a gap in sediment
What is an uncomformity
The only liquid layer of the earth
What is the outer core
The part (zone) of a river where the water is actively eroding (hint: also the most youthful part of a river).
What is the zone of production
A type of mass wasting that does not involve a frictional force
A fall
This is what we call the coldest parts of the earth by latitude
What are the poles
Material deposited with ice contact
What is a glacial till
The reason why we cycle through light and dark each day
What is Earth's rotation around it's axis
What is a half life?
The amount of time it takes for half of a radiometric isotope to decay.
This scale measures the intensity of an earthquake (not the magnitude)
What is the Mercalli scale
Where water in a river channel moves the fastest
What is the center of a channel near the surface
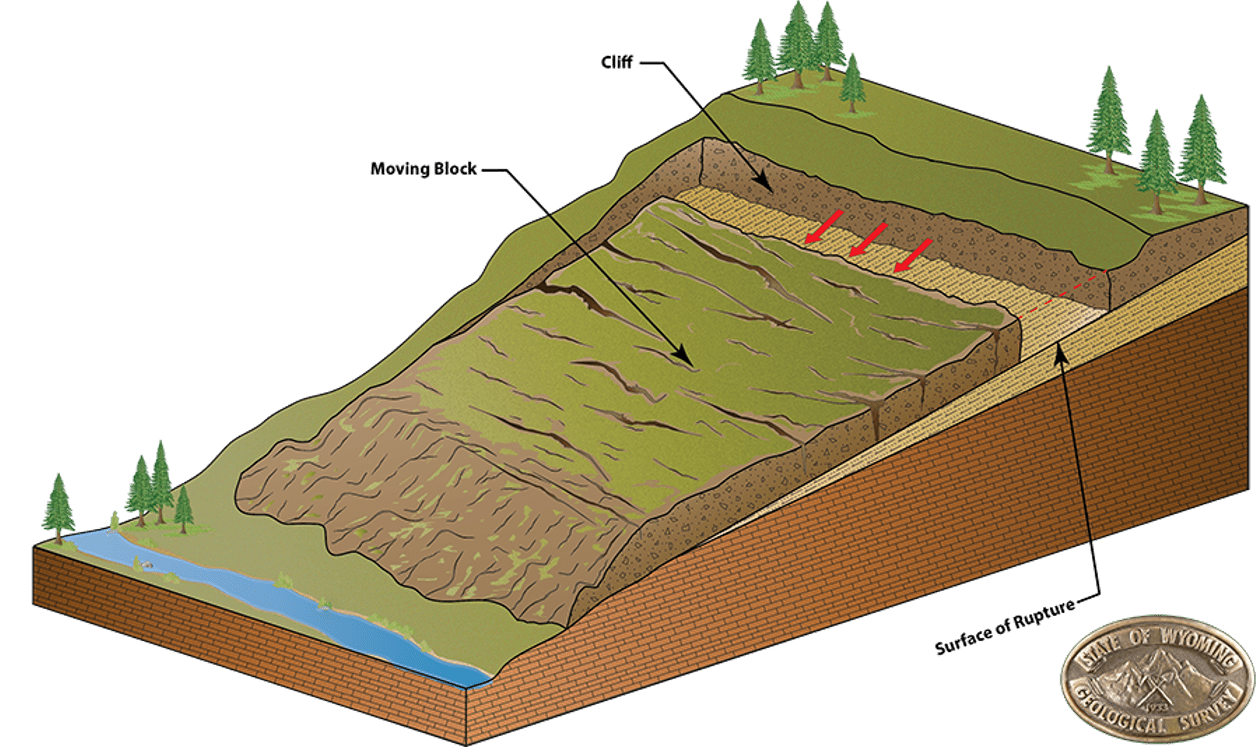
What is a translational slide
This is why we have seasons
What is axial tilt (sun angle variations)
A bowl-shaped depression carved out of a mountain by a glacier
What is a cirque
The rapid increase of this greenhouse gas from fossil fuel combustion is the primary driver of modern climate change.
