Which one doesn't belong when referring to climate variables:
A) the humidity of the air.
B) the temperature of the air.
C) the pressure of the air.
D) the chemical composition of the air.
E) the type and amount of cloudiness.
Chemical Composition
What is the approximate date of the summer solstice?
June 21st or 22nd
Does the area near Kansas & Oklahoma have a small or large temperature gradient?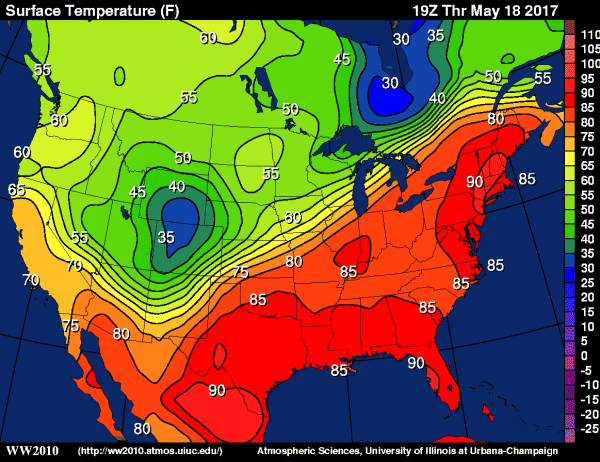
Large
Relative humidity depends on the water vapor present in the air and the:
A) altitude.
B) dew point.
C) latitude.
D) air temperature.
E) pressure.
air temperature
All of the following are necessary ingredients for cloud formation EXCEPT:
A) warm surface air temperatures.
B) rising, cooling air.
C) adequate water vapor content.
D) condensation nuclei.
warm surface air temperatures
Which of the following spheres is composed exclusively of water?
A) biosphere
B) lithosphere
C) hydrosphere
D) atmosphere
Hydrosphere
The primary cause of Earth's seasons is:
A) changes in atmospheric thickness.
B) varying orbital speed.
C) tilt of Earth's rotation axis, which causes sun angles and daylight length to vary.
D) regular changes in radiation emitted by the Sun.
E) varying distance from the Sun, which changes how much radiation Earth receives from the Sun.
tilt of Earth's rotation axis, which causes sun angles and daylight length to vary.
What does it mean to have a large temperature gradient?
Large temperature change over a short distance
As the temperature of air is reduced to its dew point, which of these is most likely to occur?
A) freezing
B) condensation
C) melting
D) supercooling
E) evaporation
condensation
The most common way for air to be cooled in order that a cloud may form is by:
A) sinking and contracting.
B) emitting radiation.
C) evaporating water.
D) rising and expanding.
E) reflecting radiation.
rising and expanding
Which of the following is the MOST important atmospheric component with regard to the earth's climate and the formation of weather systems?
A) water vapor
B) ozone
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen
E) argon
Water Vapor
In meteorological terminology, the primary difference between convection and advection is:
A) Convection represents vertical heat transfer and advection represents horizontal heat transfer.
B) Convection represents horizontal heat transfer and advection represents vertical heat transfer.
C) Convection represents upper atmosphere heat transfer and advection represents surface heat transfer.
D) Convection represents surface heat transfer and advection represents upper atmosphere heat transfer.
E) None of the above; the terms are used interchangeably.
Convection represents vertical heat transfer and advection represents horizontal heat transfer.
The annual temperature range at most latitudes in the Southern Hemisphere is much smaller than that in the Northern Hemisphere. The reason for this is that:
A) less area is covered by desert in the Southern Hemisphere.
B) there is a greater percentage of water surface in the Southern Hemisphere.
C) a greater proportion of the land surface is mountainous in the Southern Hemisphere.
D) rainfall and cloudiness are greater in the Southern Hemisphere.
E) the earth is closest to the Sun during the Southern Hemisphere summer.
there is a greater percentage of water surface in the Southern Hemisphere.
Which type of lifting mechanism results from warm air lifting over cold air?
A) orographic lifting
B) convective lifting
C) convergence
D) frontal wedging
Frontal wedging
The process by which a cloud droplet first forms is:
A) condensation.
B) supercooling.
C) collision and coalescence.
D) evaporation.
E) precipitation.
condensation
The ozone layer is found in the:
A) thermosphere.
B) stratosphere.
C) troposphere.
D) mesosphere.
E) ionosphere.
Stratosphere
Of the following choices, the surface with the HIGHEST albedo is:
A) fresh snow.
B) grass.
C) sand.
D) water (Sun near zenith).
Fresh Snow
A place located along a windward coast:
A) will probably have summer temperatures that are very similar to an inland place at the same latitude.
B) will probably have warmer summer temperatures than an inland place at the same latitude.
C) will probably have cooler summer temperatures than an inland place at the same latitude.
will probably have cooler summer temperatures than an inland place at the same latitude.
Sinking or subsiding air cannot form clouds due to the:
A) release of latent heat.
B) loss of particulates.
C) removal of water vapor.
D) formation of unstable layers.
E) warming temperatures.
Warming Temperatures
Salt, dust particles, and smoke are all examples of:
A) anthropogenically-produced cloud nuclei.
B) freezing nuclei.
C) hydrophobic nuclei.
D) condensation nuclei.
condensation nuclei
Put the four thermal layers of the atmosphere in order beginning from the surface are:
stratosphere, troposphere, mesosphere, thermosphere.
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere
The fraction of the total radiation encountered that is reflected by a surface is called its ________
Albedo
) During the night, clouds:
A) keep the air warmer by reflecting shortwave energy back to the surface.
B) keep the air warmer by absorbing and re-emitting longwave energy back to the surface.
C) keep the air cooler by reflecting shortwave energy back to space.
D) keep the air cooler by accelerating longwave energy loss to space.
keep the air warmer by absorbing and re-emitting longwave energy back to the surface.
Which of the following would not be associated with stable atmospheric conditions?
A) buildup of pollutants
B) temperature inversion
C) widespread fog
D) afternoon thunderstorms
Afternoon thunderstorms
The cloud form that is best described as sheets or layers that cover much or all of the sky is termed:
A) cirrus.
B) mackerel sky.
C) alto.
D) cumulus.
E) stratus.
stratus