This is responsible for energizing electrons in the light-dependent reactions.
What is light?
These two pigment molecules absorb nearly all colors of light?
What are chlorophyll and carotenoids?
This is another name for the Calvin Cycle.
What is light-independent reaction?
This adaptation causes plants to form a 4 carbon chain before the Calvin Cycle?
What is C4 photosynthesis?
This is why most plants are green.
What is reflection of green light?
Where light-dependent reactions take place.
What are thylakoid membranes?
This molecule is pulled from the air to begin the Calvin Cycle.
What is carbon dioxide?
This many NADPH are spent by the Calvin Cycle each turn.
What is 6?
This factor affects the rate of photosynthesis in this way.
What is temperature?
The equation for photosynthesis.
What is 6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
The structure seen in number 5.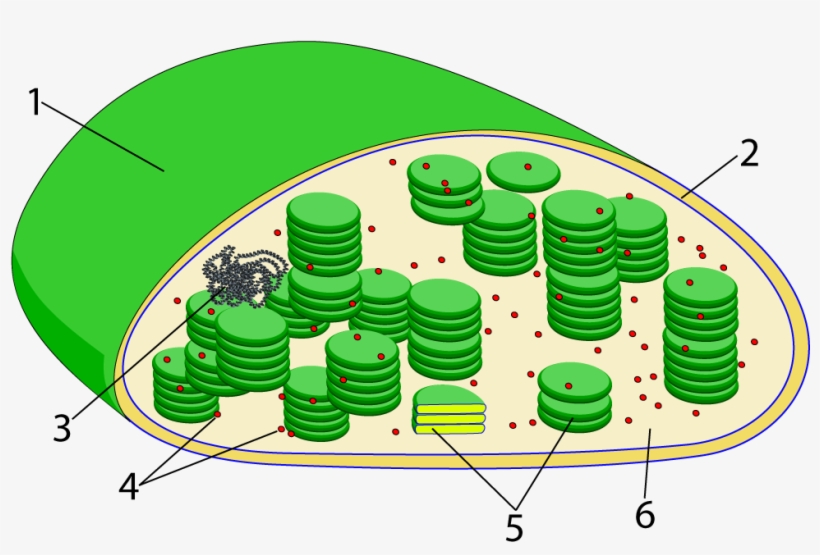
What is thylakoid?
This molecule is the energy currency of life.
What is ATP?
This many ATP are spent during the Calvin cycle to create one molecule of glucose.
What is 18?
These factors affect photosynthesis in this way.
What are carbon dioxide concentration and light intensity?
This is why photosystem II is not named photosystem I.
What is it was discovered second?
The liquid space inside of a chloroplast, as seen in number 6.
What is stroma?
This molecule accepts electrons at the end of the light-dependent reactions.
What is NADP+?
This many 3 carbon chains exit the Calvin Cycle each turn.
What is 1?
This is how CAM plants conduct photosynthesis.
What is open stomata for Calvin Cycle at night?
This wet molecule is split to replenish electrons in photosystem II.
What is water?