What is CO2
The law that explains why B is the youngest unit
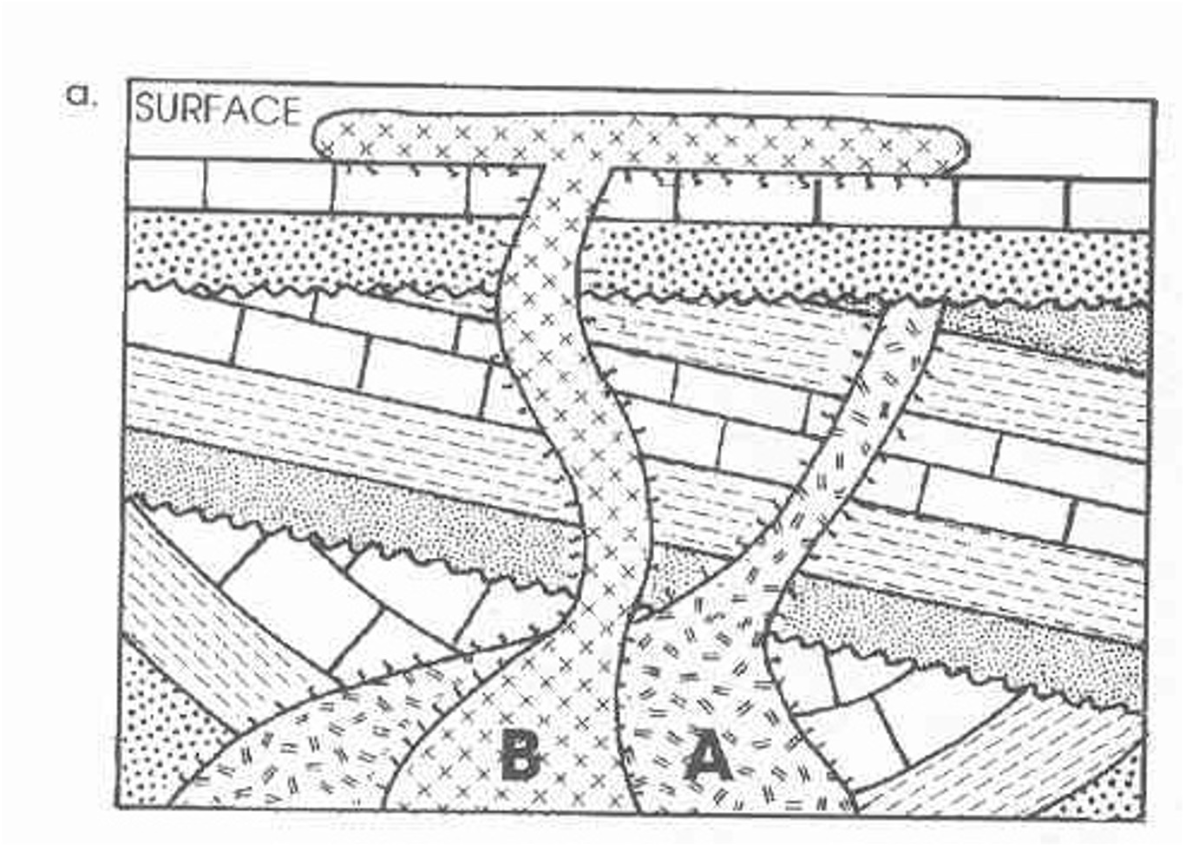
What is the law of cross cutting
This layer of the early contains all of earth's crust and the uppermost layer of the mantle
What is the lithosphere
This type of river has nearly equal amounts of water and sediment
What is a braided stream
Factors that can lead to mass wasting
What is an earthquake
What is a major precipitation event
What is the removal of vegetation
What is an overlysteep slope
The meteorological equator
What is intertropical convergent zone (ITCZ)
Type of glacier

What is a piedmont glacier
The temperature threshold that the paris agreement attempting to maintain?
What is 1.5 degrees C
Steno's laws only apply to these rocks
What are sedimentary rocks
When a wave (i.e., seismic) cannot enter a new medium (material) because its trajectory is too low of an angle.
What is reflection?
Material carried by a stream that does not change with velocity
What is dissolved load
When the pore space of sediment becomes completely saturated with water
What is liquefaction
Regions where wet air is rising
What is a low pressure zone
A pile of material deposited in front of a 'paused' glacier
What is an end moraine
This scientific tool uses trapped air bubbles to reveal that today’s CO₂ levels are higher than at any time in the past 800,000 years.
