What does AMA stand for?
Active Matrix Array
What is an advantage of SPR compared to traditional x-ray?
results in less scatter and better resolution
Name the two types of latent image formation.
indirect and direct capture
Name the three layers of a flat panel detector.
Capture element
Coupling element
Collection element
direct
How is TFT DEL size related to spatial resolution in cassetteless digital imaging?
The smaller the DEL size, the better the spatial resolution.
pixel size
What is the primary factor influencing image contrast in digital imaging?
LUTs
What device is used to measure the luminance of image display monitors and their uniformity; in what unit is it measured?
photometer; cd/m2
The process of transmitting images remotely, and viewing remote images is termed _____.
teleradiology
A digital image is made up of a 2D array of numbers called a ______.
matrix
What does DEL represent?
detector element
Name the two main types of digital radiography.
CR and direct digital
direct does not require a light conversion step
Name the three types of capture elements for DR.
Amorphous Selenium
Gadolinium Oxysulfide
Name the relationship between DQE and patient dose.
inverse
How is increased mA likely to affect SNR?
increased mA = increased SNR
In DR, the brightness of the image is determined by ______.
pixel values
Once VOIs are assigned, what process then adjusts an over/underexposed image?
rescaling
If a grid used in CR has a frequency similar to the CR processor's scan frequency, what type of artifact can result?
Aliasing/Moire effect
What is the postprocessing function that enables addition of text to an image?
Annotation
The extent/number of exposure intensities an image receptor can accurately detect is termed ______.
Dynamic range
_____, a term that refers to x-ray absorption efficiency.
Why does film screen have better spatial resolution than CR/DR?
An ideal imaging system would have an MTF of ___.
1
Name the type of capture element used in CR.
Bariumfluorohalide phosphor in the PSP layer
If mAs is increased, SNR would...
increase.
In digital systems, pixel pitch is related to spatial resolution. The _____ the pixel pitch, the better the spatial resolution.
smaller
Name a tissue that would have low spatial frequency.
The representation of reference luminance values that assess input intensities and assign predetermined VOI describes _____.
LUTs
TG 18-QC test pattern is used for ____.
monitor image geometric distortion
Name the term used to describe the number of gray shades that can be displayed within a pixel.
What term is used to describe the distance from the center of one pixel to the center of the adjacent pixel?
pixel pitch
What does VOI stand for?
How many shades of gray with film screen vs. digital?
Film: ~30 shades of gray
Digital: ~10,000 shades of gray
What is the photodetector generally used with a TFT array in indirect capture digital imaging?
Amorphous silicon (a-Si)
Name three options for coupling elements.
Lens assembly
Fiber optic assembly
Contact layer (either a-Si or a-Se)
If FOV is fixed and matrix size increases, pixel size will...
Decrease
How is receptor exposure related to quantum mottle/noise?
As receptor exposure (quantity of x-ray photons) decreases, the likelihood of quantum noise increases.
What do FPDF units use to convert x-rays directly into electrical charges?
An amorphous selenium photoconductor (a-Se)
Name the postprocessing function that serves to suppress image noise.
Smoothing
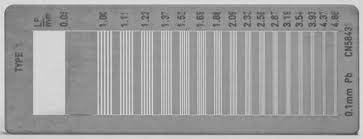 This tool shown is used to measure what image quality? In what unit is this quality measured?
This tool shown is used to measure what image quality? In what unit is this quality measured?
resolution/recorded detail
lp/mm
Lack of adequate collimation and/or selection of incorrect processing algorithm is likely to cause ______ errors.
histogram analysis
What formula is used to determine pixel size?
FOV/ matrix size
What is the common language that enables communication and exchange between image acquisition modalities, display stations, and storage?
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine)
What type of imaging system/modality has the highest DQE?
DR
What is the photoconductor generally used with a TFT array in direct capture digital imaging?
Amorphous Selenium (a-Se)
Name two types of collection elements.
Photodiode or CCD
TFT
How is the use of CCDs related to spatial resolution, SNR, DQE, and patient dose?
