Define Wave
A disturbance that moves through a medium or vacuum
Define Wavelength
Distance between any two corresponding points on a wave
Define Diffraction
When a wave encounters an object in its path and bends around it
Define Digital Signal
Signals represented by a series of numbers
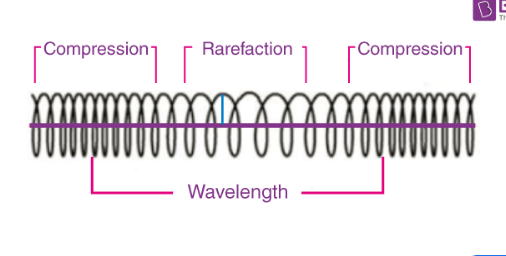
Draw a longitudinal wave and label a compression, refraction and wavelength.
tbd
Draw a Longitudinal wave and label a compression, refraction and wavelength
A wave with a frequency of 5 Hz is observed. Determine the period of this wave
.2 s
Define Medium
The material through which a wave moves
Define Refraction
Energy waves changing direction and speed as they move from one object to another
Define Analog Symbol
Signals represented by a continuous wave
How is amplitude measured in a transverse and a longitudinal wave?
Transverse is the height of the crest or the depth of the trough measured from the rest position. Longitudinal is the maximum displacement of particles of the medium from their equilibrium position, measured along the direction of wave travel.
A wave has a frequency of 3.2 Hz with a wavelength of 10m. What is the velocity of the wave?
32 m/s
If the period of a wave is measured to be .2 seconds, what is its frequency?
5 Hz
Define Period
The time in seconds required for one complete wave cycle.
Define Mechanical Waves
Waves that transfer energy through a medium
Define Reflection
Energy waves bouncing off of an object
Describe the difference between electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves and give examples of each.
Mechanical waves cannot travel through a vacuum, but electromagentic waves can. Electromagnetic waves: Radio, Microwave, Infrared, Ultraviolet. Mechanical Waves: Soundwaves, seismic waves, surface waves
Define Mechanical waves. Do they need a medium to travel through.
Mechanical waves require a material medium, such as air, water or solids to transfer energy. Yes they do.
Explain the relationship between loudness, intensity, amplitude and pitch in relation to sound waves.
Loudness is the subjective human perception of the intensity of a wave it is measured in pitch and is a direct result of the amplitude of a wave.
A wave travels at a speed of 300 m/s and has a frequency of 75 Hz. What is the wavelength of this wave?
4 m
Define Frequency
Number of wave cycles that pass a given point in time
Define Electromagnetic Spectrum
entire range of all types of electromagnetic radiation. 1. Radio Waves 2. Microwaves 3. Infrared Radiation 4. Visible Light 5. Ultraviolet Radiation 6. X-Rays 7. Gamma Rays
Define Absorption
Waves are absorbed by a material and converted to other forms like heat
Explain the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves.
Longitudinal waves are particle compression and expansion, a transverse wave particles vibrate perpindiuclar.
Are Light waves Mechanical or electromagnetic?
Electromagnetic
A wave travels 1.5 m/s with a frequency of 0.45 Hz. What is the wavelength of the wave?
3.3 m
A wave has a wavelength of 2 m and a frequency of 250 Hz. Calculate the velocity of this wave.
500 m/s
Define Amplitude
Height of wave from origin to crest
Define Hertz
Unit that frequency is measured in
Define Interference
Occurs when two or more waves meet and combine as they travel through the same medium
Draw a transverse wave and label a crest, trough, wavelength and amplitude

Are Sound waves mechanical or electromagnetic?
Mechanical
The period of a sound wave is 0.002 seconds. The speed of sound is 344 m/s. Find the frequency and wavelength of the soundwave.
F = 500 Hz, Wavelength = .688 m