Who am I?
my Exocrine cells secrete buffers and digestive enzymes:
my Endocrine cells secrete hormones.
Pancreas
Antidiuretic hormone _____the blood volume
Antidiuretic hormone _increases_the blood volume
Blood consists of
1.
2.
3.
1. Plasma
2. Red Blood cells
3. ‘Buffy coat” WBC + Platelets
Describe the barriers used in innate defense
Barriers used by the innate defense include epidermis, mucus, hairs, cilia, lacrimal apparatus, saliva, urine, vaginal secretions, sebum, perspiration and gastric juices.
Name six main types of nutrients
1.Water
2.Carbohydrates
3.Lipids
4.Proteins
5. Minerals
6.Vitamins
Haemostasis is the process of...?
blood coagulation
Salivary glands secrete saliva, which contains the enzyme ___________.
This enzyme digests ______________ into simple sugars.
Salivary glands secrete saliva, which contains the enzyme salivary amylase.
This enzyme digests startch_ into simple sugars.
Aldosterone is secreted by _______. What does it do?
adrenal cortex.
~ Blood volume in Adults?
in % and litres?
8% of body weight or ~5 L
True or False?
Lymphatic capillaries merge to form lymphatic vessels, which have thin walls and many valves.
True
Describe the vitamins and minerals required in the diet, their food sources and their contribution to body function.
Minerals
– Mg, magnesium - catalysing ADP to ATP
-Calcium and phosphorus for bone integrity
-Potassium and Sodium for the creation of the action potential for nerve and muscle function
Vitamins
Fat soluble – Vit A, D, E, K (necessary for effective blood clotting)
Water soluble – Vit B and C
Which Vitamin is needed for normal clot formation?
Vitamin K
What is the role of the Muscularis Externa?
Peristalsis
Veins: carry blood toward the heart;
________ blood, except for _________ veins
Veins: carry blood toward the heart;
deoxygenated blood, except for pulmonary veins
Which is not a component of blood?
a) Water
b) Albumin
c) Lipase
d) Electrolytes
Lipase is an enzyme
• The lymphatic system functions to:
1. Drain ....
2. Transport ...
3. Carry out ....
• The lymphatic system functions to:
1. Drain interstitial fluid (2-4 L /day)
2. Transport dietary fats
3. Carry out immune responses
Name the Hormone associated with the small intestine and the arrival of Chyme in the duodenum. What is it's role?
CCK - Cholecystokinin
Stimulates the digestion of Fat and Protein
Inhibition of hunger
What is the hormone Thrombopoietin responsible for?
Under the influence of the hormone thrombopoietin, haemopoietic stem cells differentiate into platelets.
What is the difference between Cheif cells and Parietal cells?
Chief cells – Produces pepsinogen which becomes pepsin in the presence of HCl
Parietal cells – produces HCl
– Intrinsic factor (Binds to B12 for absorption in small intestine)
Arteries: carry blood ______ from the heart; oxygenated blood, except for _______ circulation and ___________ of a foetus
Arteries: carry blood away from the heart; oxygenated blood, except for pulmonary circulation and umbilical vessels of a foetus
Of the White Blood cells, which is the most abundant?
Neutrophils @60-70%
T lymphocytes (helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells)
mature in the _____.
Thymus
Learning Outcome - Describe the three major classes of macronutrients in the diet, their food sources and their contribution to body function and health.
Carbs – Cereals, Short term energy
Fats/lipids – Oils, nuts,, Long term energy storage
Protein – Meat, Provides building blocks of all proteins in body. Tissues to transport molecules.
True or False?
Arteries have less elastic tissue and less smooth muscle than veins
False
Veins have less elastic tissue and less smooth muscle than Arteries.
The role of the liver is to...
Synthesize_____
and storage of________.
Synthesize Bile salts (emulsify fats)
Storage of Glycogen, Vit, Minerals
Which type of Arteries are also known as the Conducting Arteries?
they function as pressure reservoirs.
Elastic arteries
larger diameter and more elastic fibers than muscular/distributing arteries
Name some 4 functions of blood
• Transport – O2, CO2 – nutrients/ waste – heat – hormones
• Regulation – pH – Temperature – water content of cells
• Protection – blood loss (clotting) – infection (immune system)
The process whereby neutrophils and other white blood cells are attracted to an inflammatory site is called ________.
