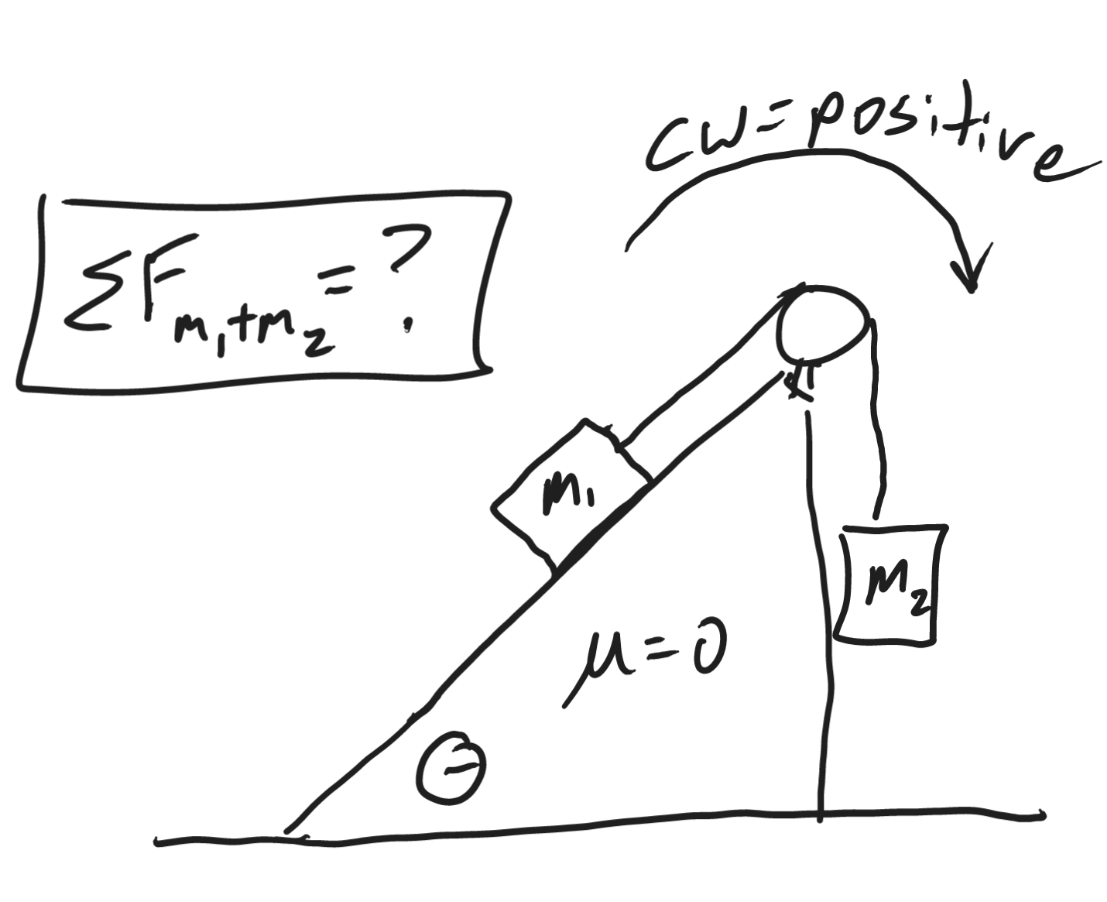
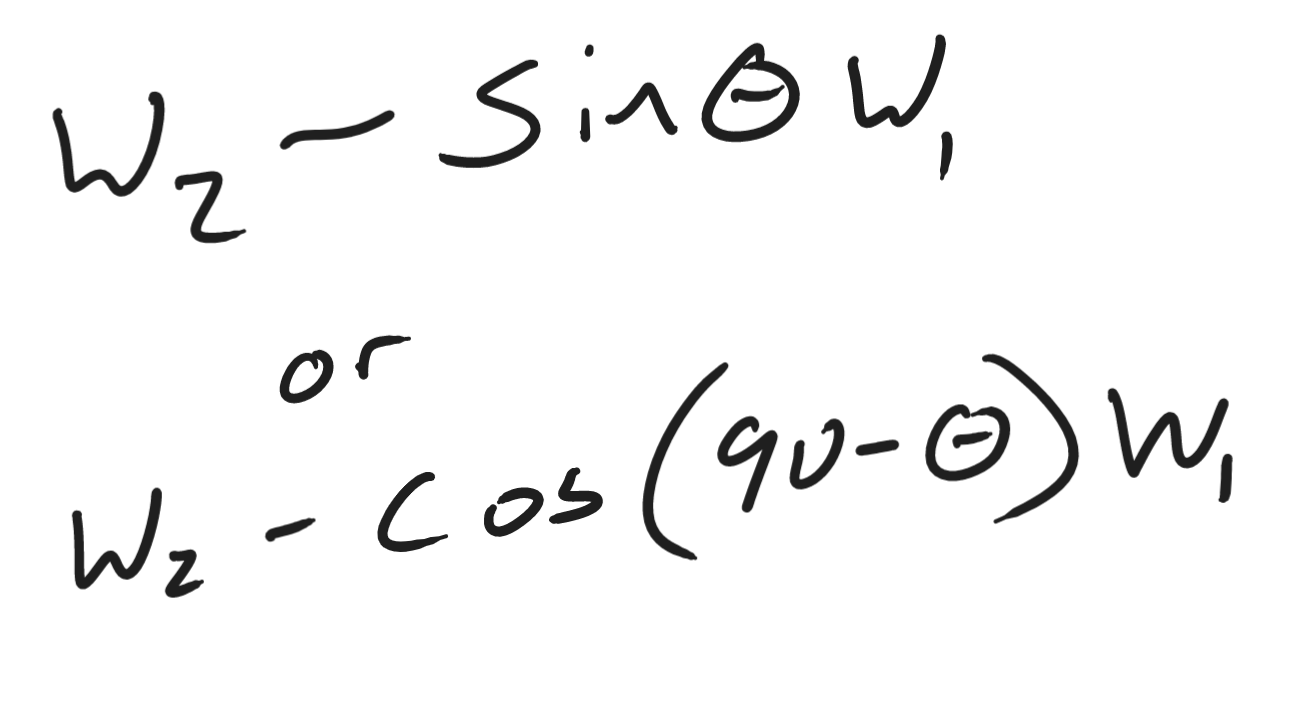Net force
ma
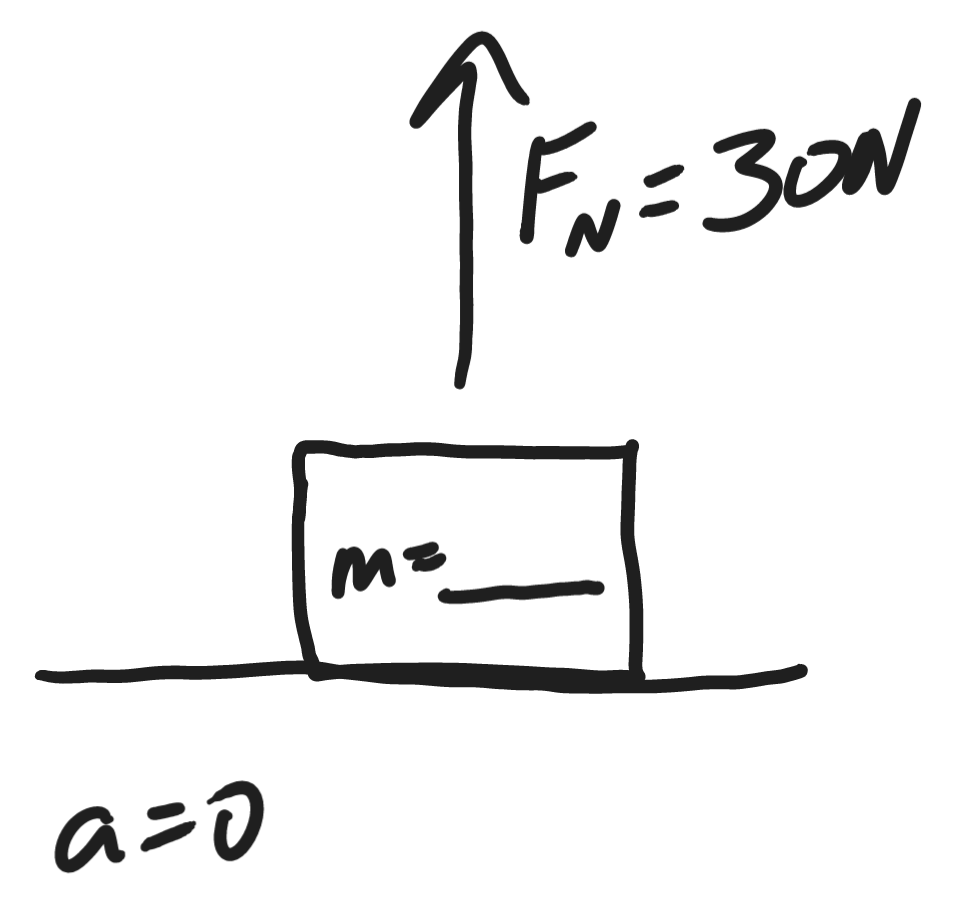
3kg
