What does the slope of a distance time graph represent?
Velocity
What is the formula for average velocity?
v=Δt/Δd
Who discovered the Universal Law of Gravitation?
Isaac Newton
What is Newton’s First Law?
An object in motion will stay in motion. (or at rest) unless acted on by an outside force
What is the formula for work?
W=fd
On a velocity–time graph, what does the area under the curve represent?
Displacement/Distance
Define acceleration.
The rate of change of velocity over time.
State Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation.
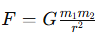
State Newton’s Second Law.
F = ma
What are the SI units for work and energy?
Joules
A straight, horizontal line on a distance–time graph shows what kind of motion?
The object is at rest.
A car increases its speed from 10 m/s to 30 m/s in 5 seconds. What is its acceleration?
4 m/s^2
If the distance between two masses doubles, what happens to the gravitational force?
It becomes one-fourth as strong.
Give an example of Newton’s Third Law.
lots of examples
A person pushes a box with 40 N of force for 5 meters. How much work is done?
200J
How can you tell if an object is accelerating on a velocity–time graph?
The line is sloped (not horizontal).
What does a negative acceleration mean?
The object is slowing down or changing direction.
What are the units on the constant for the universal law of gravity
N m^2/Kg^2
A net force of 20 N acts on a 4 kg object. What is its acceleration?
5 m/s^2
A 10 kg object is lifted 2 m vertically. How much work is done against gravity?
196J
A car’s velocity–time graph shows a negative slope. What does this mean physically?
The car is decelerating or moving in the opposite direction.
A runner moves with an acceleration of 2 m/s² for 6 seconds starting from rest. What is their final velocity?
12 m/s
The gravitational force between two 10 kg masses is 6.67×10−9 N. How far apart are they?
1m
A 2 kg block slides on a frictionless surface at a constant velocity. What is the net force acting on it?
Zero (balanced forces, constant motion).
What happens to the amount of work done if the angle between force and displacement increases?
Work decreases as the angle decreases