Describe Laminar Flow
Basic: The type of flow where a fluid moves in parallel layers without disruption between the layers (aka, fluid travels smoothly and in a regular path)
Barash: Below critical flow rates that create turbulent flow, gas proceeds through a straight tube as a series of concentric cylinders that slide over one another. Fully developed flow has a parabolic profile with zero velocity at the cylinder wall and a maximum velocity at the center of the advancing “cone.”
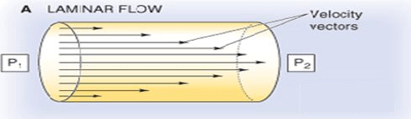
Extras:
- Laminar flow is typical when fluid is moving slowly, through a relatively small channel and/or with high velocity
-Described by a low Reynolds number (Re<2300)
-This type of streamlined flow is usually inaudible
What does Charle's Law state? (Give the mathematical equation)
Charle's law states that if pressure and mass remain constant, a gas's volume varies directly with changes in absolute (Kelvin) temperature.

If pressure is held constant:
- Doubling the temperature of a gas will double its volume.
- Decreasing the temperature of a gas by half will halve its volume.
- Mathematically stated:
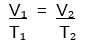
Define boiling point. What is one factor that can affect a substance's boiling point?
Definition: the point at which the vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure
Things that affect boiling point:
-intermolecular forces: stronger IMFs increase boiling point as more energy is needed to overcome the forces
-Molecular weight or shape: increase in weight increases boiling point (more Van der Waals forces in larger molecules)
-Atmospheric pressure: boiling points are lower at lower atmospheric pressures
What do partition coefficients tell us about an anesthetic?
A partition coefficient is a general method for expressing the solubility of an anesthetic in various substances (gas, blood, tissue).
A partition coefficient is given as the ratio of anesthetic concentrations in each of the two phases where equilibrium exists between the phases. Equilibrium exists when there is no further tendency for a phase to take up additional anesthetic at a given concentration.
A balloon has a volume of 2.0 liters at a temperature of 20°C. If the temperature is increased to 60°C, what will the new volume of the balloon be, assuming pressure remains constant?
2.27 liters

Describe Turbulent Flow
In physics, turbulent flow refers to a type of fluid (liquid or gas) movement characterized by chaotic, irregular fluctuations in velocity and pressure. In turbulent flow, the fluid exhibits eddies and swirls, making it highly unpredictable compared to laminar flow, where the fluid moves in smooth, parallel layers.
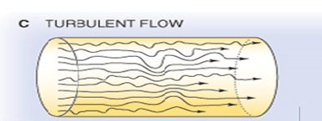
Extra:
-described by a HIGH Reynolds number (Re >4000)
-occurs when one or all three exist: flow is high, gas is dense, large tubular radius
EXAMPLE: water in a rapidly flowing river. As the water moves over rocks and bends, it creates swirling patterns and unpredictable currents. In contrast, flowing slowly and smoothly in a straight pipe would demonstrate laminar flow.
What does Gay-Lussac's Law state? Give the mathematical equation
Gay-Lussac’s Law states that if the volume and mass remain constant, the pressure exerted by a gas varies directly with the absolute (Kelvin) temperature.
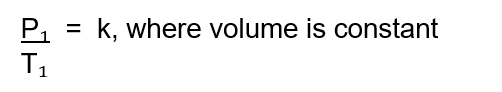
If the temperature of a gas doubles, the pressure the gas exerts will also double.
Mathematically stated:
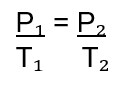
Define Specific Heat Capacity.
Specific heat is the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of substance by 1 degree C (AKA the heat capacity per g of that substance)
More on specific heat:
The higher the specific heat, the more heat is required to raise the substance’s temperature.
Materials with high specific heat respond more slowly to environmental temperature change. Because heat loss occurs during vaporization, vaporizers must be constructed of materials with high specific heat to provide a more stable environment for the liquid anesthetic.
What are Van der Waals forces?
Van der Waals forces are weak intermolecular forces that occur between molecules. They arise from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution, which create temporary dipoles. There are three main types of van der Waals forces:
London Dispersion Forces
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Dipole-Induced Dipole Forces
Van der Waals forces are generally much weaker than covalent or ionic bonds but play a significant role in determining the physical properties of substances, such as boiling points, melting points, and solubility.
A gas in a fixed container at a temperature of 50°F exerts a pressure of 150 atm. If the pressure in the container rises by 50 atm, what is the temperature of the gas?
377K
Gay-Lussac's Law
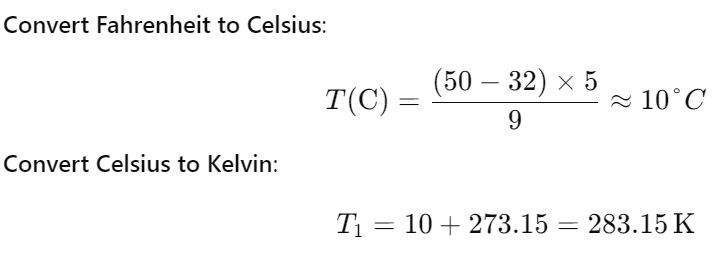
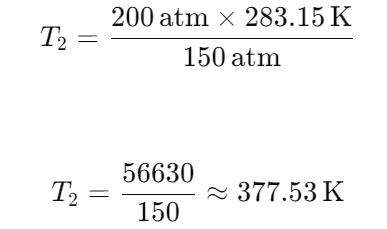
What the Hagen-Poiseuille equation?
