What do all organic compounds have?
Carbon
What is a substituted hydrocarbon?
What is the most simple form of carbohydrate?
Glucose
What are benzene rings?
Hydrocarbons with six carbon atoms in a ring shape. There are a few double bonds between the carbon atoms
What are proteins made of?
Amino acids
What replaces a hydrogen atom in aldehydes? Where
Carbonyl group (C=O)
At the end of a chain
What is a source of carbohydrates?
Fruits
Veggies
Grains
Daily Double
What is the difference between hexane and hexene?
Hexane has more hydrogen atoms, and all single bonds.
Hexene has less hydrogen atoms, and at least one double or triple bond.
What are isomers?
Two molecules with the same molecular formula but have different structures
Which substituted hydrocarbon has a carbonyl group replace a hydrogen atom somewhere not on the end of a chain?
Monomers
What is the name of this hydrocarbon?
Ethene
Give two characteristics of carbon that make it ideal to make massive molecules.
Has four spots where the carbon atom can bond with other atoms
Can make single, double, or triple bonds
Has a smaller size (means stronger bonds)
What are three uses of alcohols?
Solvents
Detergents
Fuel additives
What is DNA needed for?
What is RNA needed for?
RNA - needed for protein synthesis and cell communication
DNA - needed for reproduction and growth of cells
What is the name of this hydrocarbon? Is it saturated or unsaturated?
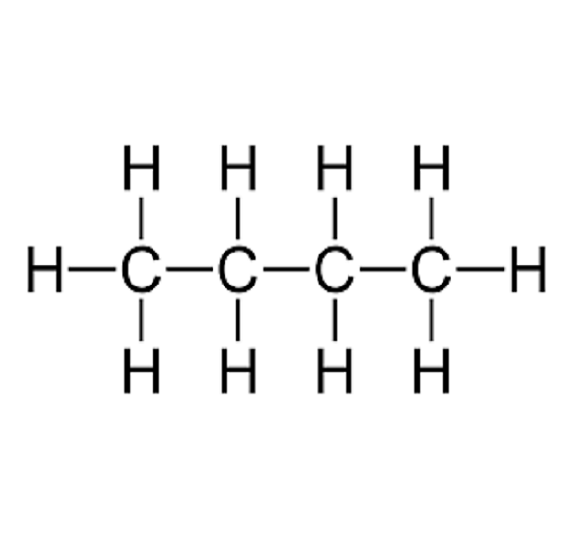
Butane, saturated
What do all aromatic hydrocarbons have?
A benzene ring
What are two uses of ketones?
Solvents
Medicine
What are two differences between saturated fats and and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats - have only a single bond between carbon atoms, are typically solid at room temperature, and are called "fats"
Unsaturated fats - have one or more double bonds, typically are liquid at room temperature, are called "oils", and are usually healthier
Which type of substituted hydrocarbon is this?
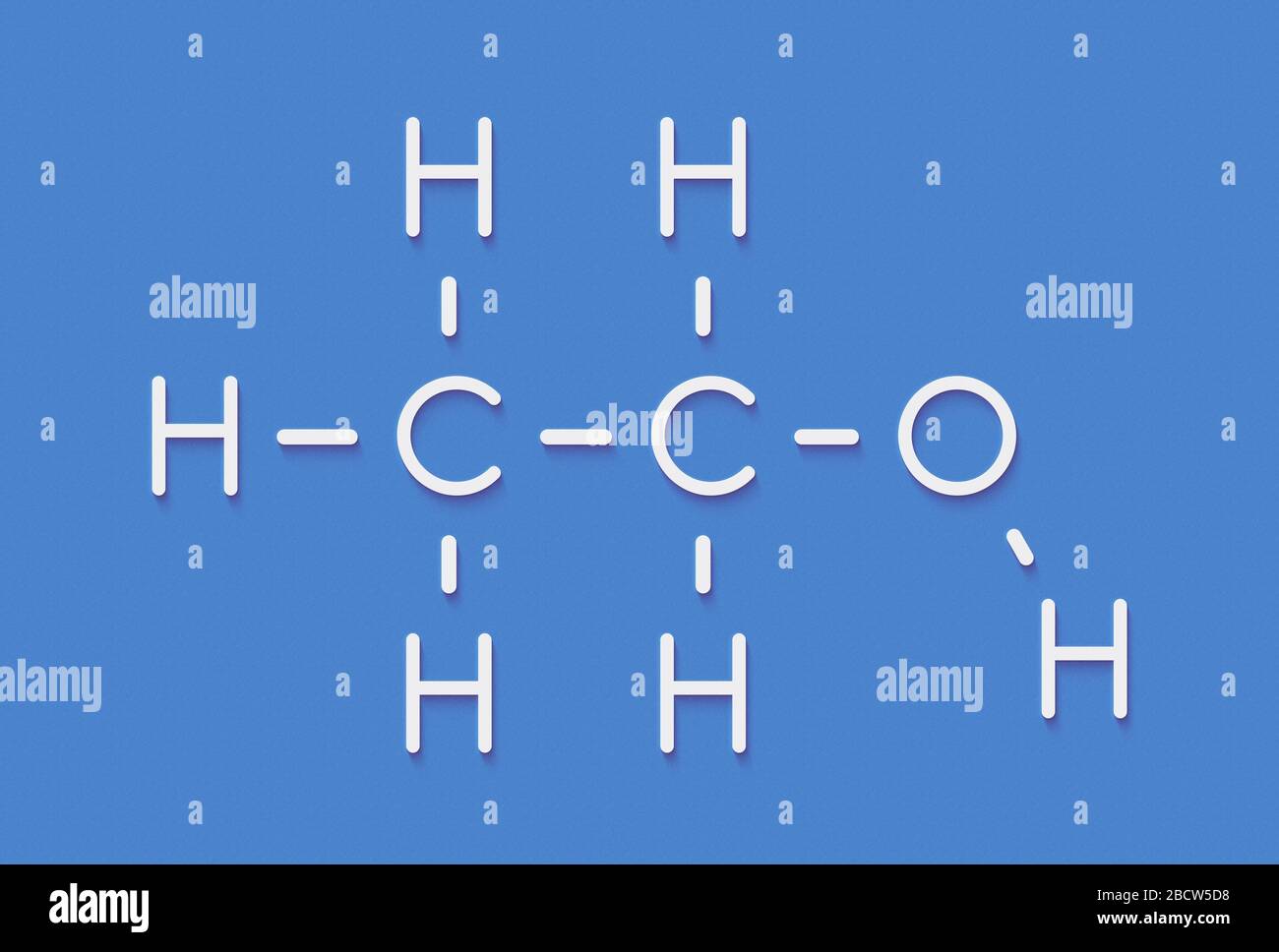
alcohol