What is the chemical equation of photosynthesis?
6H2O + 6CO2 + light energy -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is the chemical equation of cellular respiration?
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20 + ATP
Where does the light reactions occur?
Thylakoid membrane
Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
Plant cells only have chloroplasts which are used to produce energy
False, plants have both chloroplasts and mitochondria to produce energy
What are the three categories of organisms based on how they get nutrients?
Photoautotrophs - make their own organic compounds using light energy and carbon dioxide
Autotrophs - make most/all of their organic compounds from inorganic materials
Heterotrophs - acquire their nutrients from consuming other organisms
What does wavelength mean?
It is the difference/length between two peaks
Photosystem II (PSII)
ETC
Photosystem I (PSI)
ATP synthase
What is carbon fixation? What enzyme does it use?
Carbon fixation = addition of carbon dioxide (CO2) to an organic compound
Use of the enzyme Rubisco
How many cycles need to occur to produce 1 glucose molecule?
For every three cycles, 1 G3P molecule is made
It takes 2 G3P molecules to make 1 glucose
So, the Calvin cycle needs to occur 6 times to produce 1 glucose molecule
What is light? What are the two natures that which light can behave as?
Bonus question: Which is associated with a wavelength and which is associated with photons?
Light = electromagnetic radiation as energy
Wave behavior that is characterized by wavelength
Particle behavior that is made up of discrete packets of energy called photons
What is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of location and reaction type?
Photosynthesis is an endergonic reaction that occurs in the chloroplast
Cellular respiration is an exergonic reaction that occurs in the mitochondria and cytosol
What occurs in PSII?
Photons and water are brought into the photosystem
Water is used as an electron donor and gets broken into 1/2 O2 and H+
The photons (from light energy) excite the electrons that came from the water and are passed through the ETC
What organic compound is carbon (from the CO2) added to? How many of these compounds are used?
RuBP is a 5 carbon organic molecule to which CO2 is added to, there are 3 used in the cycle
What are the reactants for the light reactions? What are the products?
Products = 1/2 O2 + (H+) + NADPH + ATP
What is a pigment? What are the two types of pigments? Describe them
Bonus question: what are the two types of carotenoids?
Pigment = molecules that absorb photons of specific wavelengths
Chlorophylls = absorb red and blue while reflecting green and is necessary for photosynthesis
Carotenoids = absorb blue and green while reflecting red, orange, and yellow; may or may not be present in a cell
Carotenoids = carotenes + xanophylls
Describe the energy cycle between photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Photosynthesis + light energy make organic molecules and oxygen gas
These organic molecules + oxygen gas are the reactants of cellular respiration which produce carbon dioxide + water + ATP
The carbon dioxide + water are the inputs of photosynthesis
What is the point of the ETC? Where does the H+ (aka protons) come from?
The ETC uses the flow of electrons to bring in 2 H+ from the stroma and into the thylakoid space/lumen
Along with the pulled in H+, the H+ from the PSII are used to create the electrochemical gradient which will later be used by the ATP synthase to produce ATP
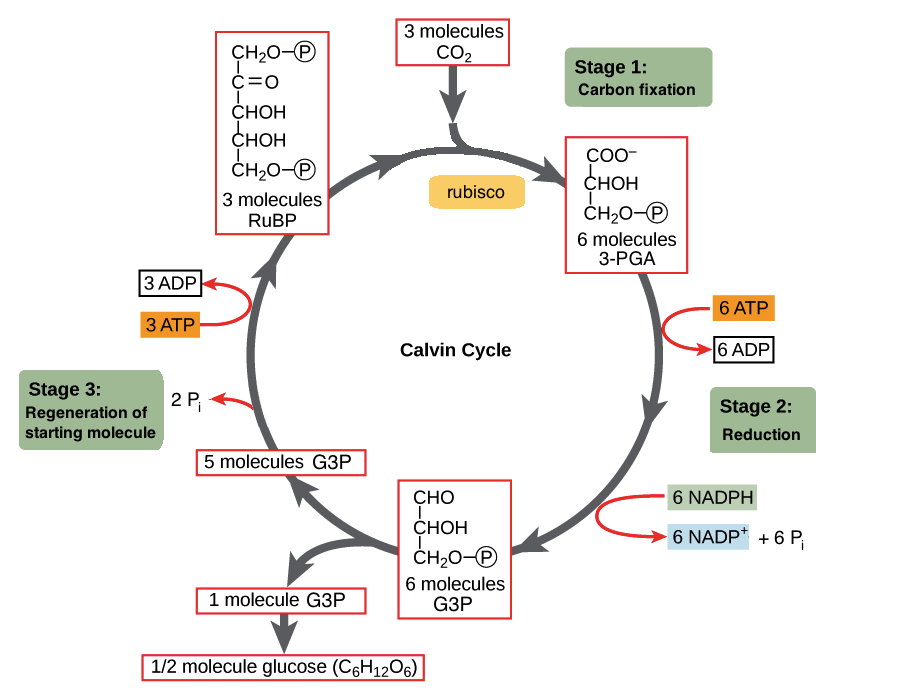
What are the 3 phases of the Calvin cycle in order?
Fixation phase = carbon dioxide is fixated
Reduction + carbohydrate production phase = produces G3P using ATP
Regeneration phase = uses G3P to restore the substrate for the fixation phase using ATP
What are the reactants of the Calvin cycle? What about the products?
Reactants - 3 carbon dioxides from the environment + 9ATP and 6NADPH from the light reaction
Products - after 3 cycles, one G3P exits + 9 ADP (and Pi) + 6 NADP+ (and H+)
Describe the organization from a plant leaf to the chloroplast
Mesophyll cell - contains organelles, including chloroplasts
Chloroplasts - double membraned with an intermembrane space + inner stroma fluid + granums which are stacked thylakoids + thylakoids which have an inner thylakoid space
What visible color has the smallest wavelength? What would be its numerical value? Would this have higher energy or lower energy?
Purple has the smallest wavelength of the visible light. The wavelength would be about 400 nm and would have the highest energy of the visible light
What occurs in PSI and what does this have to do with NADP+?
The PSI uses light energy to excite the electrons that flow through it
These electrons are then used to reduce NADP+ to create NADPH (an electron carrier)
Draw out the Calvin cycle as described in class
Should be somewhat similar to:
What are the 4 steps of light reactions?
1A) Photons excite electrons in the PSII, which enters the ETC -> movement of (-) charge pulls H+ from the stroma and into the thylakoid space/lumen
1B) Water donates electrons -> breaks apart into 1/2 O2 + 2H+
2) The traveling electrons reach PSI and are excited by light energy
3) NADP+ accepts 2 electrons and 2 protons (H+) to form NADPH + one H+
4) ATP synthase uses the H+ electrochemical gradient to produce ATP from ADP + Pi