What is Thermal Energy?
The energy associated with the molecular motion of an object (also known as heat).
In Evaporation, the substance transitions from the _______ phase to the _______ phase.
Liquid Phase to Solid Phase
Name each phase of matter!
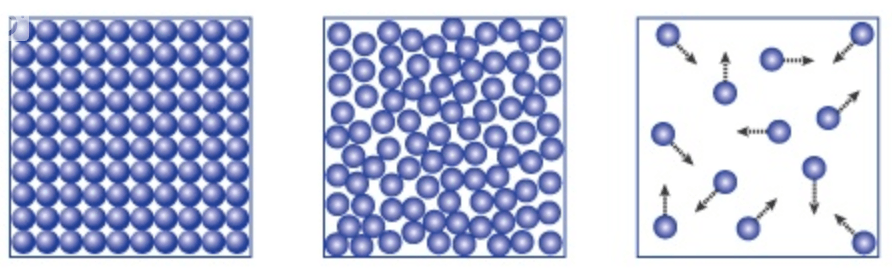
Solid, Liquid, and Gas
Melting because we see the atoms beginning to flow around each other as the solid disappears.
What State of Matter is shown?
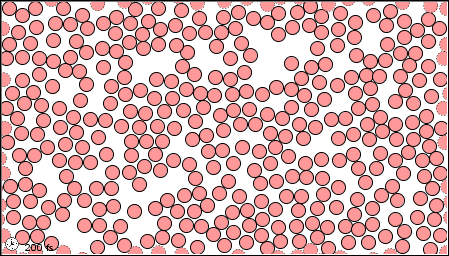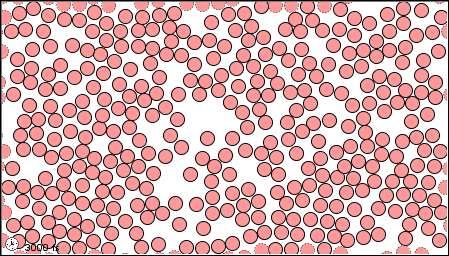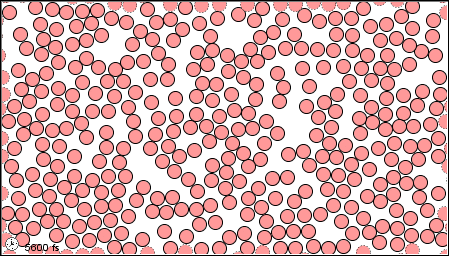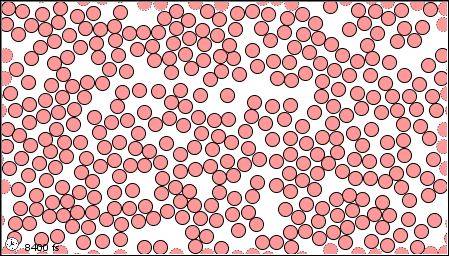
Liquid
What is Temperature?
A measure of thermal energy (hotness or coldness).
In Condensation, the substance transitions from the _______ phase to the _______ phase.
Gas phase to the liquid phase.
What phase of matter has the highest energy level?
Gasses have the highest energy level of all three States of Matter.
Freezing, because we see the liquid become rigid and unable to flow.
What State of Matter is shown?
What is a Phase Transition?
The addition or removal of energy when a substance changes from a solid, liquid, or gas state to a different state.
In Sublimation, the substance transitions from the _______ phase directly to the _______ phase.
Solid phase directly to the gas phase.
What phase of matter has the lowest energy level?
Solids have the lowest energy level of all three States of Matter.
Condensation because the water vapor in the air is slowing down and condensing on the cold glass
Describe the molecular motion of a solid.
The molecules of a solid vibrate slightly in place.
What is the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
Heat transfers from an object of higher temperature to objects of a lower temperature.
In Deposition, the substance transitions from the _______ phase directly to the _______ phase.
Gas phase directly to the solid phase.
What are the properties of a solid? Name all three.
Rigid, Fixed Shape, and Fixed Volume
Evaporation, because the molecules of the liquid are evaporating into invisible water vapor
Describe the molecular motion of a liquid.
A liquid’s atoms flow freely around each other but do not expand to fill their container.
What is Freedom of Movement?
The degree of particle movement within a substance. This movement is achieved through the particles gaining thermal energy.
What phase transition is shown?
H2O (l) ---> H2O (s)
Freezing
What are the properties of a Liquid? Name all three.
Not rigid (flow), no fixed shape, but a fixed volume
The phase change is Deposition because it is changing from a Gas to a Solid, skipping the Liquid phase.
Describe the molecules of a gas.
The molecules of a gas move about freely and quickly with lots of space between the molecules.
What is the difference between a physical and chemical change?
In a physical change the appearance or form of the matter changes but the kind of matter in the substance does not
What phase transition is shown?
CO2 (s) ---> CO2 (g)
Sublimation
What are the properties of a Gas? Name all three.
Not rigid (flow), no fixed shape, and no fixed volume.
The phase change is Sublimation because it is changing from a Solid to a Gas, skipping the Liquid phase.
What Phase Transition has occurred?
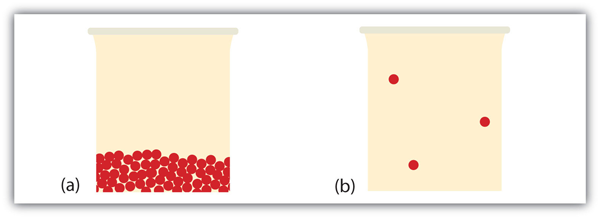
Evaporation