This property describes how well heat and electricity flow through a substance
Conductivity
What is the term for how likely a substance is to combust?
Flammability
-273.15 degrees Celsius is _______ Kelvin
0
Draw the figure that helps us remember the relationship between mass, volume, and density

Give an example of a substance undergoing physical change
Paper cut in half, ice melting, pouring some of a liquid out of a container, compressing a gas to be a smaller volume, etc.

Give an example of something undergoing chemical change
A pumpkin decomposing into fertilizer, an egg cooking, metal rusting, a person spontaneously combusting, an atom radioactively decaying, etc.
What happens at 0 Kelvin

All motion, including the electrons' motion, ceases
An object has a mass of 100 g and a volume of 20mL, what is its density in g/mL?
5 g/mL

What physical properties make metals useful in circuitry?
Ductility and electrical conductivity
True or false: chemical changes are usually easier to reverse than physical changes
False, chemical changes are usually harder to reverse, ex: it would be difficult to turn a cake back into batter
Water freezes at ____ degrees Celsius and boils at _____ degrees Celsius
0, 100
What is the mass of an object in g with density 40g/cm3 and a volume of 100 cm3
4,000 g
What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic physical properties? Give an example of each
Intrinsic does not depend on the amount of the substance (like color or density) while extrusive depends on the amount (like volume or mass)
Physical or chemical change for each:
solid to liquid
liquid to gas
gas to plasma
Physical, physical, chemical (since the third involves fundamentally changing the atom's bonds and is not easily reversible)
What is the formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit?
F = 9/5C+32
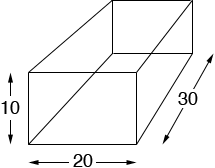
Given that the units are cm, what is the density of that box filled with water in g/cm3 if it has a mass of 6,000 g
1 g/cm3
List three common properties of metals. How does metallic bonding account for these properties?
Ductile, malleable, shiny, conductive - all valence electrons in metals freely move around (electrons are very fast and help conduct electricity and heat) and the flexible, changing metallic bonds allow the metal to bend and stretch without breaking.

Shiny bonus: Electrons emit fixed wavelengths of light when light hits them, depending on their energy levels. Most metals have so many different energy levels of electrons that are free to move and emit light that they add together to be the whole spectrum (white/silvery), a few metals are missing some energy levels of electrons, so their light is only part of the spectrum (gold or copper for example).
What is the major difference between physical and chemical properties?
Physical properties can be identified without changing the substance or combining it with other chemicals while chemical properties are only observed in chemical reactions, if you see the property the substance has changed.
What is the formula for converting Fahrenheit to Kelvin?
K=5/9(F-32) + 273.15

What is the density of the above cylinder in kg/m3 if it has a mass of 500 g. Please do unit conversion first!
325 kg/m3