These are all of the forces acting on a falling skydiver.
Weight and drag
The tension in a rope that is raising a 60kg boat crash survivor with an upward acceleration of 1m/s/s.
[assume g=10m/s/s]
660N
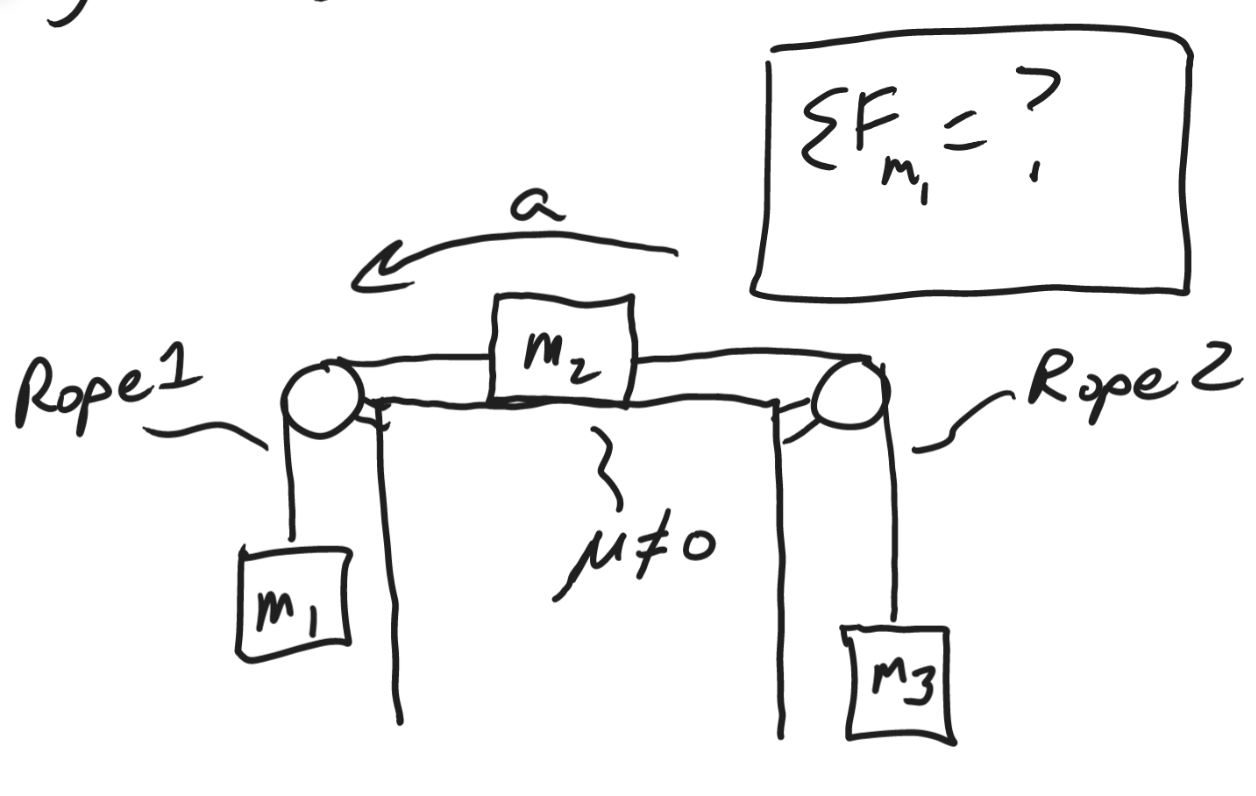
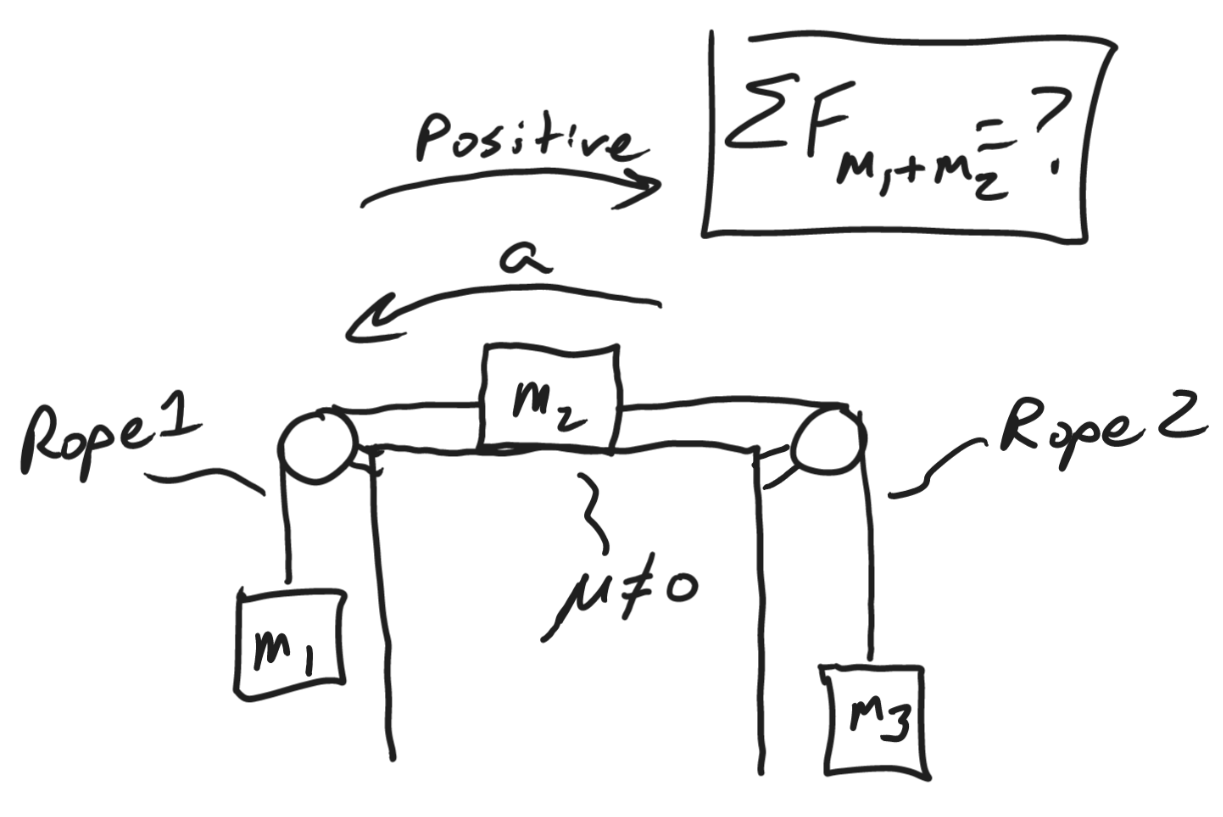
T1-w1
Weight
mg
