convert solar energy into chemical energy by ‘fixing’ carbon dioxide
Autotrophs
stacks of thylakoids
granum
•unidirectional flow of electrons from PSII to PSI and NADP+ is reduced to NADPH
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation
•Only PSI (P700) is involved
Cyclic Photophosphorylation
how many co2 molecules are inputted in the calvin cycle
3
two stages of photosynthesis
light dependent and light independent
site of light dependent reaction
thylakoid
catalyses the transfer of electrons from ferredoxin (Fd) to NADP+.
NADP+ reductase
Product of cyclic photophosphorylation
ATP
what are the limiting factors of photosynthesis
temperature, co2 concentration, light , water
chlorophyll
contains enzymes for calvin cycle
stroma
components of the first electron transport chain
plastiquone, cytochrome complex, plastocyanin
Component of electron transport chain used in cyclic photophosphorylation
ferredoxin, cytochrome complex, plastocyanin
what happens in the carbon fixation phase of calvin cycle
Co2 binds to Rubp sugar with the help rubisco
product of the light stage that enters dark stage
Hydrogen
collection of 200-300 molecules engaging in the light reaction
photosystem
The electron from ps 2 is excited by photons in ps1, it then moves down its transport chain through protein___________________
ferodoxine
products, last electron acceptor and electron source of the non cyclic photophosphorylation
atp,nadph, oxygen,
nadp
water
two 3 carbon molecules produced in the first stage of calvin cycle
3 phosphoglycerate PGA
chlorophyll containing plastids of Eukaryotes
chloroplasts
Photosystem activated by light of wavelength up to 700 nm
photosystem 1
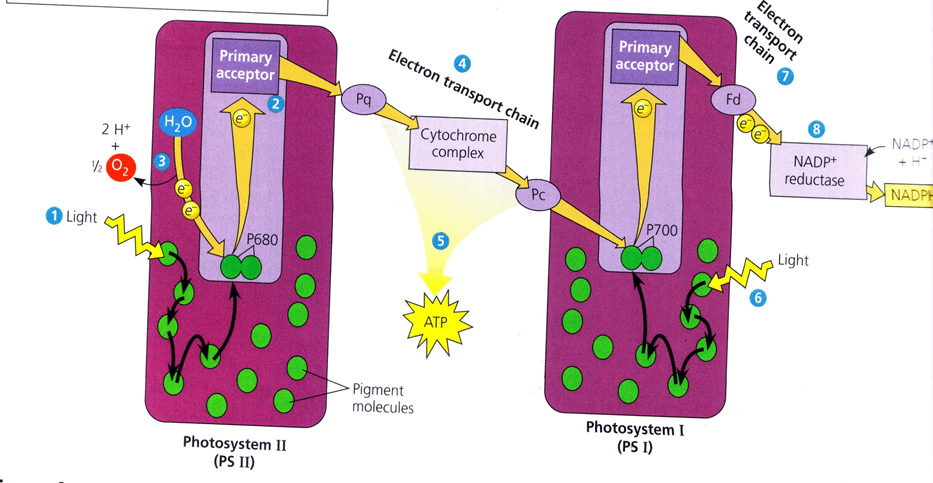
Mechanism begins with photsystem 2- purple is reaction centre, in reaction centre is p680
Photon from sunlight enters the photosystem and it hits the light harvesting complexes and bounces like a wave till it gets to p680
P680 needs an electron and it gets that electron from water, the photon excites the electron and it moves up in energy state into electron acceptor
Moves through the electron transport chain through proteins Plastiquone (Pq) (an electron carrier), a cytochrome complex, a protein – plastocyanin (Pc) until it gets to photosystem 1
As it travels the energy is lowered and this get absorbed by atp
product, electron source and last electron acceptor in cyclic phosphorylation
Atp
photosytem1
photosytem 1
During the calvin cycle what is used to build glucose molecules
triose phosphate