Ice core
Order these geologic events
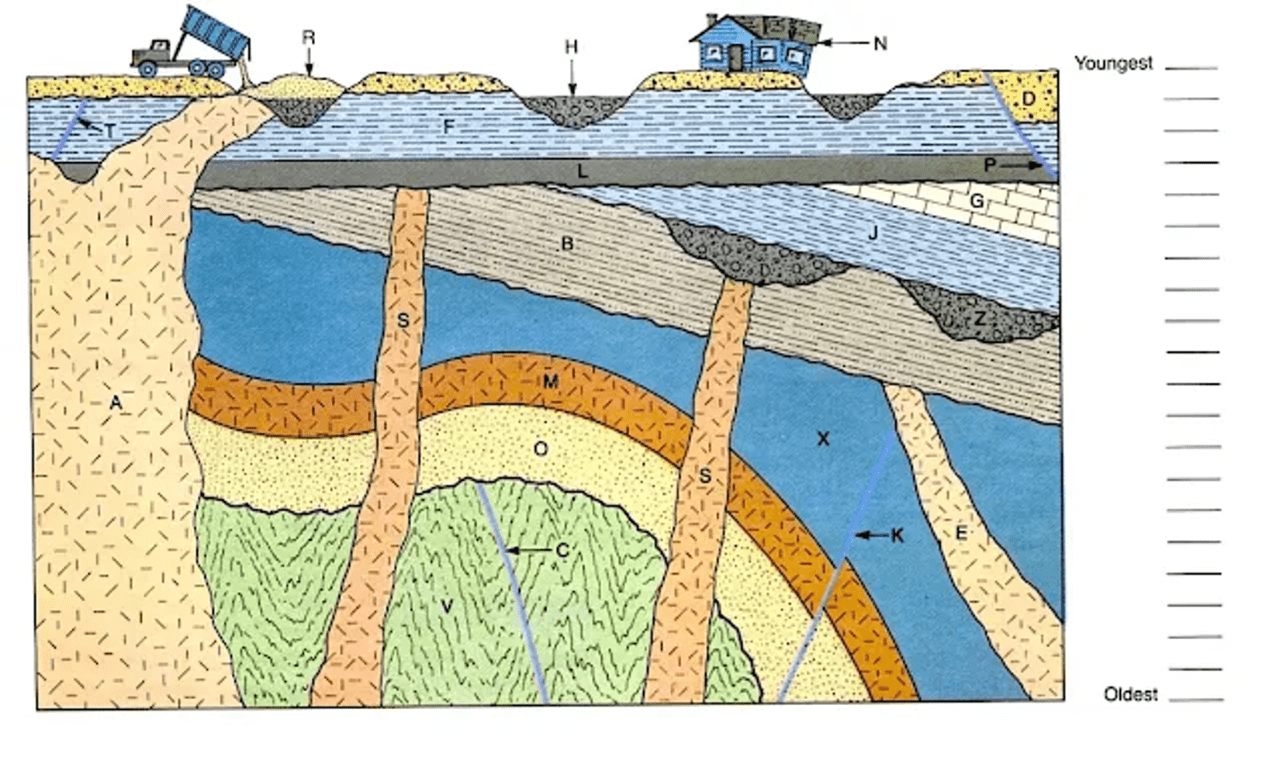
(in class)
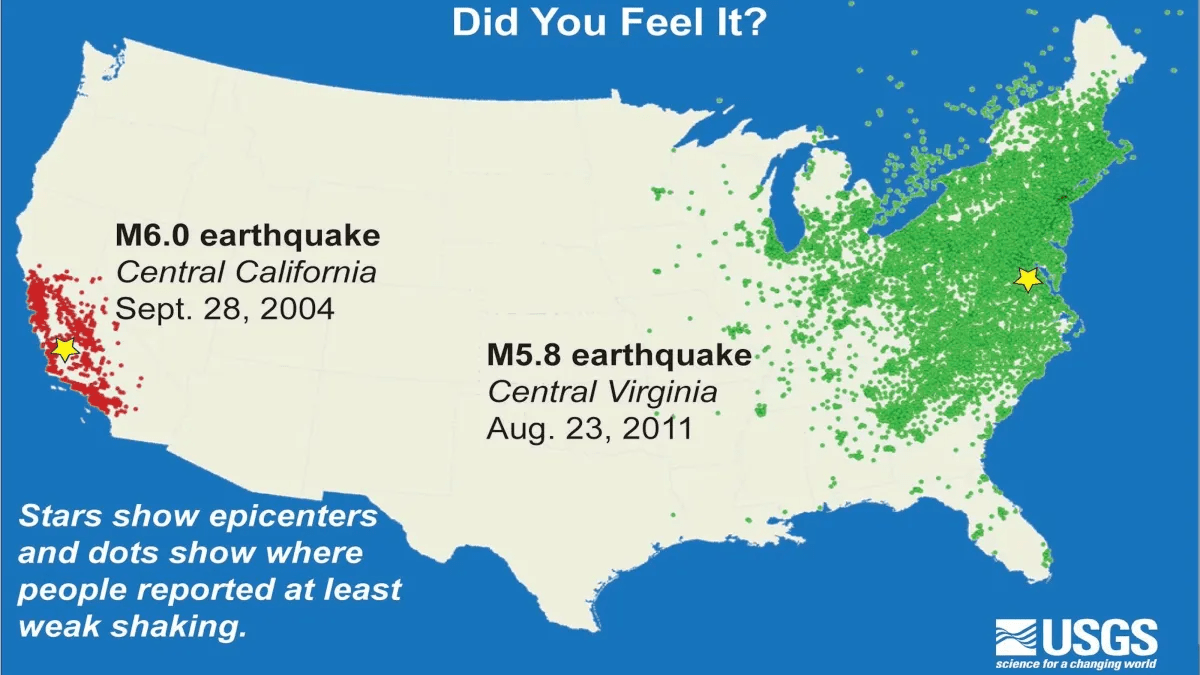
This explains why earthquakes on the West Coast do not travel as far as earthquakes on the East Coast (of comparable magnitudes).
