The amount of space that a substance or object occupies
Volume
This unit is used when measuring with a metric ruler
cm
0.5m = ___ mm
500 mm
To the nearest whole number, this is the width (shorter side) of your team's whiteboard?
23cm
In order to calculate difficult math problems we use this tool
Calculator
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Matter
This unit is used when working with a graduated cylinder
15cm = ___ m
0.15m
According to the triple beam balance, what is the mass of this object?
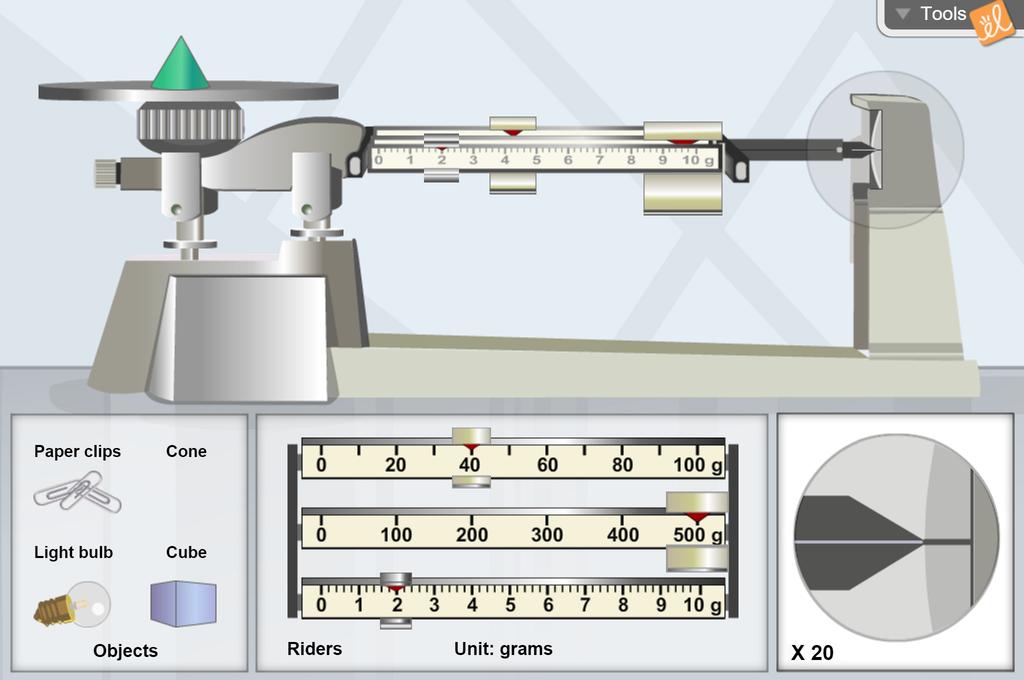
542g
When using a metric ruler to measure an object, be sure that the edge of the object is placed at this mark on the ruler.
O cm.
The amount of matter within
Mass
This unit is used to write the volume of an object
cm3
20m = ___ km
.02km
What is the interval of units that your graduated cylinder goes by?
may vary
When using a graduated cylinder, look at the bottom of this curve.
Meniscus
The force of gravity on an object
Weight
This unit is used to write the density of an object
g/cm3
What is the volume of the cube? You may use whichever method you prefer.
3.375 cm3
A triple beam balance is ready to be used when the pointer points to this.
Zero mark
Mass per unit volume
Density
Why is it important for scientists to use the same system of measurement?
To avoid errors due to confusion over units. To communicate with each other and replicate labs.
80,000 ml = ___kl
0.08 kl
If an object has a volume of 10 cm3 and a mass of 20g, what is it's density?
2 g/cm3
This may be used to measure distances, lengths, or widths that are longer than a ruler.
Measuring tape