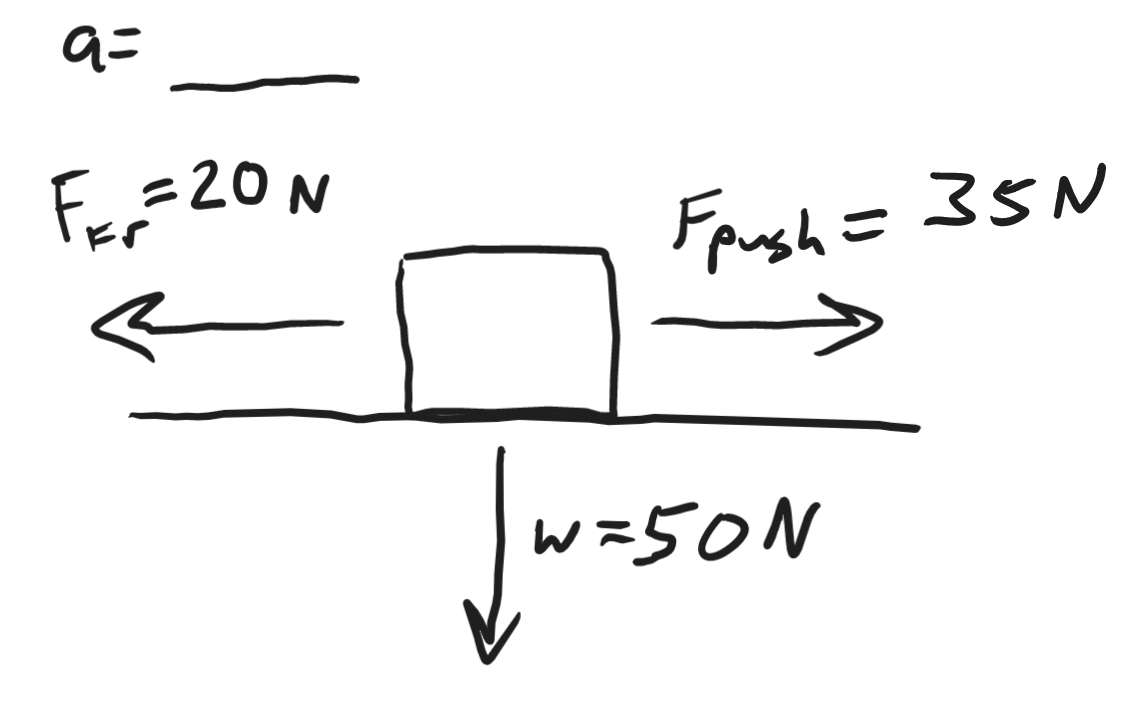
3m/s2
This describes the situation of an object that is falling through the air but not accelerating.
Terminal Velocity
If a 10 kg running child has a velocity of 5m/s one second after having a velocity of 3m/s, this is the horizontal force that the floor is exerting on the child.