CCDs provide:
high spatial resolution
high SNR
high DQE
lower patient dose
How do changes in pixel density and pixel pitch impact spatial resolution?
Increased pixel density increases spatial resolution; decreased pixel pitch increases spatial resolution
TFT size in digital systems impacts what image characteristic?
spatial resolution
During image processing, what determines the numbers assigned to pixel values resulting in brightness and contrast changes?
The feature of digital imaging that provides correction of over- or underexposure by way of histogram shift is referred to as ______.
automatic rescaling
Name the exposure error illustrated. Why is this CR image not overexposed?
double exposure; automatic rescaling
Undesirable fluctuations in image brightness, dependent on the number of x-ray photons reaching the IR, is termed ______.
quantum/image noise
What is the term used to describe the numeric value representative of the exposure the IR receives in digital radiography?
EI (exposure index)
low contrast
How does the sensitivity of digital detectors compare to the sensitivity of x-ray film?
Digital detectors are far more sensitive to environmental, background, scatter, and off-focus radiation.
What is the term used to describe a combination of rows and columns of small picture elements?
matrix
As matrix size increases, pixel size decreases.
True or False?
As sampling frequency increases, spatial resolution increases.
True
What x-ray scintillator may be used for indirect flat-panel radiographic or fluoroscopic imaging?
Cesium Iodide or Gadolinium oxysulfide
What are the two most common ways of adjusting brightness and/or contrast levels in digital imaging?
LUT and windowing
Name the test pattern used to determine resolution uniformity of the digital display device.
TG 18 PX
For the same FOV, arrange the following matrix sizes in order of increasing spatial resolution: 1024 x 1024, 512 x 512, 4096 x 4096.
512 x 512, 1024 x 1024, 4096 x 4096
What is the name of the graphic representation of the amount of exposure, and the frequency of pixels for each exposure amount?
histogram
What does the abbreviation MTF represent?
modulation transfer function
Compared to the H&D/characteristic curve typical of film, the digital image has a _______ response to x-ray exposure.
linear
Direct digital (cassetteless) systems have a fixed spatial resolution that is determined by _____.
TFT DEL size
If a 0.050mm pixel pitch yields a Nyquist of 10lp/mm, a 0.100mm pixel pitch will yield a Nyquist of ____.
5 lp/mm (Nyquist = 0.5 pixel pitch in mm)
The larger the matrix size, for a given FOV, the _______ the pixel size and the _______ the spatial resolution.
smaller; better/greater
The higher/greater the bit depth in digital imaging, the ______ the number of gray shades.
greater
What kind of dynamic range allows optimal visualization of both soft tissue and bony structures in a given image?
wide dynamic range
Name the postprocessing function that serves to increase contrast along image borders.
Name the test pattern used to determine luminance response.
TG 18 CT
What kind of image contrast results from a narrow/decreased window width?
increased/higher contrast
Scattered and off-focus radiation outside of the collimated field can have what effect on the width of the histogram?
causes widening of the histogram
What does LCD stand for?
Liquid crystal display
Objects with high spatial frequency are _____ and _____ to radiograph.
smaller; harder
In digital radiography, Nyquist is referring to what?
The sampling frequency of the digital data
Total intensity of light from a source measured in lumens is referred to as _______.
From these list of factors, select the one(s) that have an effect on digital image contrast/grayscale: pixel bit depth, window width, window level, matrix size, pixel density, LUT.
pixel bit depth
window width
LUT
From these list of factors, select the one(s) that have an effect on digital image brightness: pixel bit depth, window width, window level, matrix size, pixel density.
window level
From these list of factors, select the one(s) that have an effect on digital image resolution: pixel density, window level, pixel pitch, matrix size, window width.
pixel density, pixel pitch, matrix size
______ collimation should always be used with digital systems because excessive scatter causes _______ errors.
Precise/close; histogram analysis
Which test pattern represents the idea that one views the digital image best (with highest resolution) straight on?
TG 18-CT
What is the best way to express digital detector image resolution?
MTF
Light photons randomly scattered onto the source of a monitor that can inhibit visualization of small details is ______.
diffuse reflection