Chemotaxis
Catabolic vs Anabolic reactions?
Anabolic reactions
– Synthesis or building reactions
– Endergonic (endothermic)
– energy consuming
• Catabolic reactions
– Decomposition reactions
– Exergonic (exothermic)
– produce more energy than consumed
Why is the shape of RBC so important?
Name the disease that can interfere with this and what the consequences might be.
Biconcave discs -vastly greater surface area than a spherical cell
Disease is a genetic sickle cell anaemia (oxygen carrying capacity of the blood is reduced).
What makes up the small intestine?
1.
2.
3.
1.Duodenum
2.Jejunum
3.Ileum
What is meant by "shock"?
failure of CVS to deliver enough oxygen and nutrients to meet cellular metabolic needs
The process of producing blood cells is__________.
_________ stem cells differentiate into each of the different types of blood cells.
The process of producing blood cells is haemopoiesis (haematopoiesis).
Pluripotent stem cells differentiate into each of the different types of blood cells.
Which cell type in produces Antibodies?
B- Lymphocyte
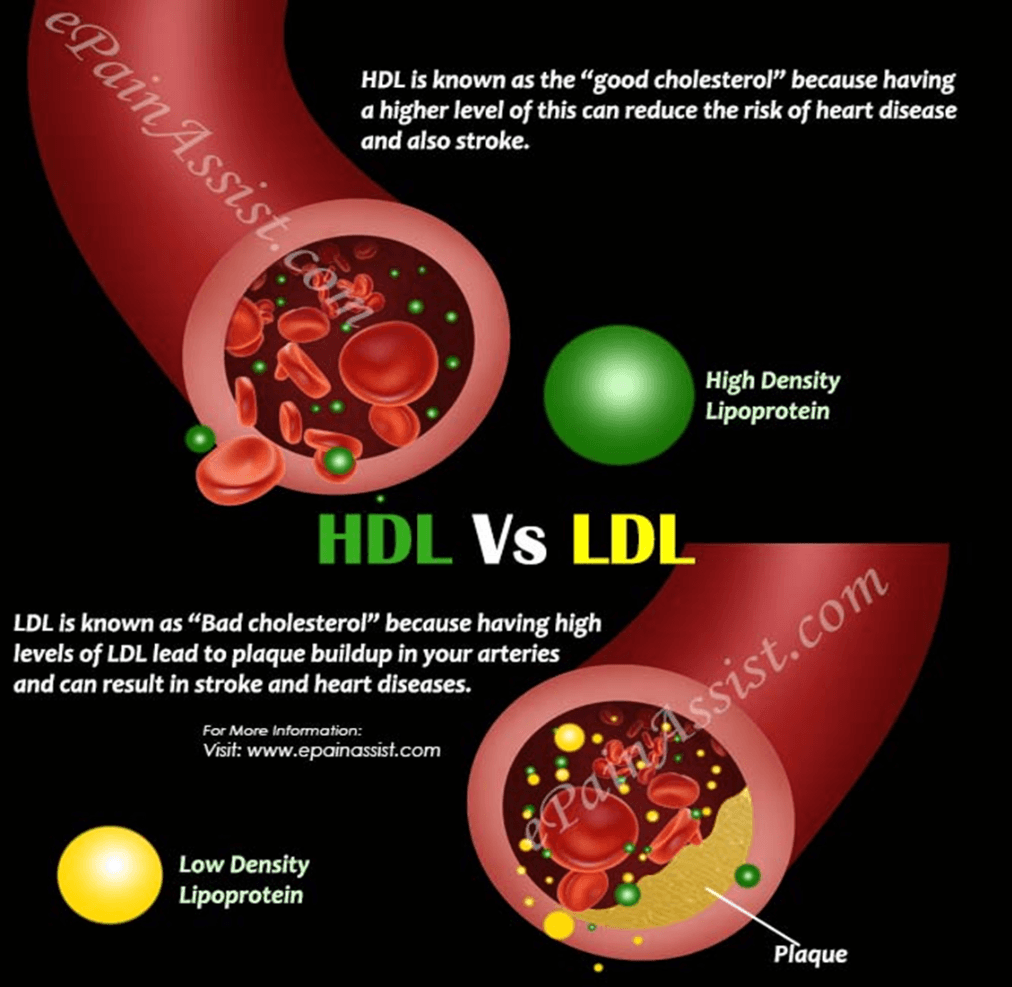
What is the function of Lipoproteins?
