Uppermost layer of the Earth that extends to an average depth of 7 km beneath the oceans and 45 km beneath the continents.
What is the crust?
Tendency of flaky minerals, like biotite or muscovite, to be aligned parallel to one another in a metamorphic rock.
What is foliation?
Seismic body waves that only move through solids and displace particles perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
What are S-waves?
Process in which seismic waves change direction as they "bounce off" Earth's internal layers.
What is seismic reflection?
66 million years ago an asteroid impact at Chicxulub caused a __________ that killed the non-avian dinosaurs and many other organisms.
What is a mass extinction?
Direction the plate shown below is moving relative to a stationary hotspot under the youngest island.
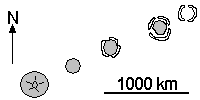
What is northeast?
Process in which the removal of early crystallized minerals rich in Ca, Fe, and Mg changes the composition of a magma?
What is fractional crystallization?
Feature of a seismogram that enables us to determine how far the focus of an earthquake is from the seismometer.
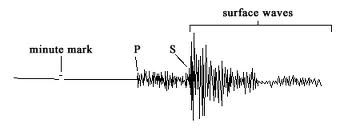
What is the S-P delay?
Dip-slip fault in which footwall moves down relative to hanging wall.
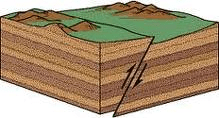
What is a reverse fault?
Fraction of parent isotope remaining in a sample after four half-lives have elapsed.
What is 1/16?
Force that moves plates apart as the slide off the thermal "welt" at a divergent plate boundary.
What is ridge push?
An aggregate of one or more minerals grown or cemented together.
What is a rock?
Small volcano made of loose basalt tephra with a funnel-shaped crater.

What is a cinder cone?
Exposed parts of the ancient cores of continents (orange in map below).
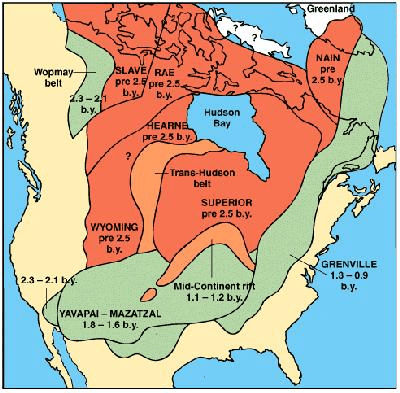
What are shields?
Relative dating principle that enables us to correlate sedimentary strata across canyons incised into them.
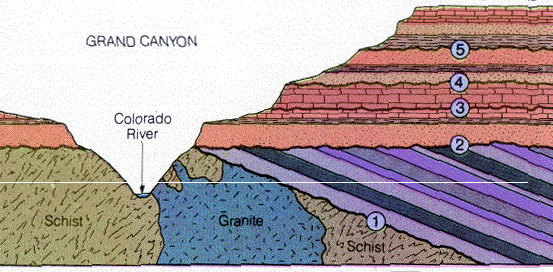
What is lateral continuity?
4.57 billion years based on radiometric dating of primitive chondritic meteorites.
What is the age of the Earth or Solar System?
Tabular body of intrusive igneous rock that is concordant with surrounding rock structure.

