellular product protects the community of microorganisms due to its impenetrable barrier against antibacterials.
 Biofilm
Biofilm
This drug combination is given as prophylaxis among persons living with HIV to prevent toxoplasmosis and pneumocystis jirovecii.
Co-trimoxazole
This antimicrobial causes the severe and life-threatening condition seen below:
Sulfonamides
This organ is an important site for the phagocytosis and killing of encapsulated bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae, Hemophilus influenzae b, and Niesseria meningitides.
Spleen