What is 'hard rock' (east coast) or What is unconsolidated sediments (west coast)
This is the maximum load of solid particles a stream can carry
What is capacity
Small amounts of 'this' can make sediments more stable but large amounts of 'this' can entirely destabilize a slope and lead to failure
What is water
At the mid-latitudes, ~30 degrees North and South, dry air returns to the earth creating high-pressure zones, leading to ______
What are midlatitude deserts
These features
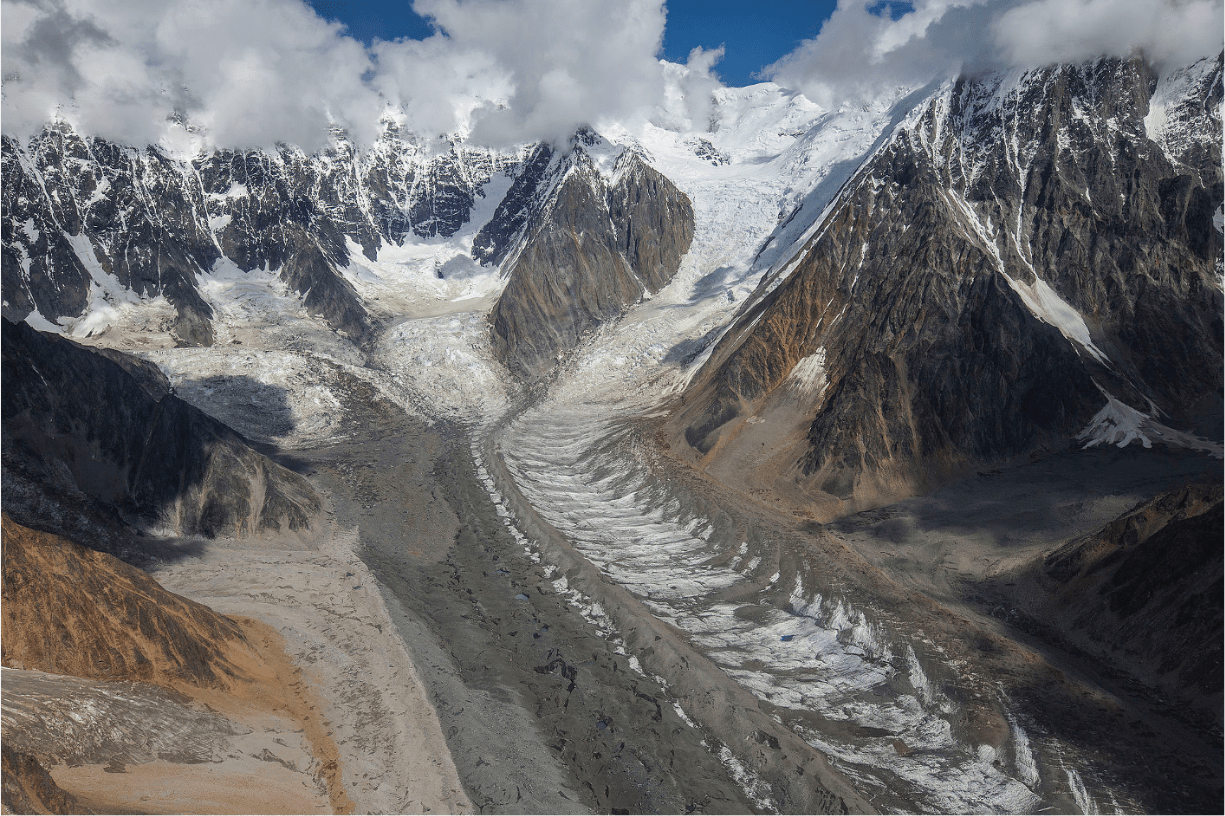

(On map)
What is a cirque
What is an arete
What is a u shaped valley
The primary cause of the ice ages
What are milankovitch cycles?