20N

Friction
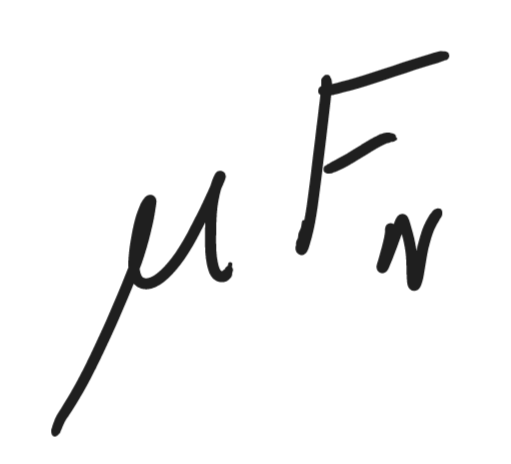
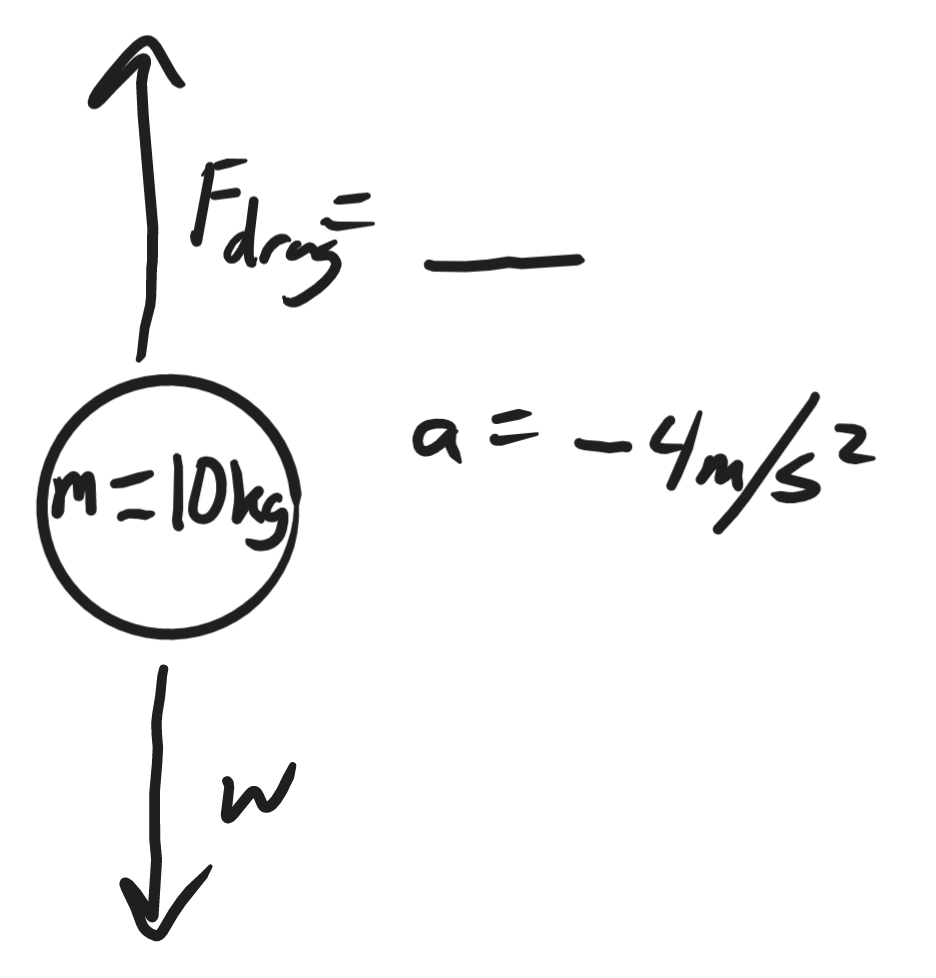
60N
The correct comparison of a skydiver's drag force at terminal velocity with a closed chute closed, versus the same skydiver's drag force at terminal velocity with the chute open. (Stronger, weaker, or the same)
Same
The weight of a 50kg person whose velocity is 8m/s after falling for 4 seconds on a strange planet.
100N

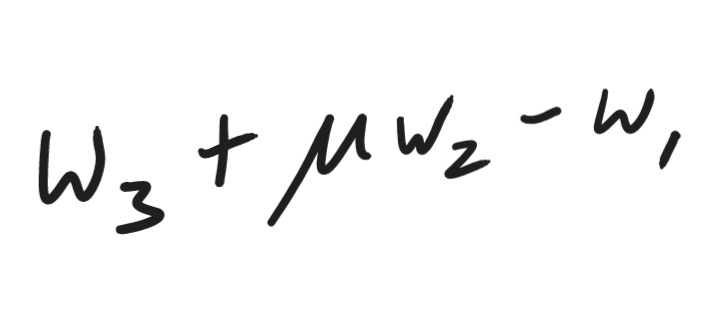
Tension in a string supporting a weight of mass m with acceleration a.
m(g+a)

0.6
The only point at which a skydiver is truly in freefall.
