Sound Waves
Conversion what would 3.2 cm be in mm:
32mm
List the two types of sound wave interference that occurs when two sound waves meet.
Constructive
Destructive
4,000,000 cycles per second, is equal to how many megahertz (MHz):
4 megahertz
What is the term used to describe the number of pulses that occur in one second?
Pulse repetition frequency
Reflection, Scattering and Absorption are all factors contributing to _______.
The amount of time that it takes a sound wave to travel 1 cm and back, in Soft Tissue:
13 microseconds
What plan does X-Axis and Y-Axis fall on (Horizonatal or Vertical)
X- axis - Horizontal
Y- axis - Vertical
Sound waves alternate between high and low pressures creating a negative and a positive peak. What is the area with a positive peak referred to?
- Compression
One complete oscillation, One set of Compression and Rarefaction:
Cycle
If Frequency is increased (high-frequency), what result will that have on the Spatial Pulse Length (SPL) and image resolution?
Shorter SPL, improved resolution
The amount of attenuation (in dB) that happens per 1 cm is referred to as:
Attenuation Coefficient
The number of pulses that happen per second:
Pulse repetition frequency
With Spectral Doppler what is displayed on the the X-axis and Y-axis (think: Time/Depth/Velocity.
X-axis = Time
Y-axis = Velocity
If two waves meet, and their compressions are not happening at the same time, in the same place, they are considered _______.
- Destructive
What term is used to refer to the TIME it takes to complete one complete cycle of sound with both areas of compression and refraction.
If the frequency is increased what happens to the wavelength?
- Becomes shorter (decreases)
Scattering that occurs when the reflectors are much smaller than the wavelength, randomly dispersing wave energy in every direction
Rayleigh Scattering
The speed of sound, as it travels through a Medium:
Propagation speed
With M-mode what is displayed on the the X-axis and Y-axis (think: Time/Depth/Velocity.
X-axis = Time
Y-axis = Depth
Sound waves alternate between high and low pressures creating a negative and a positive peak. What is the area with a negative peak referred to?
- Refraction
The speed of sound in soft tissue:
- 1.54 mm/µs
- 1,540 m/s
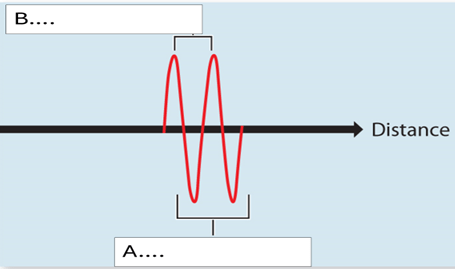
In the image above what is the letter A referring to, as it is measuring the length of a pulse in physical space.
Spatial pulse length
What is the term used when sound hits a boundary layer that is smooth and flat, creating a more powerful echo?
Specular reflection
What happens to the Pulsed Repetition Period (PRP) if the Depth of the image is changed to a DEEPER depth.
The greater the depth the longer the PRP
Ultrasound terms used to discribe the following
Bright White
Grey
Black
Hyperechoic
Hypoechoic
Anechoic
List the three acoustic variables discussed in lecture
Pressure
Density
Distance
What are the three parameters of magnitude of a sound wave
Amplitude
Power
Intensity
Five terms used to describe Pulsed Sound
Pulse duration
Pulse repetition period
Pulse repectition frequency
Duty Factor
Spatial pulse length
What is the relationship between Frequency and Attenuation Coefficient?
Direct, the greater the frequency, the more attenuation
What Spatial Pulse Length (SPL) will have the best resolution?
Higher frequency with shorter SPL