Poiseuille's Law is an adaptation of Ohm's Law that incorporates vessel diameter, viscosity, and tube length- it describes the laminar flow of an incompressible fluid through a cylindrical pipe.
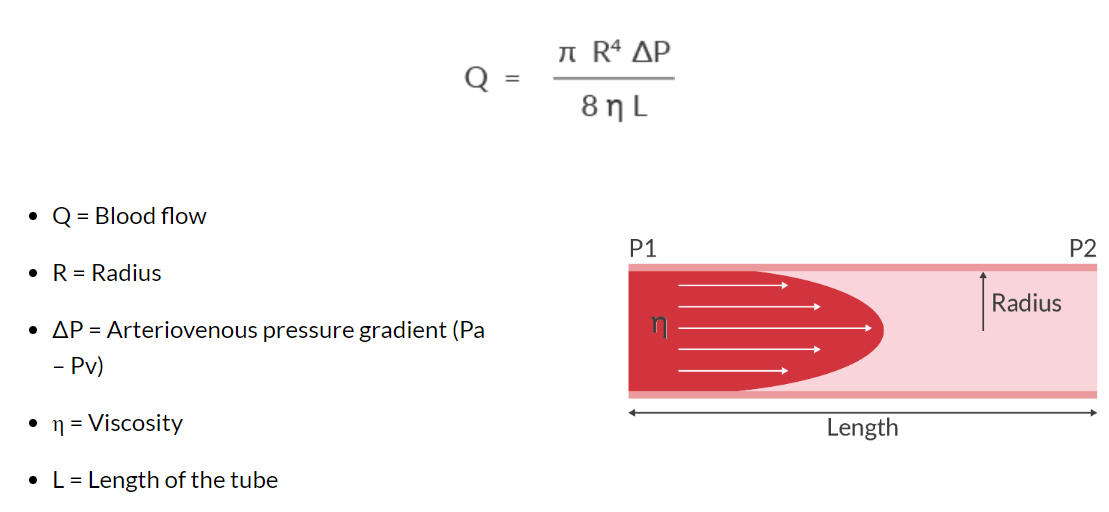
-altering the radius of the tube exhibits the most significant impact on the flow
-if the radius is doubled, flow increases by 16 (24= 16); if the radius is tripled, flow increases by 81 (34 =81)
-For example, we can deliver blood faster if we:
1. increase the radius with a bigger IV
2. increase pressure gradient with a pressure bag
3. decrease viscosity by using a fluid warmer
4. decrease the length by not using longer tubing than is necessary
There are three parts to Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures...Can you name at least 1 of them? Give the mathematical equation as well!
Three parts to Daltons law:
1. The total pressure of a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the constituent gases.
2. The partial pressure of each gas in the mixture is the pressure it would exert if it occupied the entire volume alone.
3. The partial pressure exerted by each constituent gas is proportional to its volumetric percentage of the mixture.
Mathematically stated:
Ptotal = P₁ + P₂ + . . . + Pn
What do you call the energy needed to transition a molecule from a liquid to a gas?
The latent heat of vaporization
The transition of a molecule from liquid to gas requires energy expenditure.
The latent heat of vaporization is defined as the number of calories required to vaporize 1 mole of a substance. Energy may be supplied either externally or internally.
As temperature decreases, the vaporization rate subsequently decreases.
Fick’s law states that the rate of the diffusion of gases in a gaseous medium is proportional to the concentration gradient. Therefore, the higher the concentration gradient from one area to another, the faster the gases diffuse. How can you express this mathematically?
Ficks Law: 
If the pressure drop across a section of a vessel is 100 mmHg and the volumetric flow rate through that section is 0.005 L/s, what is the resistance to flow?
Answer: 20,000 mmHg-s/L
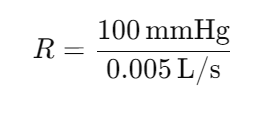
What is the equation for Resistance?
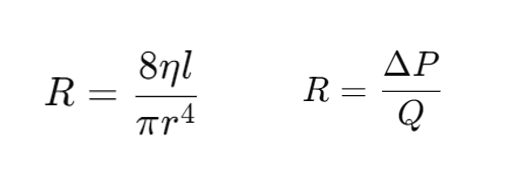
There are two significant equations we have referenced in the past regarding resistance
1. The first is an adaptation from Poiseuille's Law
2. The second states that a change in pressure divided by flow = resistance
What does Henry's Law state?
Henry's Law: the weight of a gas dissolving in a liquid at a given temperature is proportional to the partial pressure of the gas.
