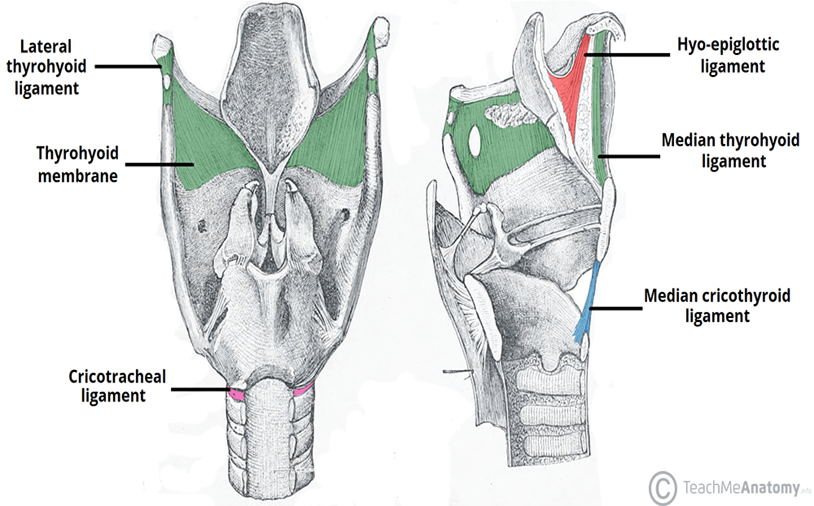
What is the name of the membrane that connects the thryoid to hyoid?
Thyrohyoid membrane
What is the primary function of the intrinsic musculature?
Movement and tension of the vocal folds
What is the name given to the muscular portion of the vocal folds?
Thyroarytenoid
What force determines the extent of vocal fold approximation?
Medial compression
What is the name of the structure located inferiorly in the laryngeal system that connects the cricoid to the trachea?
Cricotracheal ligament
BONUS - IS THIS AN INTRINSIC OR EXTRINISIC STRUCUTRE?
What are the three intrinsic muscles responsible for ADDUCTION of the vocal folds?
Lateral cricoarytenoid
Oblique arytenoids
Transverse arytenoids
What is the name of the medial fiber of the thryoarytenoid and what does it do?
Thyrovocalis - tenses the vocal folds
What is the minimal amount of subglottal pressure needed to overcome medial compression?
3-5 cmH20
Which joint provides the articulation between the thyroid and cricoid cartilages?
The cricothyroid joint.
What role do intrinsic membranes and ligaments serve for the laryngeal system?
They provide support to the framework
Which intrinsic muscle brings the cricoid and thyroid cartilages together?
The cricothyroid muscle.
BONUS: What are the names of the two fibers that make up this one muscle?
Thyromuscularis - relaxes the vocal folds
What is the name given to the explosive puff of air that escapes into the vocal tract and begins vibration?
Vocal Attack
BONUS: Name a natural variation of a vocal attack?
What are the processes of the arytenoid cartilages called?
The processes are called the vocal processes and muscular processes.
What is the name given to the group of extrinsic muscles that elevate the laryngeal system?
Suprahyoids
Name all 5 layers of the vocal folds from superficial to deep
1) Epithelium
2) Superficial Lamina Propria
3) Intermediate LP
4) Deep LP
5) Thyroarytenoid muscle
What two scientific principles contribute to sustained phonation?
Elastic recoil forces
Bernoulli effect
What is the name of the paired cartilages that sit on top of the arytenoids? (Shown in purple) 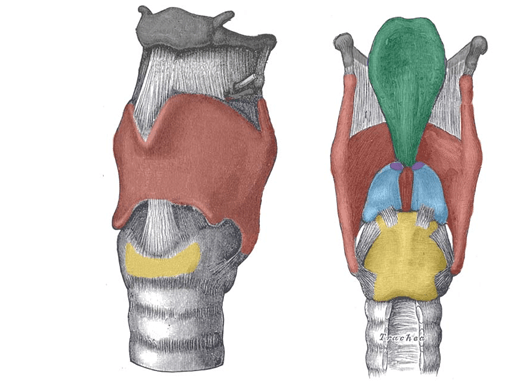
Corniculates
The glottis is divided into two main parts - what are the names given to each?
Membranous (Anterior 3/5)
Cartilaginous (Posterior 2/5)
Which intrinsic muscle originates at the posterior surface of cricoid cartilage and attaches to the muscular processes of the arytenoids?
What is its function?
The posterior cricoarytenoids.
Contraction of these muscles pull down and back on the muscular processes of the arytenoids causing the vocal processes to pull apart and ABDUCT the vocal folds.
Epithelium
Superficial layer of lamina propria
How is vibration terminated?
Activation of abductor musculature (PCA)
Moving vocal folds out of airstream, reducing turbulence
What is the name of the "floating" cartilages embedded within the aryepiglottic folds?
Cuneiform cartilages
What is the name of this structure and what is it's function?
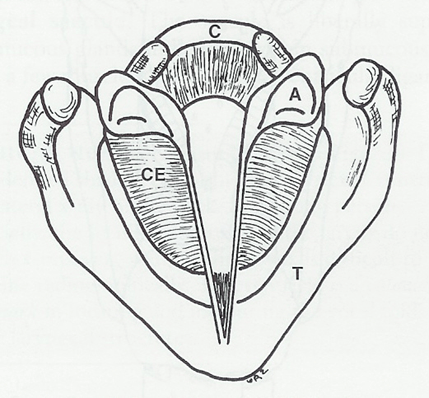
Conus Elasticus
Reduces resistance to airflow - allowing it to pass through trachea easily
The sternohyoid, omohyoid, sternothyroid, and thyrohyoid are all examples of what type of musculature?
Infrahyoids - depressors
What two layers of the vocal folds compose the "vocal ligament"?
Intermediate lamina propria
Deep lamina propria
BONUS - Is the vocal ligament passively or actively regulated?
Explain the vertical phase difference seen in vocal fold vibration during the use of modal register
Vocal folds open inferiorly to superiorly AND close inferiorly to superiorly