Would you rather have high LDLs or HDLs?
Transport lipid in blood
What is the role of the Pericardium? Composed of?
The heart is held in place by the Pericardium.
Composed of two layers
inner serous pericardium (visceral and parietal layer)
outer fibrous pericardium
Name the Enzyme
1. Protein --> Peptides
2. DNA --> Nucleotides
3. Starch --> disaccharides
4. Triglycerides --> Fatty acids
1. Pepsin or Trypsin
2. Deoxyribonucleases
3.Amylase
4.Gastric lipase
Atrial natriuretic peptide is secreted by_____
Cardiac Atria
Double Jeopardy!!- What does it do?
What is the function of hormone Erythropoietin (EPO)?
Erythropoietin helps keep the blood balanced by stimulating the marrow to make red blood cells.
Double Jeopardy!
Secreted mainly by _____?
Which of the following is/are not part of the innate immune defenses?
Inflammation
Natural killer (NK) cells
Fever
T Cells
T Cells
Gluconeogenesis is..
a)Synthesis of glycogen from glucose
●
b) Synthesis of glucose molecule from protein and lipid decomposition
●
c)Breakdown of glycogen to glucose
a)Synthesis of Glycogen from glucose. Glycogenesis, when there is an excess, stored in liver
●
b) Synthesis of glucose molecule from protein and lipid decomposition. Gluco neo genesis
●
c) Breakdown of glycogen to glucose Glycogenolysis, In liver when there is a need for more glucose
Name the two Hydrostatic Pressures in the Net filtration equation. What produces them?
Blood hydrostatic pressure – BHP
• pressure generated by pumping of heart
Interstial fluid hydrostatic pressure – IFHP
• pressure generated by water molecules in tissue fluid
What is a Chylomicron and how are they formed??
Cholesterol + Triglyceride + protein
Within the cells of the small intestine
Absorbed Fats combine with cholesterol and proteins in the intestinal cells to form Chylomicrons
removed by lymphatic system.
2 types of Osmotic pressures? In the Net filtration equation of capillaries.
• Blood colloid osmotic pressure – BCOP – pressure caused by plasma proteins in the blood
• Interstitial fluid osmotic pressure – IFOP - pressure caused by solutes in the tissue fluid
Describe the haemoglobin structure and its purpose.
Haemoglobin structure
– Protein globin: two alpha and two beta chains
– Haeme pigment bonded to each globin chain
Iron atom in each haeme can bind to one O2 molecule.
Also, regulates blood flow and BP via NOxide
Each Hb molecule can transport four (4) O2
Give an example of a Primary and Secondary Lymphoid organ and the principal difference between the two.
Primary lymphoid organs are those in which lymphocytes develop and mature (rearrange the receptor genes) eg. Bone marrow, Thymus, Bursa of Fabricius
Secondary lymphoid organs are those in which naive lymphocytes encounter antigen and are stimulated to become effector and memory cell populations. Spleen, Lymph nodes, MALT
Amino acids are absorbed via cotransport with ___?
NA+
An allergic reaction will produce which Leukocytes?
Eosinophils and Basophils
Which hormone inhibits Lipolysis?
Insulin
The opening between the right atrium and left atrium in foetal heart is known as___?
Foramen ovale
Red blood cells live for only about ____days.
Dead cells are removed from the circulation by the ______________
Red blood cells live for only about 120 days. Dead cells are removed from the circulation by the spleen and liver
What are some differences between Cell mediated immunity and Antibody mediated immunity?

not a nutrition Q...Cardiao
What factors regulate stroke volume?
·Preload: (effect of stretching)
·Contractility
·Afterload (aortic and pulmonary arterial pressure)
Explain why blood group O is considered the universal donor and AB the universal recipient.
O - absence of A and B antigens on the surface of RBC
AB- both A or B antigen on its RBC surface = no antibodies for A and B