What is the difference between Speed & Velocity?
Speed is a scalar quantity.
Velocity is a vector quantity
Define Acceleration.
Acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes with respect to time.
What does a straight, flat line on the Position vs. Time graph indicate?
It indicates a velocity of 0.
This is the resultant vector of Vectors A & B below.
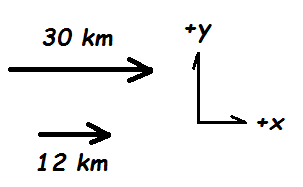
What is +42 km?

This shape is created by objects moving with a horizontal and vertical component.
What is "an arc" or "a parabola"?
This is the name of a fast-moving projectile that has found itself in orbit around a large body.
Satellite
What is the average speed of tricycle that travels 300 feet in 200 seconds?
1.5 ft/s
A car traveling at 25 mi/hr slows to a stop over a time of 2.5 s. What is the car's average acceleration?
-10 mi/hr/s or -10 mph/s
The absolute value of the slope of the Position vs. Time graph is a measure of what?
Speed
This method of finding a resultant vector involves lining up the arrows of vectors with the bases of other vectors and then finding the overall vector.
What is "Tip-to-Tail Method"?
If air resistance is negligible and the total time in travel is 12 seconds, this is the time the projectile reached the apex of its arc.
What is 6 seconds?
This type of satellite includes moons and the rocks that comprise rings around planets.
What is a natural satellite?
What is the instantaneous velocity of a moving object with no acceleration and an average velocity of 5 m/s ,North?
5 m/s, North
A ball rolls from rest at an acceleration of +5 m/s2 for 3 s. What is its final velocity?
+15 m/s
What does the slope of the Velocity vs. Time graph indicate?
Acceleration
This is the horizontal component (Vx) of the vector below.
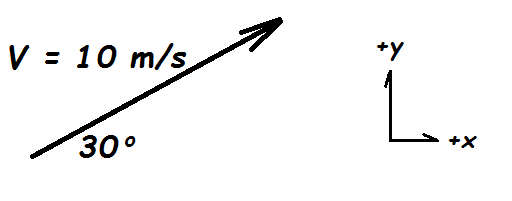
What is Vx = 1.543 m/s ?
If air resistance is negligible and the time a projectile reaches its apex is 11 seconds, then this is the total trip time.
What is 22 seconds?
These are 2 examples of artificial satellites.
What are telecommunication satellites, the International Space Station, and space debris.
Is it possible for an object with constant speed to have a changing velocity? Why or why not?
Yes, because velocity deals with direction, an object can have a constant speed but also be changing direction and therefore changing its velocity.
A driver is accelerating at +3 m/s2. If his starting velocity is 1 m/s and his final velocity is 10 m/s, then how many seconds was he accelerating for?
3 seconds.
What does the shaded area under the Velocity vs. Time graph indicate?
The total distance traveled.
This is the magnitude of the resultant vector of Vectors A & B below.
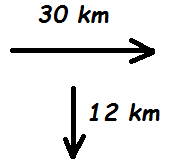
What is 32.3 km?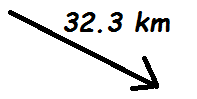
At this time, the projectile reached its peak.
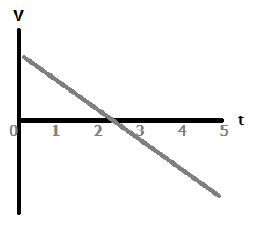
What is 2.5 s?
If a satellite travels too slowly, it is most likely to do this.
What is falling to the surface of whatever body it is orbiting?
Is it Speed or Velocity that is represented by "Displacement (relates to direction) divided by time"?
Velocity = Displacement divided by time.
Speed = Distance divided by time.
True or False: An acceleration is always positive.
False. Negative acceleration is also called "deceleration"
For the particle described by the graph:
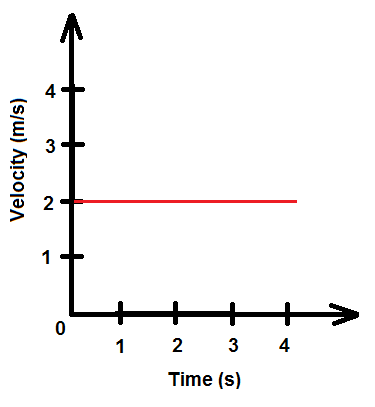
1) What is its average velocity?
2) What is its acceleration?
Bonus 500 pts: What distance has it traveled?
1) 2 m/s
2) 0 m/s2
Bonus) 8 m
These are the horizontal & vertical components of the vector below:
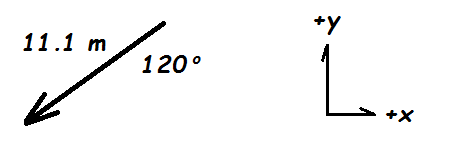
What are:
Vx = - 1.71 m
Vy = - 10.97 m
This is the vertical component of a projectile's velocity at the top of its path.
What is zero?
This is what happens to satellites that travel too fast for their current orbit.
What is launching out of the atmosphere into space?