What is Kepler's First Law?
Each planet's orbit about the Sun is an ellipse
Sinusoidal function
Which of the following relationships between the acceleration a and the displacement x of a particle involve SHM?
(a) a = 0.5x
(b) a = 400x2
(c) a = –20x
(d) a = –3x2
(c) a = -20x
The acceleration of the particle is directly proportional to the displacement of the particle and opposite to its direction. (a = -kx/m)
A 15.75-g piece of iron absorbs 1086.75 joules of heat energy, and its temperature changes from 25°C to 175°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron.
C = 0.46 J/gC
At freezing points and boiling points, what happens to the temperature?
The temperature stays the same.
What would likely happen to the Earth's revolution if the sun's mass were to increase? How can we prove that with Newton's Law of Gravity?
It would be brought closer to orbit and eventually collide with the sun as a result of the force increasing; F = (GMm)/r^2
A 0.75-kg block slides on a rough horizontal table top. Just before it hits a horizontal ideal spring its speed is 3.5 m/s. It compresses the spring 5.7 cm before coming to rest. If the spring constant is 1200 N/m, the thermal energy of the block and the tabletop must have: (inc, dec, stayed same...)
If we increase the tension of a string, what happens to the speed of transverse waves along the string?
Increases
During a phase change, what happens to the temperature? When will the temperature rise? (Consider ice --> water as an example)
The temperature remains constant; once the phase change is complete, then the temperature will rise.
The figure shows three situations involving a point particle P with mass m and a spherical shell with a uniformly distributed mass M. The radii of the shells are given. Rank the situations according to the magnitude of the gravitational force on particle P due to the shell, greatest first.

c = b > a
At what point in a planet's orbit around a star does it have the greatest velocity? Greatest angular velocity?
Greatest angular velocity = stays the same
A block with mass m = 1.92 kg is placed against a spring on a frictionless incline with angle θ = 28.6° (see the figure). (The block is not attached to the spring.) The spring, with spring constant k = 20 N/cm, is compressed 15.1 cm and then released. (a) What is the elastic potential energy of the compressed spring?

Uelastic = 22.8 J
Under the same tension, on which of these strings will transverse waves travel faster?
To what temperature will a 50.0 g piece of glass raise if it absorbs 5275 joules of heat and its specific heat capacity is 0.50 J/g°C? The initial temperature of the glass is 20.0°C
Tf = 231 C
When played in a certain manner, the lowest resonant frequency of a certain violin string is 350 Hz. What is the frequency of the (a) second and (b) third harmonic of the string?
(A) f = v/lambda = n*v/(2L); f2 = 2(350) = 700 Hz
(B) f3 = 3(350) = 1100 Hz
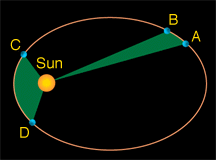
According to Kepler's Second Law, which section on the graph experiences the greatest change in area with respect to time?
Both sections experience the same area over time.
A block with mass m = 1.92 kg is placed against a spring on a frictionless incline with angle θ = 28.6° (see the figure). (The block is not attached to the spring.) The spring, with spring constant k = 20 N/cm, is compressed 15.1 cm and then released. What is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the block-Earth system as the block moves from the release point to its highest point on the incline?

22.8 J
A sinusoidal wave travels along a string. The time for a particular point to move from maximum displacement to zero is 0.15 s. What are the (a) period and (b) frequency? (c) The wavelength is 1.0 m; what is the wave speed?
(A) T = 4(0.15s)= 0.6 s
(B) f = 1/T = 1.67 Hz
(C) v = lambda/T = 1.67 m/s
What is the specific heat capacity of silver metal if 55.00 g of the metal absorbs 47.3 calories of heat and the temperature rises 15.0°C?
C = 0.057 cal/gC
The mass of a hypothetical planet is 1/100 that of Earth and its radius is 1/4 that of Earth. If a person weighs 600 N on Earth, what would he weigh on this planet?
96 N
In the figure, a central particle is surrounded by two circular rings of particles, at radii r and R, with R > r. All the particles have mass m. What are the magnitude and direction of the net gravitational force on the central particle due to the particles in the rings?
(Gm2)/r2, up
DOUBLE JEOPARDY
In the figure, a block of mass m = 1.70 kg slides head-on into a spring of spring constant k = 480 N/m. When the block stops, it has compressed the spring by 13.0 cm. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block and floor is 0.210. While the block is in contact with the spring and being brought to rest, what are (a) the work done by the spring force and (b) the increase in thermal energy of the block-floor system? (c) What is the block's speed just as the block reaches the spring?

(a) -4.056 J
(b) 0.455 J
(c) 2.30 m/s
A 300 cm length of a string is stretched between fixed supports. What are the (a) longest, (b) second-longest, and (c) third-longest wavelength for waves traveling on the string if standing waves are to be set up?
(A) lambda1 = 2L/1 = 600 cm
(B) lambda2 = 2L/2 = 300 cm
(C) lambda3 = 2L/3 = 200 cm
The specific heat of ethanol is 2.46 J/gC. Find the heat required to raise the temperature of 193 g of ethanol from 19 C to 35 C.
8.070 kJ
Double Points (This one is for fun!)
What's Angelique's favorite color?
Orange