Which cells are responsible for the acid-base buffering power and why?
RBC
They contain a large quantity of carbonic anhydrase
What is the maximum concentration of hemoglobin that red blood cells can hold?
About 34 grams in each 100 milliliters of cells.
What is the average hemoglobin content in the blood of a normal man and woman?
15 g/100 ml in men and 14 g/100 ml in women.
What is the main site of red blood cell production during the first trimester of fetal life?
RBC production begins in the yolk sac for the first trimester.
At what age does the red bone marrow of long bones mostly stop producing red blood cells?
Around 20 years of age
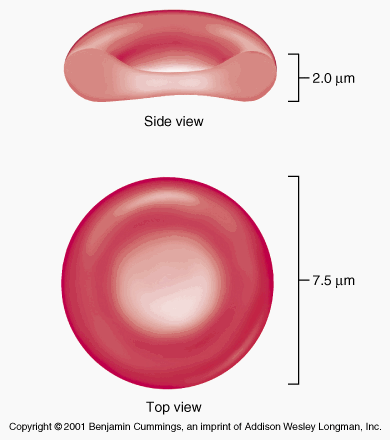
Tell the sizes of RBC (their diameter and thickness)
Diameter is about 7.8 micrometers
Thinkness of 2.5 micrometers at most
1 micrometer or less in the center
What percentage of total body iron is found in hemoglobin?
Approximately 65% of body iron is in the form of hemoglobin.
What protein transports iron in the blood plasma?
Transferrin
What is the lifespan of red blood cells?
About 120 days
What happens to iron absorbed from the intestine once it enters the blood?
It binds with apotransferrin to form transferrin, which transports iron to tissues.
Tell the average number of RBC per cubic millimeter for a healthy man
5,200,000(+-300,000) per cubic millimeter
Tell the average number of RBC per cubic millimeter for a healthy woman
4,700,000(+-300,000) per cubic millimeter
What happens when plasma iron levels fall?
Iron is released from ferritin stores and transported via transferrin to tissues like the bone marrow.
What happens to the hemoglobin released from destroyed red blood cells?
It is phagocytized by macrophages, the iron is recycled, and the porphyrin is converted to bilirubin.
How is total body iron regulated?
By controlling the rate of intestinal absorption depending on the iron storage status.
Why does the spleen play a role in the destruction of old red blood cells?
Because old red cells lose flexibility and rupture as they pass through narrow splenic capillaries (3 μm wide).
Why does deficiency of transferrin cause hypochromic anemia?
Because iron cannot be delivered efficiently to erythroblasts in the bone marrow, leading to reduced hemoglobin synthesis.
How soon after exposure to low oxygen does erythropoietin production peak?
Within 24 hours.
Why does anemia occur in patients with destroyed kidneys?
Because erythropoietin production falls drastically, reducing red blood cell formation.
What nutritional deficiencies cause red blood cell maturation failure?
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) and folic acid deficiencies.
What type of red blood cells appear in vitamin B12 or folate deficiency?
Macrocytes

What is the function of intrinsic factor in vitamin B12 absorption?
It binds B12, protects it from digestion, and enables its absorption in the ileum.
During the second trimester of pregnancy, where is the predominant site of RBC production? A) Yolk sac B) Bone marrow C) Lymph nodes D) Liver
Production in the yolk sac decreases at the beginning of the second trimester, and the liver be comes the predominate source of RBC production. During the third trimester, RBC production increases from the bone marrow and continues throughout life.
Which of the following applies to patients with ac quired immunodeficiency virus (AIDS)? A)Able to generate a normal antibody response B)Increased helper T cells C)Increased secretion of interleukins D)Decrease in helper T cells
D) Helper T cells are destroyed by the AIDS virus, leav ing the patient unprotected against infectious diseases.
How can diseases like cardiac failure or lung disease lead to increased erythropoietin production?
They reduce oxygen delivery to tissues (hypoxia), stimulating kidneys to increase erythropoietin secretion and RBC production.