Soup
Equations
This outer planet in our solar system is made of mostly hydrogen, helium, and methane gas.
What is Neptune?
This color has a longer wavelength, within the range of 620 - 750 nm.
What is red?
NASA
What is National Aeronautic & Space Administration?
F=ma
What is Newton's 2nd Law?
3 * 10^8 \frac{m}{s}
What is the Speed of Light?
This is the the apparent change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the wave source.
What is the Doppler Shift (Effect)?
While electric ____ exist, magnetic ___ have yet to be discovered.
What are monopoles?
C_6H_12O_6
What is Glucose?
This theory states that the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the E and p of matter present.
What is General Relativity?
DAILY DOUBLE
Elementary particles carry this intrinsic angular momentum.
What is spin?
This type-II supernova leaves this super dense object in its wake.
What is a neutron star or black hole?
DAILY DOUBLE
The spectrum of visible light emitted by Hydrogen, as it transitions between energy states.
What is the Balmer series?
eV
What is an Electron Volt?
e^(itheta)=costheta-isintheta
What is Euler's Formula?
iħpartial/(partialt)|psi(t)>>=hatH|psi(t)>>
What is the Schrödinger Equation?
This is the stream of charged particles ejected from the surface of a star.
What is the stellar wind?
This experiment famously demonstrated how light can behave like both a particle and a wave.
What is The Double Slit Experiment (Single Photon Double Slit Experiment)?
k_B
What is the Boltzmann constant?
Commonly a measure of randomness, related to the number of a system's accessible microstates.
What is entropy?
x=rhosinphicostheta
y=rhosinphisintheta
z=rhocosphi
What is the spherical coordinate system?
Low-mass stars will spend about 90% of their lives in this stage.
What is the Main-Sequence stage?
While Newtonian Mechanics focuses primarily on the forces in a system, ____ Mechanics focuses on the energy of a system.
What is Hamiltonian?
LIGO
What is Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory?
\sum_{n=0}^{oo} \frac{f^n(a)}{n!} (x-a)^n
What is the Taylor Series?
n_1 sin(\theta_1) = n_2 sin(\theta_2)
What is Snell's Law?
This is the process by which energy is slowed down as it travels from the core to the surface of the sun.
What is the absorption and reemission of photons?
This happens when a tachyon when loses energy.
What is it speeds up?
a_0
What is the Bohr radius of hydrogen atom?
iħgamma^(mu)partial_(mu)psi(x)-mcpsi(x)=0
What is the Dirac Equation?
For an object on the principal axis, the refracted or reflected rays cross the axis at different points, leading to this optical defect.
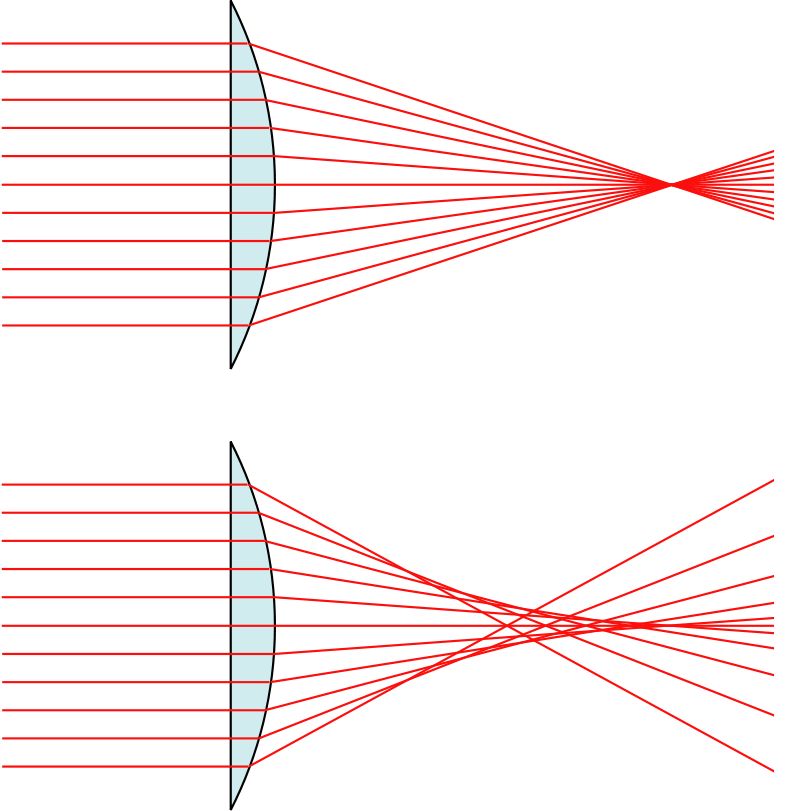
What is Spherical Aberration?