What is a sill?
Point on Earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake.
What is an epicenter?
Circular or elliptical fold in which beds dip in towards the center of the structure on all sides.
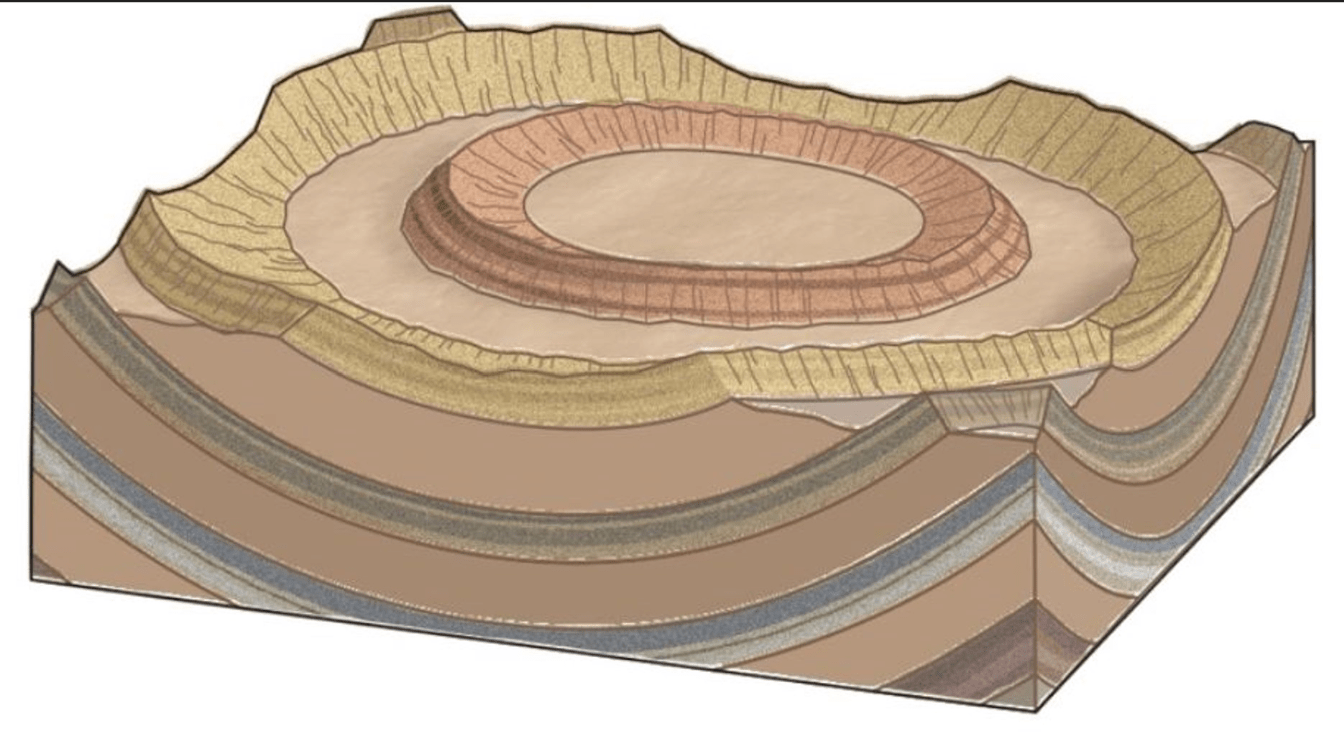
What is a basin?
Principle that ancient geologic features can be understood in terms of processes occurring today because physical laws have remained constant over time.
What is uniformitarianism?
Coarse-grained igneous rock that comprises Earth's mantle.

What is peridotite?
Family of sedimentary rocks that are comprised of pieces of older rocks cemented together.
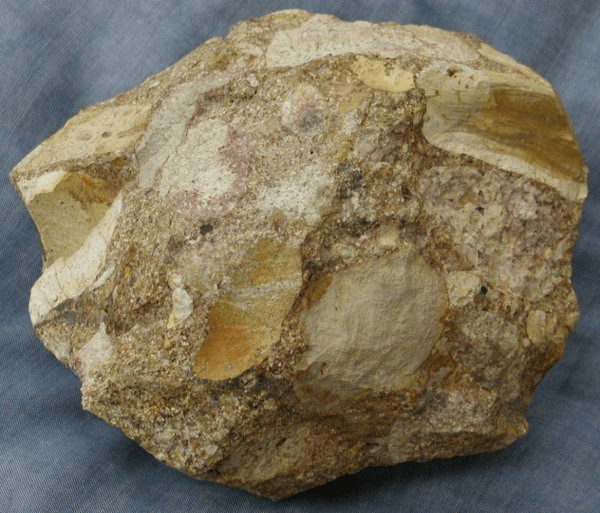

What are clastic sedimentary rocks.
Relatively large, rounded piece of tephra formed by a hot, soft piece of lava.
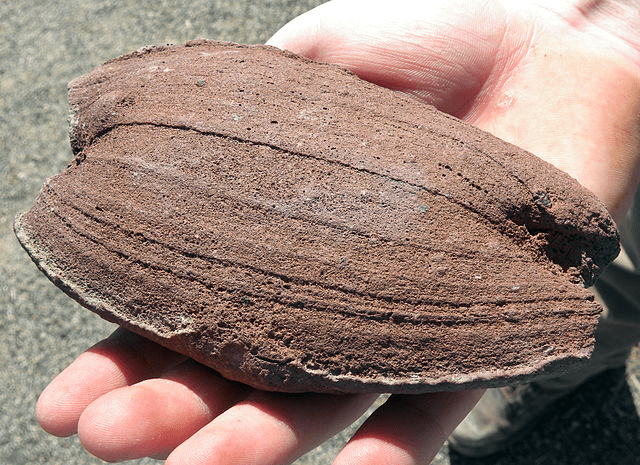

What is a volcanic bomb?
If one of two identical rock masses is buried twice as deep as another, the strength of its gravitational pull at Earth's surface will be _____ that of the first mass.
What is 1/4?
Surface separating two rock units that marks a period of erosion or non-deposition.
What is an unconformity?