The beginning
The force required to constantly accelerate a 2kg block from rest over a distance of 12m, in 2 seconds.
12N

T2-w3
Reading of a scale that is supporting a mass m in an elevator when the mass m has an acceleration a.
m(g+a)
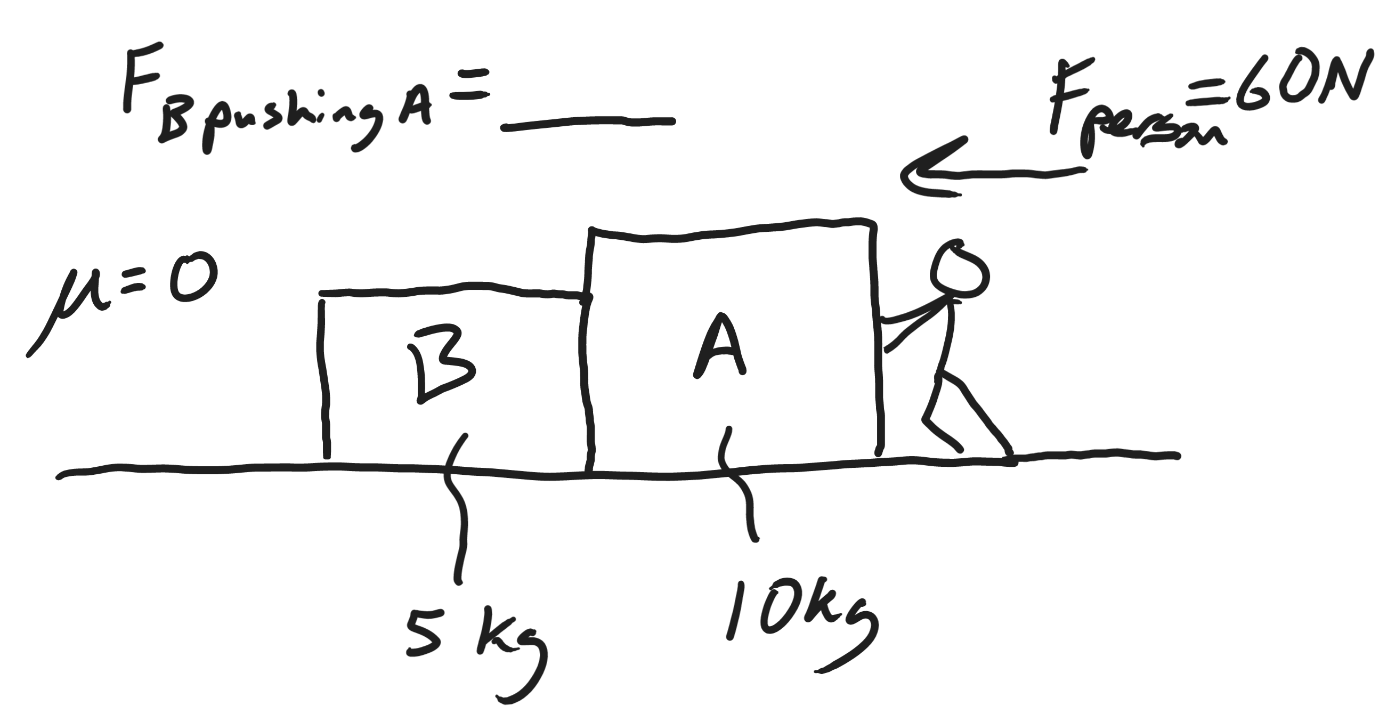
20N
The usual number of times Y acceleration enters positive territory during a skydive.
2
The approximate force of drag acting on a 100kg skydiver while descending 600m over a time of 200s, and then falling 1,200m over a time of 400s, and next further continuing to descend of 900m over the next 300s.
[assume g=10m/s/s]
1,000N