-The higher the partial pressure of a gas, the more gas will dissolve in the liquid.
Extra:
Every gas has its own solubility coefficient, a specific measure of how much a particular gas will dissolve in a specific liquid under specific conditions.
Gas solubility is also related to the temperature of the liquid. In general, gases are less soluble in a given liquid at a high temperature than when the same liquid is at a lower temperature.
Solubility coefficient of oxygen = 0.023 ml O2/ml plasma
Solubility coefficient of carbon dioxide = 0.51 ml CO2/ml plasma
(Both coefficients are calculated at 37°C and 760 mmHg)
____ is the speed with which heat flows through a substance. (fill in the blank)
Thermal Conductivity
The higher the thermal conductivity, the better a substance conducts heat
The critical temperature of Oxygen is -118°C; explain what a critical temperature is.
Critical temperature refers to the temperature at which a substance can no longer exist as a liquid or a solid. When ambient temperature exceeds critical temperature, a substance is entirely in the gaseous state.
A gas occupies a volume of 550 ml at a pressure of 765 torr. Assuming a constant temperature, at what pressure will this gas occupy 400ml?
(Hint- Boyles Law)
Answer: 1052 Torr
Boyles Law: 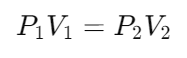
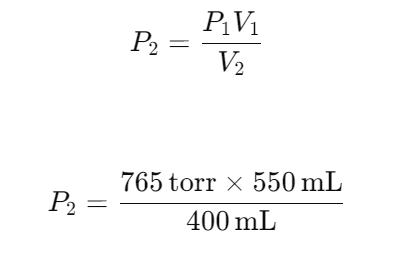
A Reynolds number of 3100 is associated with what type of flow?
Transitional Flow= 2300< Re < 4000
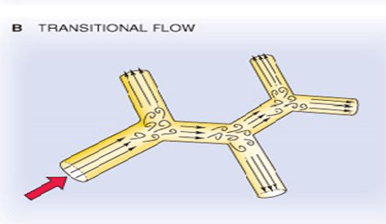
Definition: Transitional flow is a mixture of laminar and turbulent flow, with turbulence in the center of the pipe and laminar flow near the edges.
What is Graham's Law?
Graham's Law states that the rate of diffusion of a gas through a liquid medium is directly proportional to the gas's solubility and inversely proportional to the square root of its density or gram molecular weight.
It is best utilized to compare the relative diffusivities of gases.
Extras:
o ONLY applies to diffusion of gases through POROUS PARTITIONS --> does not apply to bulk flow through tubes
EXAMPLE: The diffusivity of CO2 to O2 is as follows:
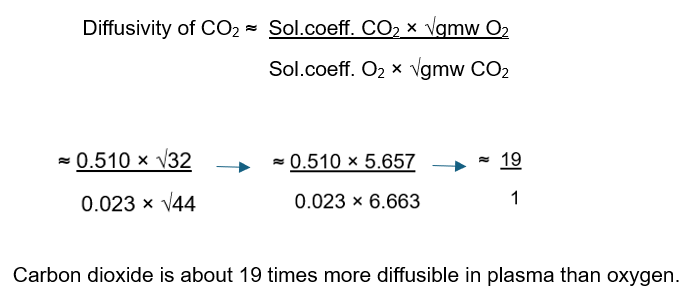
Define vapor pressure. What is the vapor pressure of sevoflurane?
Vapor pressure: In a closed container, molecules from a volatile liquid escape the liquid phase and enter the gas phase until a dynamic equilibrium is reached. The molecules in the gas phase exert pressure on the walls of the container, which we call the vapor pressure.
Vapor pressure is independent of atmospheric pressure and dependent on temperature and the physical characteristics of the liquid itself.
VP of Sevo= 157 mmHg
True or False: The law of Laplace states that the pressure gradient across the wall of a sphere is equal to 2 times the radius divided by the surface tension.
False: The law of Laplace states that the pressure gradient across the wall of a sphere is equal to 2 times the surface tension divided by the radius.
P=2T/R
The composition of alveolar air is 6.18% water, 5.26% CO2, 13.83% oxygen, and 74.73% nitrogen. What is the partial pressure of each gas at atmospheric pressure?
- 47 mmHg H2O
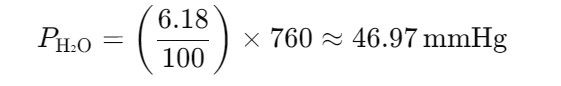
- 40 mmHg CO2
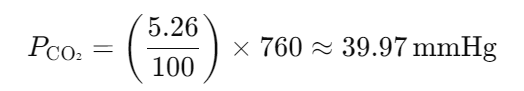
- 105 mmHg O2
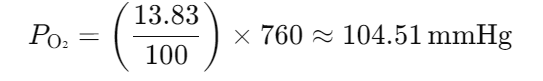
- 568 mmHg N2
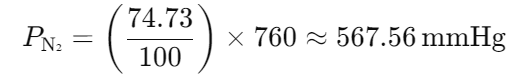
47 + 40 + 105 + 568 = 760 mmHg