Variables that do not change in an experiment to make tests comparable.
What are constants?
The way that distance and displacement can equal different numbers.
What is changing direction during motion?
The value for acceleration of objects dropped near earth.
What is 9.8 m/s/s (or 10) down?
The "big misconception" about projectiles that we explored using the monkey and the hunter and the equipment in the picture.
What is that objects spend more time in the air if they move sideways when they are dropped or launched in the air? (they don't)
A good definition of inertia.
What is resistance to change in motion (mass)?
The variable that is placed on the vertical axis of a scatterplot.
What is the dependent variable?
The position graph for a person who starts not moving, and accelerates backwards.
What is this?
The reason that heavier objects do not accelerate more than lighter objects when falling.
What is inertia, or resistance to acceleration?
The initial vertical velocity of the cannonball shown below.
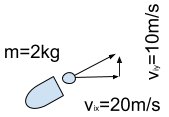
What is 10 m/s up?
The way that a theory can turn in to a law.
Theories never turn into laws! Accepted scientific theories are just as "proven" as laws, but answer different types of questions.
A properly labeled graph for an experiment that tested how the length of skis affects the speed of a skier.
What is an x-y axis with ski length on the x-axis with a unit like meters and speed on the y-axis with a unit like meters per second?
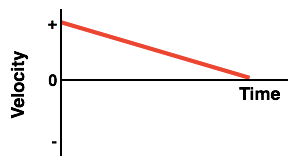
The velocity graph for an object that is moving forward at first, but slows to a stop over a few seconds.
The height of a cliff if it took 2 seconds to fall from the top to the bottom.
What is about 20 meters? (a=-10m/s/s, vi=0,
Delta y = 0)
Everything we know about projectiles at the top of their flight (at least two pieces of information).
What are acceleration = -10m/s/s, vertical velocity = 0, and horizontal velocity is the same as initial horizontal velocity.
A motion map for a marble that starts on the left side of the ramp in the picture.
What is this?
The mathematical tool (on a graph) for describing the value of a dependent variable when the independent variable is zero.
What is y-intercept?
The average velocity of the object in the motion map below.
velocity = displacement / time
velocity = +1.5m / 7s
The initial velocity of a car who comes to a sudden stop in 3 seconds and travels 45 meters while stopping.
What is 30 m/s?
The distance that would be travelled by an object launched off of the cliff shown below before it hit the ground.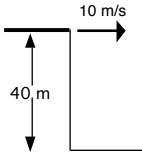
What is 28.3 meters? (initial vertical velocity is 0 m/s, vertical acceleration is -10 m/s/s, vertical displacement is -40, and horizontal velocity is 10 m/s)
A description that matches both objects in this velocity graph.
What is speeding up?
A claim supported by evidence based on the information about the pendulum in this table with independent variables mass, length, and amplitude and dependent variable time. 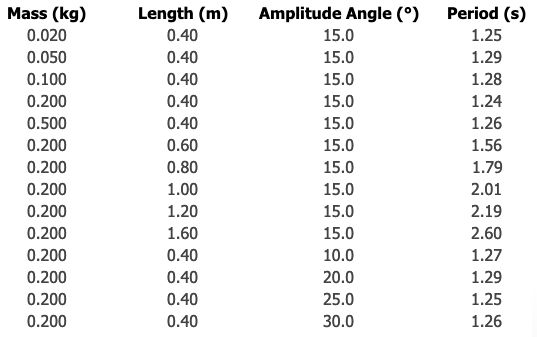
What is as ________ _________s, __________ _________s as shown in the data in rows _____?
A position graph for the motion map shown below:
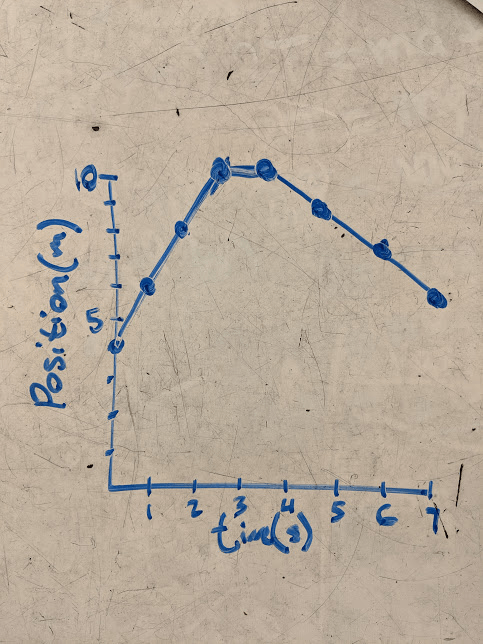
A CER style conclusion written about the data shown in this graph using shapes on the graphs or specific numbers to predict what the car was doing.
There are many answers to this. ex:
Claim: At time 2.5s the car was not moving
Evidence: The position graph is flat and the velocity graph is at v=0 at time 2.5s.
Reasoning: A flat position graph means that velocity is zero because the slop of the position graph is the velocity.
A CER conclusion that can be made based on the data in this experiment where initial velocity and launch angle of a projectile were changed.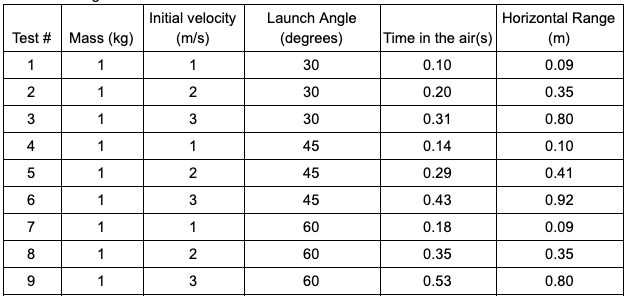
There are many answers to this
ex: Increasing the angle that the cannon is launched at from 30 degrees first increases, then decreases the range of the cannon. 45 degrees appears to give the maximum range. Tests 1, 4, and 7 all have the same mass and initial velocity, but yield different ranges with tests 1 and 7 having the same range, and 4 having more. This is because high angles give high vertical velocity, which makes the projectile have a long hang time. Low angles have high horizontal velocity, which means the object moves quickly sideways. 45 degrees has equal parts vertical and horizontal velocity.
The maximum height reached by a projectile launched as in the picture.

What is 5 m in the air? (initial vertical velocity is +10 m/s, final vertical velocity is 0 m/s, vertical acceleration is -10 m/s/s)